21-22 The best Tutorial on Cylinder head of Diesel Engine
The cylinder head is a crucial component of a diesel engine. It is responsible for sealing the combustion chamber and allowing the fuel and air mixture to be properly compressed and ignited. The cylinder head also houses the valves, which control the flow of air and exhaust gases in and out of the engine. Understanding the workings of the cylinder head is essential for anyone looking to maintain or repair a diesel engine.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the importance of the cylinder head in a diesel engine and delve into its various components and functions. We’ll also discuss some common issues that can arise with cylinder heads and how to address them. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or just starting out, this post will provide valuable insights into one of the most critical parts of a diesel engine.
In this post on Cylinder head marine Diesel Engine, I will explain the following topics.
- The complete details of cylinder heads,
- including- Cylinder head mountings,
- Cylinder head fittings maintenance,
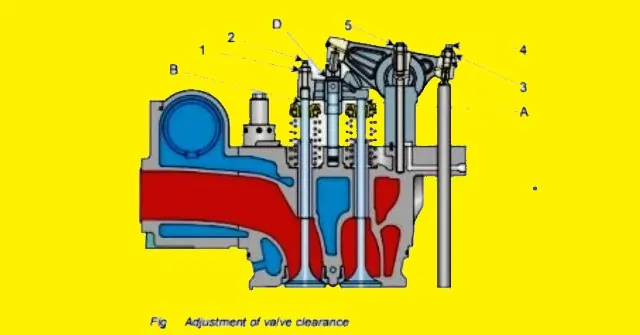
- Tappet clearance adjustment.
What is Cylinder Head of Diesel Engine ?
The cylinder head is manusfactured from cast iron and seals the combustion chamber by enclosing the cylinder liner —the cylinder head is fitted on the cylinder liner.
Construction of cylinder head
Cylinder Head Fittings (Cylinder Head of Diesel engine)
- Cylinder Cover
- valve spindles( Inlet and exhaust)
- Valve guides
- Fuel Valve Bushing
- Mechanism for valve operation
- Safety Valve with Indicator valve
Diesel Engine Cylinder Head Fittings
Cast iron is the material for the design of Cylinder head. Charge air receiver is integral part of cylinder head. Bottom wall of cylinder head is thick having provisions for cooling the bore.
Cylinder head central bore accommodate the following fittings
- Fuel Injector
- Inlet and exhaust valves
- Indicator valve for the measurement of compression and peak pressure. Also it is used for the drawing of indicator diagrams.
Each valve has a spring and valve rotator. The yoke and rocker arm operates the valve opening and closing operation.
Inlet and exhaust valve seats are installed for all the valves. These seats can be replaced as and when required. Seats have the cooling arrangement by the water circyulating around.
The cylinder head also has a safety valve for the release of excessive pressure in high maximum pressure or pressure built-up during hydraulic lock inside the cylinder.
Marine Diesel Engine Cylinder Head Mountings
Location of the fuel injection valve is in the interchangeable sleeve in the centre of cylinder head. Comprehensive water cooling of the nozzle tip space makes it possible feasible to eliminate direct injection nozzle cooling.
Cylinder head assembly also includes an air starting valve for starting the engine.
Other assemblies are Rocker arms for actuating the inlet and exhaust valves.
A coaming on the cylinder head encloses the valve gears. Screw tightening of the top cover on coaming makes it possible for oil sealing of the complete chamber and complete cylinder head full-face covering. An inspection cover in the coaming facilitates the inspection of valve rotators.
Specific intake swirl is possible by 20 Degree turnings of the valve pattern. 4 nuts and studs tighten the cylinder head over cylinder liner with cylinder head gasket making it leak-free against the high combustion pressure inside the combustion chamber. Tightening of the nuts is by hydraulic jacks.
The cylinder head is part of the combustion space/chamber and needs overhauling /maintenance at regular intervals for high performance and reliable operation.
Check holes in the cylinder head indicate any leakage of mating surfaces between the cylinder head and cylinder liner.
Air Inlet and Exhaust Valvesof Cylinder Head Marine Diesel Engine
The inlet and exhaust valve are of satellite coated seat, nickel-based alloy valve, and nemonic spindle.
Valve rotators provide a slight rotation to Valves. This valve rotation increases the life of the valve spindle.
Valve seats and valve guides are identical for inlet and exhaust valves. Valve seats and valve guides are interchangeable for inlet and exhaust valves.
The seat rings are of heat resistance steel, with direct hardening on the seat surface, and the water cools the seat ring for the assurance of low valve temperature.
Valve Rotator
Advantages of Valve Rotators in Cylinder Head Marine Diesel Engine
1. Carbon accumulation on the valve guide and seat.
2. Maintains uniform valve temperature
3. Prevents pitting due to hot spots.

The valve rotator retainer body (1) has several pockets in the circumferential direction.
The ball race (3) acts as a ball track in the opposition direction.
The inner rim of the retainer body holds the spring washer (4)to create the opposite springing action. Sealing collar (5) surrounds the spring washer by overlapping it.
Retaining ring (6) holds the assembled valve rotator while removing.
Dismantling Cylinder Head Marine Diesel Engine
1. Drain the cooling water from the engine.
2. Remove the top cover of rocker arm..
3. Remove both side crankcase covers.
4. Remove the cover of exhaust.
5. Take out the cylinder head clamps and receiver for the exhaust gas .
6. Take out the HP pipe for fuel oil.
7. Remove the clams for locking the freshwater connection between cylinder heads.
8. Remove the cooling oil inlet and outlet pipes.
9. Remove the rocker arm lubricating oil pipes
10. Remove the thermometer attachment branch.
11. Remove the exhaust pipe flanges
12. Loosen out the cylinder head hydraulic tightening nuts by using the hydraulic tool.
13. Fit the cylinder head lifting tool.
14. Lift the cylinder head with the help of lifting tool.
Exhaust and Inlet valve dismantling.

Exhaust and Inlet valve dismantling of Cylinder Head Marine Diesel Engine
1. Mount the cylinder head on a working table
2. Install the valve spindle supporting device on the head
3. Remove the spring-loaded valve bridge.
4. Fit the tool as per the fig
5. Tighten the nut ( B) to Compress the spring
6. Remove the valve cones/collets/valve locks.
7. Remove the valve rotators after removing the nut (B) and Traverse (C).
8. Remove the valve supporting device under the working table and draw out the valves.
Valve seats and valve spindle inspection
9. Carry out the lapping procedure in case the pitting or valve seat burn-out is minor.
10. In case of excessive pitting, perform the valve seat grinding process on the grinding machine.
Valve Guide Inspection (Cylinder Head Diesel Engine )
11. Valve guide is to be inspected for any pitting marks or symptoms of exhaust gas leakage.
12.Measure the valve guide bore.
Change the valve guide if the bore dimensions are found excessive than the prescribed limits.