3 Way Solenoid Valve
In the complex world of marine engineering, the efficient management of fluid systems is crucial for the optimal performance and safety of vessels. At the heart of many of these systems lies the 3-way solenoid valve, a versatile and powerful component that plays a pivotal role in controlling fluid flow. Whether it’s managing fuel systems, ensuring effective cooling, or handling ballast water, these valves are indispensable in enhancing marine operations.
This blog post will delve into the seven most powerful marine uses of 3-way solenoid valves, exploring their functions, benefits, and real-world applications. By understanding these key uses, marine engineers and industry professionals can harness the full potential of 3-way solenoid valves to improve efficiency, safety, and reliability on their vessels. Join us as we uncover the essential role these valves play in modern marine engineering.
Basics of 3-Way Solenoid Valves
Explanation of What a 3-Way Solenoid Valve Is
A 3-way solenoid valve is an electromechanical device used to control the flow of fluids or gases in various systems. Unlike standard solenoid valves that have only two ports (inlet and outlet), a 3-way solenoid valve features three ports, providing greater flexibility and control. This design allows the valve to divert flow between two different outlets or to mix two inputs into a single outlet, making it an essential component in complex fluid management systems.
Parts of 3-Way Solenoid Valves and Their Functions
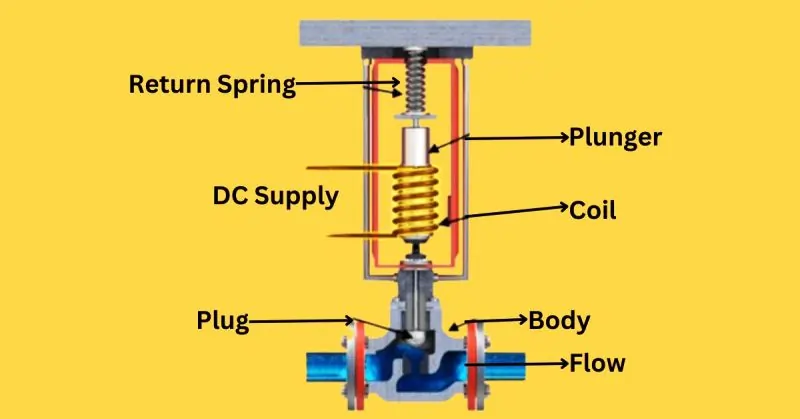
Body
The body of a 3-way solenoid valve serves as the main housing, encompassing all internal components and providing structural integrity. It typically features three ports: one common port, one normally closed port, and one normally open port. The material composition of the body is crucial for durability and compatibility with various fluids. Common materials include:
- Brass: Ideal for general applications due to its good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
- Stainless Steel: Preferred for harsh environments and corrosive fluids, offering superior strength and resistance to corrosion.
- Plastic: Used in specific applications where chemical resistance and lightweight properties are needed.
Coil
The coil is an essential component that generates the magnetic field required to move the plunger. It consists of numerous windings of insulated copper wire, which, when energized by a DC supply, create a magnetic field. This electromagnetic force is critical for actuating the valve. Key points about the coil include:
- Role: Converts electrical energy into magnetic energy to move the plunger.
- Material: Typically made of copper for efficient conductivity.
- Protection: Often enclosed in a protective casing to prevent damage and ensure safe operation.
Plunger
The plunger is a movable core inside the solenoid valve that responds to the magnetic field generated by the coil. Its movement is central to controlling the valve’s flow paths. When the coil is energized, the plunger is pulled into the coil, altering the flow direction within the valve. Key functions include:
- Flow Control: Moves to open or close different ports, directing the flow of fluid or gas.
- Material: Usually made of ferromagnetic materials such as iron or stainless steel to ensure responsiveness to the magnetic field.
Return Spring
The return spring plays a vital role in ensuring the plunger returns to its default position when the coil is de-energized. This component provides the necessary force to push the plunger back, allowing the valve to revert to its original flow path. Important aspects include:
- Function: Ensures the plunger returns to the normally closed or normally open position, maintaining consistent operation.
- Material: Typically made of stainless steel or other resilient metals to withstand repeated compression and release cycles.
DC Supply
The DC supply is the electrical power source for the solenoid valve’s coil. The supply voltage must match the coil’s specifications to ensure proper operation. Key considerations include:
- Importance: Provides the necessary power to energize the coil and create the magnetic field.
- Voltage: Common supply voltages include 12V, 24V, and 48V, depending on the valve’s design and application requirements.
- Regulation: Ensuring a stable and consistent DC supply is crucial for reliable valve operation.
Plug
The plug is responsible for sealing the valve and maintaining system integrity. It prevents leaks and ensures that the valve operates within its designed parameters. Key roles include:
- Sealing: Provides a tight seal to prevent fluid or gas leakage.
- Maintenance: Easily removable for maintenance and inspection, ensuring the longevity of the valve.
- Material: Often made of the same material as the valve body to ensure compatibility and durability.
Flow
The flow within a 3-way solenoid valve is directed and controlled by the movement of the plunger. The valve’s design allows it to switch between different flow paths or combine two inputs into one output. Key points about flow control include:
- Direction: The plunger’s position determines whether the flow is directed from the common port to the normally open or normally closed port.
- Control: Precise control of flow paths ensures efficient operation of marine systems, such as fuel management, cooling, and ballast systems.
- Efficiency: Proper flow control enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of the system, reducing operational costs and downtime.
5 The Most Powerful Marine Uses
Fuel System Management
Detailed Explanation of How 3-Way Solenoid Valves Are Used in Marine Fuel Systems
In marine fuel systems, 3-way solenoid valves are essential components that enhance the control and management of fuel flow. These valves provide the ability to switch between different fuel tanks, direct fuel to various parts of the engine, and manage fuel return lines efficiently. Here’s how they are typically used:
- Fuel Switching: 3-way solenoid valves allow seamless switching between multiple fuel tanks. This is crucial for balancing fuel usage and maintaining optimal weight distribution on the vessel. By directing the flow from one tank to another, these valves ensure continuous fuel supply without the need for manual intervention.
- Fuel Transfer: They facilitate the transfer of fuel between tanks, enabling the redistribution of fuel to maintain stability and trim of the vessel. This transfer capability is particularly important in long voyages where fuel management is critical.
- Engine Fuel Supply: 3-way solenoid valves control the fuel supply to different engine components, such as injectors and pumps. By directing the fuel precisely, they ensure that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel, enhancing performance and reducing the risk of fuel-related issues.
- Fuel Return Management: These valves also manage the return of excess fuel from the engine back to the fuel tanks. By controlling the return flow, they help maintain proper pressure within the fuel system and prevent overfilling of tanks.
Benefits in Terms of Fuel Efficiency, Safety, and Control
The use of 3-way solenoid valves in marine fuel systems offers several significant benefits:
- Fuel Efficiency: By providing precise control over fuel flow and distribution, these valves minimize fuel wastage and ensure optimal usage. Efficient fuel management translates to cost savings and extended operational range for the vessel.
- Safety: Enhanced safety is a critical benefit of using 3-way solenoid valves. By automating the switching and transfer of fuel, these valves reduce the need for manual handling, lowering the risk of spills and accidents. Additionally, they ensure that the fuel system operates within safe parameters, preventing issues such as overpressure and leaks.
- Control: These valves offer superior control over the fuel system, allowing for automated and remote operation. This level of control is essential for modern marine vessels, where advanced fuel management systems are integral to overall performance and reliability.
Ballast Water Treatment
Role of 3-Way Solenoid Valves in Ballast Water Management Systems
3-way solenoid valves play a crucial role in ballast water management systems by enabling precise control and distribution of ballast water. These systems are designed to manage the intake, treatment, and discharge of ballast water to ensure the stability and trim of the vessel while preventing the transfer of invasive species and pathogens between different marine environments. Here’s how 3-way solenoid valves are utilized:
- Ballast Water Intake and Discharge: 3-way solenoid valves control the flow of water into and out of ballast tanks. By switching the flow paths, they allow for the efficient intake of ballast water from the sea and its discharge back into the ocean, ensuring proper vessel stability and draft adjustments.
- Ballast Water Treatment: These valves direct water through various treatment stages, such as filtration, chemical disinfection, and UV irradiation. By precisely controlling the flow, they ensure that the ballast water undergoes thorough treatment to meet regulatory standards.
- System Integration: 3-way solenoid valves integrate seamlessly with automated ballast water management systems, allowing for remote operation and monitoring. This automation is critical for modern vessels, enabling efficient ballast operations without manual intervention.
Importance for Compliance with International Regulations and Environmental Protection
The use of 3-way solenoid valves in ballast water management systems is essential for compliance with international regulations and the protection of marine environments:
- Regulatory Compliance: International conventions, such as the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) Ballast Water Management Convention, mandate stringent requirements for ballast water treatment and discharge. 3-way solenoid valves ensure that ballast water is properly managed and treated to meet these standards, helping vessels avoid penalties and port entry restrictions.
- Environmental Protection: Untreated ballast water can introduce invasive species and pathogens to new environments, causing significant ecological and economic damage. By controlling the treatment process, 3-way solenoid valves help prevent the spread of harmful organisms, protecting biodiversity and marine ecosystems.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficient ballast water management, facilitated by 3-way solenoid valves, enhances the operational efficiency of vessels. Automated and precise control reduces the time and labor required for ballast operations, leading to smoother and more efficient voyages.
Cooling Systems
Application of 3-Way Solenoid Valves in Marine Engine Cooling Systems
In marine engine cooling systems, 3-way solenoid valves are integral components that facilitate the regulation and distribution of coolant flow. These valves enable precise control over the coolant’s direction, ensuring that the engine maintains optimal operating temperatures under varying conditions. Here’s how 3-way solenoid valves are typically utilized:
- Coolant Flow Regulation: 3-way solenoid valves control the flow of coolant between different parts of the engine and cooling circuits. By switching the flow paths, they ensure that the coolant is distributed efficiently to the areas that need it most.
- Heat Exchanger Management: These valves are used to direct coolant through heat exchangers, where the heat absorbed from the engine is transferred to seawater or other cooling media. This process is crucial for maintaining engine temperature within safe limits.
- Bypass Control: In situations where the engine does not require full cooling, such as during startup or in cooler environments, 3-way solenoid valves can divert some of the coolant flow away from the heat exchangers, ensuring rapid engine warm-up and efficient temperature control.
Installation Tips and Maintenance Practices
To ensure the effective operation of 3-way solenoid valves in marine engine cooling systems, proper installation and maintenance are essential. Here are some tips and best practices:
Installation Tips:
- Correct Sizing: Ensure that the valve is appropriately sized for the cooling system. This includes matching the flow capacity and pressure rating to the system’s requirements.
- Proper Orientation: Install the valve in the correct orientation as specified by the manufacturer. Incorrect installation can lead to malfunction and reduced efficiency.
- Secure Mounting: Mount the valve securely to minimize vibrations and potential damage. Use appropriate brackets and fittings to ensure a stable installation.
- Electrical Connections: Ensure that the electrical connections to the solenoid coil are secure and properly insulated. Use waterproof connectors if the installation is exposed to moisture.
- Integration with Control System: Integrate the valve with the engine’s cooling system control unit. Ensure that it is compatible with the existing control mechanisms for seamless operation.
Maintenance Practices:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Pay particular attention to the valve body, seals, and electrical connections.
- Cleanliness: Keep the valve and surrounding area clean to prevent debris from entering the system. Regularly clean the valve to ensure that it operates smoothly.
- Seal Replacement: Periodically replace the seals to prevent leaks and ensure tight closure. Use high-quality seals that are compatible with the coolant used in the system.
- Functional Testing: Perform functional tests to verify that the valve operates correctly. This includes checking the response time and ensuring that the valve switches flow paths accurately.
- Lubrication: If recommended by the manufacturer, apply appropriate lubrication to the moving parts of the valve to reduce friction and wear.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and replacements. This helps in tracking the valve’s performance and identifying any recurring issues.
Hydraulic Systems
Integration of 3-Way Solenoid Valves in Marine Hydraulic Systems
3-way solenoid valves are integral components in marine hydraulic systems, providing essential control over fluid power distribution. These valves enable precise management of hydraulic fluid flow, ensuring efficient operation of various hydraulic equipment and systems on board vessels. Here’s how 3-way solenoid valves are integrated into marine hydraulic systems:
- Flow Direction Control: 3-way solenoid valves are used to direct hydraulic fluid flow between different circuits. By switching the flow paths, these valves can control the direction and destination of the hydraulic fluid, which is essential for the operation of hydraulic actuators, cylinders, and motors.
- Pressure Regulation: These valves help in maintaining and regulating hydraulic pressure within the system. By diverting excess fluid or controlling the flow rate, they ensure that the hydraulic components operate within their optimal pressure ranges, preventing damage and ensuring consistent performance.
- System Isolation and Safety: 3-way solenoid valves can isolate different sections of the hydraulic system for maintenance or emergency purposes. This ability to cut off or reroute hydraulic fluid flow enhances safety and allows for easier troubleshooting and repair of hydraulic components.
- Automation and Remote Control: Integrated with electronic control systems, 3-way solenoid valves enable automated and remote operation of hydraulic systems. This integration is crucial for modern vessels where precision and efficiency are paramount.
Examples of Specific Marine Applications Utilizing Hydraulic Systems with 3-Way Solenoid Valves
- Steering Systems: In marine steering systems, 3-way solenoid valves control the hydraulic fluid that powers the steering actuators. This precise control ensures responsive and accurate steering, enhancing the maneuverability and safety of the vessel.
- Anchor Handling and Mooring: Hydraulic systems used in anchor handling and mooring operations rely on 3-way solenoid valves to manage the flow of hydraulic fluid to winches and capstans. This ensures smooth and controlled deployment and retrieval of anchors and mooring lines.
- Cargo Handling Equipment: On cargo ships, 3-way solenoid valves are integral to the operation of hydraulic cranes, lifts, and other cargo handling equipment. They enable precise control of hydraulic actuators, ensuring safe and efficient loading and unloading of cargo.
- Hatch Cover Operation: Hydraulic systems that operate hatch covers on bulk carriers and container ships use 3-way solenoid valves to control the opening and closing mechanisms. This reliable control ensures the secure sealing and easy access to cargo holds.
- Stabilizer Systems: In marine stabilizer systems, 3-way solenoid valves regulate the hydraulic fluid that adjusts the stabilizer fins. This helps in maintaining vessel stability, reducing roll, and enhancing passenger comfort during rough seas.
- Hydraulic Winches and Windlasses: These systems, used for anchoring and towing operations, benefit from the precise control offered by 3-way solenoid valves. The valves manage the hydraulic fluid flow, ensuring smooth and powerful operation of winches and windlasses.
Fire Suppression Systems
Role of 3-Way Solenoid Valves in Marine Fire Suppression Systems
3-way solenoid valves are vital components in marine fire suppression systems, playing a crucial role in managing the flow of fire suppression agents. These valves ensure that the system can quickly and effectively respond to fire emergencies by directing agents such as water, foam, or gas to the affected areas. Here’s how they are used in marine fire suppression systems:
- Agent Distribution: 3-way solenoid valves control the distribution of fire suppression agents to various sections of the vessel. By switching the flow paths, they can direct the agent to specific compartments or areas where a fire is detected.
- System Activation: Upon receiving a signal from the fire detection system, these valves quickly open or close to allow the suppression agent to flow from storage tanks to the distribution network. This rapid response is critical for controlling and extinguishing fires before they spread.
- Redundant Control: In more advanced systems, multiple 3-way solenoid valves are used to provide redundancy. This ensures that even if one valve fails, others can take over, maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of the fire suppression system.
Importance for Safety and Rapid Response in Emergency Situations
The integration of 3-way solenoid valves in marine fire suppression systems offers several key benefits, particularly concerning safety and emergency response:
- Rapid Response: The primary advantage of using 3-way solenoid valves is their ability to respond quickly to fire detection signals. This rapid activation is crucial in marine environments where fires can spread rapidly due to confined spaces and the presence of flammable materials.
- Enhanced Safety: By ensuring the swift and precise delivery of fire suppression agents, these valves significantly enhance the safety of the vessel and its crew. They help to quickly control and extinguish fires, minimizing damage and reducing the risk of injury or fatalities.
- Automated Control: The valves enable automated control of the fire suppression system, reducing the need for manual intervention. This automation is vital in emergency situations, where human reaction time can be a limiting factor.
- System Reliability: The reliability of 3-way solenoid valves ensures that the fire suppression system will function correctly when needed. Regular maintenance and testing of these valves can further enhance system reliability, providing peace of mind for vessel operators.
Technical Details and Real-Life Examples of Effective Use
Technical Details:
- Material Composition: 3-way solenoid valves used in fire suppression systems are typically made from materials that can withstand high pressures and corrosive environments, such as stainless steel or brass.
- Pressure Rating: These valves must have a high-pressure rating to handle the force of the fire suppression agents being deployed. This ensures they can operate effectively under the demanding conditions of a fire emergency.
- Response Time: The actuation time of the valve is critical. High-quality solenoid valves are designed to respond almost instantaneously to activation signals, ensuring no delay in the deployment of the suppression agent.
- Seal Integrity: To prevent leaks and ensure the efficient delivery of suppression agents, the valves feature high-integrity seals. These seals are designed to maintain their integrity under high pressure and in the presence of various fire suppression chemicals.
Real-Life Examples:
Case Study 1: Cargo Ship Fire Suppression A cargo ship equipped with a comprehensive fire suppression system experienced a fire in one of its cargo holds due to overheating cargo. The 3-way solenoid valves in the system responded immediately to the fire detection signals, directing a foam agent to the affected area. The rapid deployment of the foam quickly suppressed the fire, preventing it from spreading to adjacent holds and causing further damage. The crew was able to control the situation without injury, demonstrating the effectiveness of the valves in ensuring safety and rapid response.
Case Study 2: Passenger Ferry Safety A passenger ferry operating in the Mediterranean Sea implemented 3-way solenoid valves as part of its upgraded fire suppression system. During a routine drill, the system was tested, and the valves successfully directed water mist to various sections of the vessel, simulating a real fire emergency. The test confirmed that the valves could deliver a rapid and targeted response, significantly enhancing the safety of passengers and crew by ensuring any fire would be quickly controlled.
Case Study 3: Offshore Oil Rig An offshore oil rig faced a fire outbreak in one of its engine rooms. The fire suppression system, equipped with 3-way solenoid valves, activated immediately upon detection. The valves directed a CO2 agent to the engine room, effectively suffocating the fire within minutes. The quick and precise action of the solenoid valves prevented extensive damage to the rig’s equipment and infrastructure, highlighting their crucial role in maintaining safety in hazardous environments.
FAQ on “3 Way Solenoid Valve”
Q: What is a 3-way solenoid valve used for?
A: It controls fluid or gas flow between three ports.
Q: How does a 3-way solenoid valve work?
A: It uses an electromagnetic coil to move a plunger, changing flow paths.
Q: Why are 3-way solenoid valves important in marine systems?
A: They provide precise control and enhance safety.
Q: What materials are 3-way solenoid valves made of?
A: They are made from brass, stainless steel, or high-grade plastics.
Conclusion
3-way solenoid valves are essential components in various marine applications, including fuel system management, ballast water treatment, cooling systems, hydraulic systems, and fire suppression. Their ability to provide precise control, enhance safety, and improve efficiency makes them invaluable in the maritime industry. By integrating these valves into marine systems, engineers can ensure optimal performance, compliance with regulations, and the protection of both vessel and crew. Whether it’s preventing fires, maintaining engine temperatures, or managing ballast water, 3-way solenoid valves play a crucial role in modern marine operations, underscoring their importance in enhancing the overall safety and functionality of maritime vessels.
