Turbocharger Problems
Turbochargers play a critical role in enhancing the performance of Diesel Engines and Diesel Generators, especially in demanding marine and industrial applications. These devices boost engine efficiency and power, making them indispensable in high-performance environments. However, turbochargers are not immune to issues; common problems like overheating, oil leaks, and pressure inconsistencies can severely impact engine performance and longevity. Addressing these issues promptly is essential to maintaining optimal engine function. In this post, we’ll delve into the seven most powerful remedies for common turbocharger problems, offering practical solutions to keep your engines running smoothly and efficiently.
Turbocharger Lag
Problem Explanation:
Turbocharger lag is the delay between when the engine is accelerated and when the turbocharger starts delivering additional power. This lag occurs because the turbocharger relies on exhaust gases to spin the turbine and build up pressure, which takes time. During this lag, the engine may feel sluggish and unresponsive, particularly at lower RPMs, which can negatively impact overall performance, especially in situations requiring immediate power output in marine diesel engines.
Powerful Remedy 1:
One of the most effective solutions for turbocharger lag in marine diesel engines is optimizing the wastegate operation. By fine-tuning the wastegate, exhaust flow can be controlled more precisely, allowing the turbocharger to spool up faster and reduce lag. Another powerful remedy is upgrading to a more responsive turbocharger designed to minimize lag, such as those with a lighter turbine or advanced variable geometry technology. This upgrade can significantly enhance acceleration and overall engine responsiveness in marine applications.
Turbocharger Overheating
Problem Explanation:
Turbocharger overheating is a critical issue that can lead to severe damage in marine diesel engines. Overheating typically occurs due to inadequate lubrication, which causes excessive friction and heat within the turbocharger components. Additionally, excessive exhaust temperatures, often exceeding the safe operating limit of around 650°C to 750°C (1,202°F to 1,382°F) for most turbochargers, can overwhelm the turbocharger’s ability to dissipate heat. Operating beyond this temperature threshold can result in reduced efficiency, potential damage to the turbocharger, and, in extreme cases, engine failure.
Powerful Remedy 2:
To effectively combat turbocharger overheating, several remedies can be implemented. Improving the cooling systems is essential; this may involve upgrading or optimizing the existing cooling infrastructure to ensure it can handle the heat load effectively. Ensuring proper oil flow is also crucial, as adequate lubrication helps dissipate heat and reduce friction within the turbocharger. Regular maintenance checks are vital to monitor the condition of the turbocharger, identify early signs of overheating, and take corrective actions before severe damage occurs. Monitoring exhaust temperatures closely to ensure they remain within safe limits is also critical for preventing overheating.
Turbocharger Oil Leaks
Problem Explanation:
Oil leaks in a turbocharger can significantly reduce engine efficiency and, if left unaddressed, may lead to serious engine damage. The turbocharger relies on a steady supply of oil to lubricate its moving parts and maintain optimal performance. When oil begins to leak, it can cause the turbocharger to run hotter, increase friction, and reduce its overall efficiency. Additionally, oil leaks can lead to contamination of the air intake system, causing fouling of the compressor and intercooler, which further degrades engine performance. If the leaks are severe, they can result in insufficient lubrication, potentially leading to turbocharger failure or even engine seizure.
Powerful Remedy 3:
To effectively address oil leaks in a turbocharger, several steps should be taken. Begin by thoroughly inspecting the seals within the turbocharger for any signs of wear or damage; if any are found, they should be promptly replaced to prevent further leakage. Damaged gaskets should also be replaced, as they are common sources of oil leaks. Ensuring the correct oil pressure is maintained is crucial, as both high and low oil pressure can contribute to leaks. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the oil supply system can prevent leaks from developing and ensure the turbocharger continues to operate efficiently.
Compressor Wheel Damage
Problem Explanation:
The compressor wheel in a turbocharger is a critical component that compresses incoming air to increase the engine’s power output. However, it is vulnerable to damage from foreign objects or debris that may enter the turbocharger. Even small particles can cause significant damage, leading to nicks, cracks, or imbalances in the compressor wheel. This damage can result in poor turbocharger performance, reduced engine efficiency, and potentially costly repairs. In severe cases, a damaged compressor wheel can lead to complete turbocharger failure, compromising the engine’s overall operation.
Powerful Remedy 4:
To prevent compressor wheel damage, it is essential to take proactive measures. Installing high-quality air filters is one of the most effective ways to block debris from entering the turbocharger. These filters should be chosen based on the operating environment and should be regularly maintained to ensure they are functioning properly. Additionally, conducting regular inspections of the turbocharger and air intake system can help identify any potential issues early on. By catching signs of wear or damage early, preventive maintenance can be performed, thereby extending the life of the turbocharger and maintaining optimal engine performance.
Turbocharger Bearing Failure
Problem Explanation:
Bearing failure is a common and serious issue in turbochargers that can lead to significant engine problems. Bearings in a turbocharger support the shaft that connects the turbine and compressor wheels, allowing them to spin at high speeds. However, these bearings are highly sensitive to lubrication quality and cleanliness. Improper lubrication, whether due to using low-quality oil, infrequent oil changes, or inadequate oil supply, can cause excessive friction and heat, leading to premature bearing wear. Contamination in the oil, such as dirt or debris, can also damage the bearings, causing them to wear out more quickly and potentially leading to catastrophic turbocharger failure.
Powerful Remedy 5:
Preventing turbocharger bearing failure requires a focus on proper lubrication and oil management. Using high-quality oil specifically designed for turbocharged engines is essential to ensure that the bearings receive adequate protection. Regular oil changes are also crucial to prevent the buildup of contaminants that can lead to bearing wear. Additionally, monitoring oil cleanliness through regular oil analysis can help detect contamination early, allowing for corrective actions before significant damage occurs. By maintaining proper lubrication practices and closely monitoring oil quality, the risk of turbocharger bearing failure can be significantly reduced, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the turbocharger and engine.
Boost Pressure Issues
Problem Explanation:
Boost pressure is a critical factor in the performance of a turbocharged engine. Incorrect boost pressure, whether too high or too low, can lead to significant engine inefficiency or even damage. If the boost pressure is too low, the engine may suffer from a lack of power, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased exhaust emissions. On the other hand, if the boost pressure is too high, it can cause excessive stress on the engine components, leading to potential damage such as head gasket failure, piston damage, or even catastrophic engine failure. Maintaining the correct boost pressure is essential for optimal engine performance and longevity.
Powerful Remedy 6:
To address boost pressure issues, several remedies can be implemented. Recalibrating the boost controller is a key step to ensure that the turbocharger is providing the correct amount of boost pressure for the engine’s needs. It is also important to check for leaks in the intake system, as even small leaks can lead to significant pressure losses and affect engine performance. Ensuring proper wastegate function is another crucial aspect; a malfunctioning wastegate can either cause the turbocharger to overboost or underboost, leading to the issues mentioned above. Regular inspections and maintenance of the boost control system can help prevent these problems and maintain the engine’s efficiency and reliability.
Turbocharger Surge
Problem Explanation:
Turbocharger surge occurs when there is a sudden reversal of airflow within the turbocharger, usually due to a mismatch between the engine’s air demand and the turbocharger’s air supply. This phenomenon typically happens when the throttle is closed rapidly, causing the compressed air to back up and create a surge of pressure. The surge can lead to oscillations in the turbocharger’s speed and pressure, which can cause significant instability in engine performance. In severe cases, turbocharger surge can result in damage to the compressor wheel, bearings, or other components, leading to reduced efficiency and potential engine failure.
Powerful Remedy 7:
To prevent turbocharger surge, several effective remedies can be employed. Adjusting the blow-off valve (or bypass valve) is one of the most common solutions, as it allows excess pressure to be released when the throttle is closed, preventing the buildup of pressure that leads to surge. Installing an anti-surge system is another effective measure, especially in high-performance or heavily modified engines, as it helps manage airflow and prevent surge conditions. Additionally, upgrading to a more suitable turbocharger, specifically designed to operate efficiently within the engine’s parameters, can reduce the likelihood of surge and improve overall engine stability. Regular maintenance and proper tuning are essential to keeping the turbocharger and engine in optimal condition.
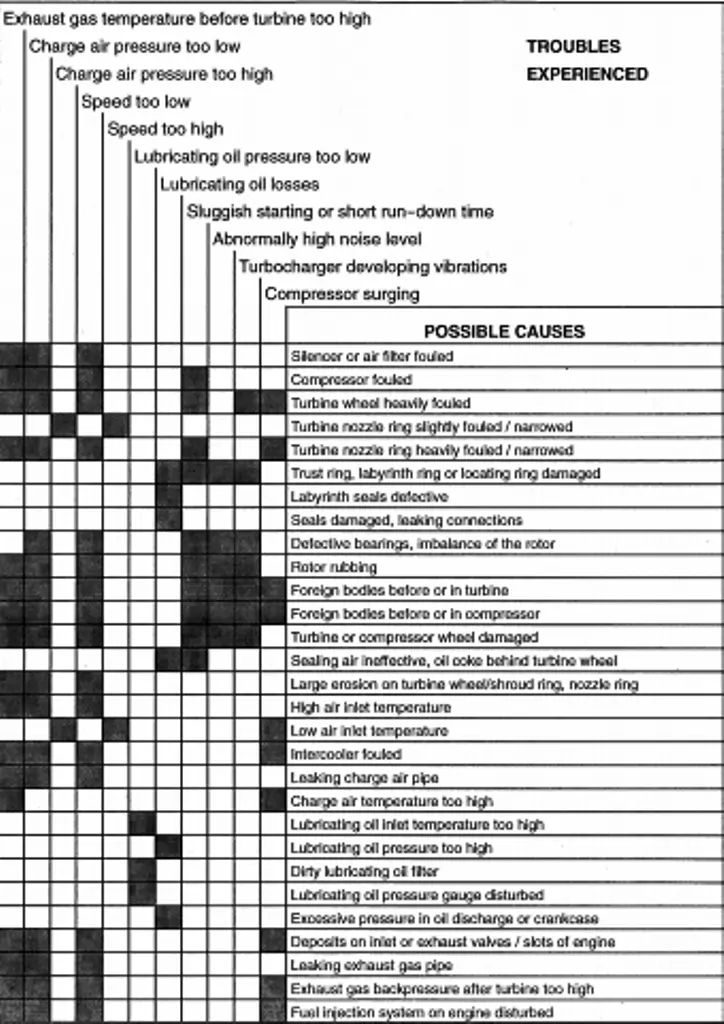
Troubleshooting
Possible remedies for failures
| Exhaust temperature too high | |
| Engine | Cause:- Malfunction in the injection system |
| Remedy:- Repair, or contact the manufacturer. | |
| Turbocharger | Cause:-Air starvation, e.g. air filter clogged with dirt Remedy:- Clean |
| Cause:- Compressor / turbine soiled Remedy:- Clean | |
| Cause:- Exhaust counter pressure too high Remedy:- Clean or repair boiler or exhaust silencer | |
| Cause:- Turbine damaged or worn Remedy:- Contact an official ABB Turbo Systems service station. | |
| Charge-air cooler | Cause:- Cooler soiled Remedy:- Clean |
| Cause:- Insufficient coolant water quantity Remedy:- Replenish | |
| Cause:- Coolant water inlet temperature too hot Remedy:- Clean/inspect cooling system | |
| Cause:- Ventilation inadequate Remedy:- Improve ventilation | |
| Charge-air pressure too low (Engine output and speed unchanged Intake condition normal) | |
| Engine | Cause:- Air receiver leaking Remedy:- Repair |
| Cause:- Gas line between engine and turbine leaking Remedy:- Repair | |
| Cause:- Injection misadjusted Remedy:- Correct adjustment | |
| Cause:- Valve control misadjusted Remedy:- Correct adjustment | |
| Turbocharger | Cause:- Manometer display faulty Remedy:- Replace manometer |
| Cause:- Leak in line to the manometer Remedy:- Repair leak | |
| Cause:- Air filter dirty, causing excessive loss of pressure Remedy:- Clean | |
| Cause:- Compressor / turbine soiled Remedy:- Clean | |
| Cause:- Compressor / turbine damaged Remedy:- Contact an official Manufacturer Turbo Systems service station. | |
| Cause:- Excessive exhaust counter pressure Remedy:- Clean boiler or exhaust silencer | |
| Charge-air pressure too high (Engine output and speed unchanged Intake condition normal) | |
| Engine | Cause:- Malfunction in the injection system Remedy:- Correct adjustment |
| Cause:- Engine output higher than expected Remedy:- Check engine output | |
| Cause:- Injection misadjusted Remedy:- Correct adjustment | |
| Turbocharger | Cause:- Manometer display faulty Remedy:- Replace manometer |
| Vibrations | |
| Turbocharger | Cause:- 1. Rotor imbalance due to heavy fouling of compressor/turbine 2. Turbine or compressor damaged 3. Bearing defective Remedy: – Contact an official Manufacturer Turbo Systems service station. |
| Noises during run-out | |
| Turbocharger | Cause:- Turbocharger dirty Remedy: – Clean |
| Cause: – 1. Bearing damaged 2. Rotor grazing 3. Foreign bodies in the turbocharger Remedy: – Contact an official Manufacturer Turbo Systems service station. | |
| Run-out time too short | |
| Turbocharger | Cause: – Turbocharger dirty Remedy:- Clean |
| Cause: – 1. Bearing damaged 2. Rotor grazing 3. Foreign bodies in the turbocharger Remedy: – Contact an official ABB Turbo Systems service station. | |
| Sluggish start-up | |
| Turbocharger | Cause: – Turbocharger dirty Remedy:- Clean |
| Cause: – 1. Bearing damaged 2. Rotor grazing 3. Foreign bodies in the turbocharger Remedy: – Contact an official ABB Turbo Systems service station. | |
| Lubricating oil pressure too low | |
| Engine | Cause: – Oil filter heavily soiled Remedy: – Clean |
| Cause: – Oil pump in the lubricating system defective Remedy: – Inspect | |
| Cause: – Manometer provides false reading Remedy: – Replace manometer | |
| Turbocharger | Cause: – Axial clearance of the rotor too big Remedy: – Contact an official ABB Turbo Systems service station. |
| Constant surging of the turbocharger | |
| Engine | Cause: – 1. Exhaust pressure to the turbine elevated because boiler or exhaust silencer is dirty 2. Trap dirty Remedy: – Clean |
| Turbocharger | Cause: – 1. Charge-air filter or silencer dirty 2. Heavy deposits of contamination in the turbine Remedy: – Clean |
Troubles experienced
Symptoms of a Faulty Turbocharger in Marine Diesel Engines
A faulty turbocharger can severely impact the performance of marine diesel engines. Here are key symptoms to be aware of:
Excessive Exhaust Smoke: If you notice an unusual amount of exhaust smoke, particularly black or blue smoke, it could indicate that your turbocharger is leaking oil into the exhaust system or that the engine is running rich due to turbo failure. This is a clear sign that your engine needs immediate inspection.
Poor Acceleration or Throttle Response: A failing turbocharger may struggle to provide the necessary boost, resulting in sluggish acceleration and poor throttle response. This loss of power is often one of the first signs of turbocharger issues in marine engines.
Loud Noises Upon Startup: Unusual noises such as whining, whistling, or grinding sounds during startup or acceleration can indicate that the turbocharger’s internal components, like the bearings or compressor wheel, are damaged.
Reduced Fuel Economy: A drop in fuel efficiency is another common symptom. A faulty turbocharger can cause the engine to burn more fuel to compensate for the lack of power, leading to increased fuel consumption.
Engine Warning Systems: In marine diesel engines, engine warning systems may trigger alarms or indicators if there is an issue with the turbocharger or related components. These warnings should be taken seriously, as they often indicate a critical problem that requires immediate attention.
What Is the Average Life of Marine Engine Turbocharger Components?
The lifespan of a marine engine turbocharger largely depends on the durability of its main components:
- Nozzle Ring:
Typically, the nozzle ring can last between 20,000 to 40,000 operating hours, depending on the quality of the materials and the operating conditions. Regular inspections can help detect wear and tear early. - Compressor Wheel:
The compressor wheel generally has a lifespan of 40,000 to 60,000 operating hours. Its longevity is influenced by the air quality entering the turbocharger, with debris and contaminants significantly shortening its life. - Turbocharger Bearings (TC Bearings):
- Ball or Roller Bearings: These bearings usually have a shorter lifespan, typically around 8,000 to 12,000 running hours. They require precise maintenance and proper lubrication to maximize their life.
- Bush Bearings: Typically last around 40,000 to 50,000 operating hours. These bearings are more durable but still require regular lubrication and maintenance to avoid premature wear.
- Labyrinth Ring:
The labyrinth ring, responsible for sealing and preventing oil leaks, has an average lifespan of 30,000 to 50,000 operating hours. Its life can be affected by oil quality and operating temperatures.
Key Formulas for Diagnosing Turbocharger Problems
1. Boost Pressure Calculation
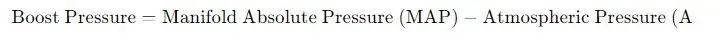
- Explanation: Boost pressure is the pressure increase provided by the turbocharger. It’s calculated by subtracting the atmospheric pressure from the manifold absolute pressure. Incorrect boost pressure can indicate problems such as leaks, wastegate issues, or turbocharger inefficiency.
2. Air-Fuel Ratio (AFR) Calculation
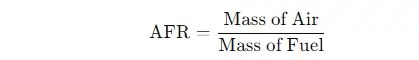
- Explanation: The air-fuel ratio is crucial for engine efficiency and performance. A turbocharger that isn’t working correctly can affect the AFR, leading to poor engine performance or excessive exhaust smoke. Monitoring the AFR can help identify turbocharger problems.
3. Turbocharger Efficiency

- Explanation: This formula calculates the efficiency of the turbocharger by comparing the power it generates (increasing air pressure) to the power it consumes (from exhaust gases). Lower efficiency can indicate issues such as compressor wheel damage or turbine inefficiency.
4. Compressor Wheel Speed
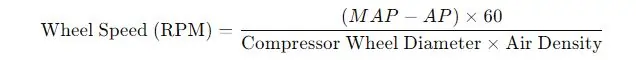
- Explanation: The speed of the compressor wheel is critical to the turbocharger’s performance. If the wheel speed is too low or too high, it could indicate issues with the turbocharger or related components.
5. Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT)
- Guideline:
- High EGTs can indicate that the turbocharger is not operating efficiently or that there is excessive back pressure, potentially leading to overheating and failure.
- No specific formula, but monitoring EGT is essential for diagnosing potential turbocharger problems.
FAQ on “Turbocharger Problems”
Q: What causes turbocharger lag?
A: Turbocharger lag is caused by the time it takes for the turbo to build pressure.
Q: How can I prevent turbocharger overheating?
A: Ensure proper cooling and oil flow, and perform regular maintenance checks.
Q: What leads to turbocharger oil leaks?
A: Oil leaks are often caused by worn seals or gaskets and incorrect oil pressure.
Q: How can turbocharger surge be avoided?
A: Adjust the blow-off valve or install an anti-surge system to manage airflow.
Conclusion
In this post, we’ve explored the seven most powerful remedies for common turbocharger problems: optimizing the wastegate operation to reduce lag, improving cooling systems to prevent overheating, inspecting and replacing seals to stop oil leaks, installing better air filters to avoid compressor wheel damage, maintaining proper lubrication to prevent bearing failure, recalibrating boost controllers to correct pressure issues, and adjusting blow-off valves to eliminate turbocharger surge. Each of these remedies plays a crucial role in ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your turbocharger.
Regular maintenance and timely interventions are essential in preventing these issues from escalating into more serious problems. By staying proactive, you can protect your engine, improve efficiency, and avoid costly repairs. Implement these remedies in your maintenance routine, and don’t hesitate to consult with professionals if you encounter severe turbocharger issues. Taking action now will save you time, money, and potential headaches in the future.