Types of Boiler Burner
Boiler burners play a critical role in both industrial and marine applications, ensuring efficient combustion and energy generation. By controlling the fuel and air mixture, burners directly influence the boiler’s performance, energy efficiency, and environmental impact. Whether it’s powering industrial processes or driving marine vessels, the right burner can make a significant difference in operational effectiveness.
This post explores the various types of boiler burners, from gas and oil to dual-fuel and low NOx options, and their specific advantages. Understanding the differences between these burner types is essential for selecting the most suitable one for your boiler’s needs. Whether you’re focused on fuel efficiency, emissions control, or overall system performance, choosing the correct burner type can optimize both operation and costs. Read on to discover the best burner for your application in 2024.
What Are Boiler Burners?
Definition
A boiler burner is a critical component of a boiler system responsible for mixing fuel and air in the correct ratio to ensure efficient combustion. The burner ignites the fuel, generating heat that transfers to the water or steam in the boiler, creating the energy needed for various industrial, marine, or heating applications. The type of burner used determines how effectively the fuel is burned and how efficiently energy is produced.
Importance
Choosing the right burner is essential for optimal boiler efficiency and performance. A properly selected burner improves fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, and ensures reliable operation under different load conditions. The right burner also minimizes maintenance costs by reducing wear and tear, and it helps in meeting environmental regulations by controlling harmful emissions. Whether for industrial plants or marine vessels, the efficiency of a boiler system heavily depends on the performance of its burner, making it a key factor in operational success.
Types of Boiler Burners
Boiler burners are classified based on the fuel type they use and their specific applications. The choice of burner can significantly impact boiler performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Below is an overview of the major types of boiler burners.
1. Gas Burners

How they work: Gas burners operate by mixing natural gas or other gases with air in the proper ratio to create efficient combustion. A spark or pilot flame ignites the gas, producing heat.
Applications: Gas burners are commonly used in marine, industrial, and residential boilers due to their cleaner combustion and efficiency.
2. Oil Burners

Functionality: Oil burners use fuel oils such as diesel or heavy oil, which are atomized into fine droplets for combustion. The burner ignites these droplets, creating heat.
Applications: Oil burners are widely used in diesel generators, marine vessels, and heavy industrial boilers for high heat demand.
3. Dual-Fuel Burners
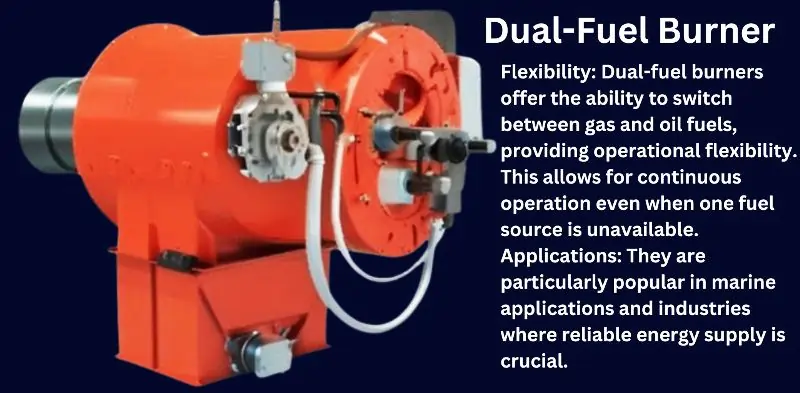
Flexibility: Dual-fuel burners offer the ability to switch between gas and oil fuels, providing operational flexibility. This allows for continuous operation even when one fuel source is unavailable.
Applications: They are particularly popular in marine applications and industries where reliable energy supply is crucial.
4. Pulverized Coal Burners

Combustion Method: Pulverized coal burners grind coal into fine particles and mix it with air for efficient combustion. This method provides consistent heat and power.
Applications: These burners are typically used in large-scale industrial settings like power plants due to their ability to handle high loads and provide steady energy output.
5. Low NOx Burners

Environmental Benefits: Low NOx burners are designed to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, a major contributor to air pollution. By controlling combustion temperatures and oxygen levels, they minimize NOx production.
Applications: They are widely used in modern, energy-efficient systems where strict environmental regulations apply, such as in industrial and marine boilers.
Each type of burner offers unique advantages depending on the application and fuel availability, making it crucial to choose the right burner to meet specific operational and environmental needs.
Key Features of Each Burner Type
| Burner Type | Efficiency Comparison | Fuel Versatility | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Burners | High efficiency due to clean combustion and precise control of fuel-air mixture. | Limited to natural gas or other gaseous fuels. | Lower emissions of CO2 and NOx compared to oil and coal burners. |
| Oil Burners | Moderate efficiency, though lower than gas burners. Efficiency depends on oil type used. | Works with various fuel oils (diesel, heavy oil), offering some flexibility. | Higher emissions of CO2 and sulfur oxides; stricter regulations on sulfur content. |
| Dual-Fuel Burners | High efficiency, especially when using gas. Switching fuels does not impact performance. | Highly versatile, can switch between gas and oil based on availability or pricing. | Emissions depend on the fuel used; gas produces fewer emissions than oil. |
| Pulverized Coal Burners | Lower efficiency compared to gas or oil due to the handling and preparation of coal. | Limited to coal, though suitable for large-scale industrial operations. | High emissions of CO2, particulates, and sulfur compounds, requiring treatment systems. |
| Low NOx Burners | High efficiency with a focus on reducing waste heat and maintaining optimal combustion. | Typically designed for specific fuels like gas or oil, with less versatility. | Significantly reduced NOx emissions, meeting strict environmental regulations. |
Choosing the Right Burner for Your Boiler
Factors to Consider
When selecting a burner for your boiler, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance:
- Efficiency: The efficiency of the burner directly affects fuel consumption and energy output. Gas burners tend to offer higher efficiency, while oil and coal burners might be less efficient but can handle larger energy demands. Choosing a burner with higher efficiency can result in significant cost savings over time.
- Fuel Type: The availability and cost of fuel play a major role in burner selection. Gas burners are ideal for areas with a steady gas supply, while oil burners are better suited for locations where oil is more readily available. Dual-fuel burners offer flexibility to switch between fuels depending on availability and pricing.
- Application Size: The size of the boiler and the energy requirements of the application are critical. Larger industrial applications may require pulverized coal or oil burners to meet high power demands, while smaller systems can rely on gas or dual-fuel burners for more precise control.
- Environmental Regulations: Emission standards and environmental regulations must be considered. Low NOx burners are designed to minimize harmful emissions like nitrogen oxides, making them essential for operations subject to strict environmental controls. Choosing the right burner helps in compliance with these regulations and reduces the carbon footprint.
Marine vs. Industrial Boilers
The choice of burner varies significantly between marine and industrial boilers due to differences in operational environments and fuel availability:
- Marine Boilers: In marine applications, dual-fuel burners are highly favored due to their flexibility in using either gas or oil, ensuring that the ship can operate efficiently regardless of fuel availability. Marine burners are typically designed to handle fluctuating loads and work efficiently under tough sea conditions.
- Industrial Boilers: Industrial boilers often rely on oil, gas, or even pulverized coal burners, depending on the size and energy demands of the facility. Industrial burners are designed for more stable operational conditions and higher energy output, with an emphasis on maximizing efficiency and reducing operating costs. Environmental concerns in industrial settings may require the use of low NOx burners to comply with local emissions standards.
Burner Maintenance and Safety
| Burner Type | Maintenance Requirements | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Burners | Regular inspection of fuel lines, ignition system, and air-to-fuel ratio settings. Clean burner ports and verify flame sensors. | Check for gas leaks, ensure proper ventilation to prevent gas buildup, and verify functioning flame detection systems to avoid misfires. |
| Oil Burners | Clean nozzles, flame sensors, and combustion chamber regularly. Replace oil filters frequently for smooth fuel supply. | Handle oil carefully to prevent spills and fires. Keep burners free of soot/carbon deposits. Install sensors for temperature/pressure monitoring. |
| Dual-Fuel Burners | Maintain both gas and oil systems. Check the fuel-switching mechanism regularly for smooth operation between fuels. | Test the fuel-switching system. Ensure clean fuel supplies for both gas and oil. Install pressure relief valves for fuel pressure fluctuations. |
| Pulverized Coal Burners | Regular cleaning and inspection of coal feeding system, combustion chamber, and ash removal mechanisms. | Prevent coal dust accumulation with proper ventilation and dust collection systems. Inspect coal feeders to avoid feeding malfunctions. |
| Low NOx Burners | Routine tuning and calibration of combustion settings to ensure emission levels stay within limits. Monitor combustion temperature. | Monitor temperature closely to avoid excessive NOx production. Install fail-safes and alarms for detecting temperature or pressure deviations. |
FAQ: Types of Boiler Burners
Q. How many types of boiler burners are there?
A. There are diesel, gas, and biomass burners.
Q. What is a boiler burner?
A. A boiler burner provides the heat to turn water into steam in the boiler and is connected to the boiler.
Q. What is the most common type of burner?
A. Gas burners are the most common type.
Q. What is burner firing rate?
A. The firing rate is the amount of fuel a burner can burn over a specific time.
Conclusion
In this post, we’ve explored the different types of boiler burners, including gas, oil, dual-fuel, pulverized coal, and low NOx burners. Each burner type comes with its unique features—gas burners offer clean and efficient combustion, oil burners handle higher heat demands, dual-fuel burners provide flexibility, pulverized coal burners are ideal for large-scale industrial applications, and low NOx burners focus on reducing emissions for a cleaner environment.
When selecting the right burner for your needs in 2024, consider factors such as fuel availability, efficiency requirements, and environmental regulations. For marine applications, dual-fuel burners may offer the best flexibility, while low NOx burners are ideal for industries needing to meet strict emission standards. By carefully evaluating your specific requirements, you can choose a burner that optimizes performance, reduces costs, and ensures compliance with environmental standards.
