Marine Diesel Engine Piston
Welcome to the Marine Diesel Engine Piston Guide 2025—your expert resource for everything you need to know about pistons in modern marine diesel engines. The piston in an engine is like a busy worker, playing a central role in transforming the energy from burning fuel into mechanical power that drives the vessel. In every marine diesel engine, the piston performs multiple critical functions: it seals off the combustion chamber, keeps the internal environment orderly, and acts as a “door” to contain the explosive force of burning fuel.
Beyond its sealing role, the piston guides the connecting rod—a vital link between the piston and the engine’s crankshaft—to ensure smooth up-and-down motion. As fuel combusts inside the cylinder, the resulting pressure pushes the piston downward. This movement, much like the force that propels a balloon when released, turns the engine’s crankshaft and delivers the power needed to operate marine machinery.
Finally, the piston plays a key role in heat management, dissipating the intense heat produced during combustion and helping maintain safe engine temperatures. In summary, as explained in this Marine Diesel Engine Piston Guide 2025, the piston is a multitasking component: it seals the combustion chamber, directs the connecting rod, converts combustion pressure into movement, and protects against overheating for optimal marine engine performance.
The purpose of a Piston in the engine
The piston is the most important unit of any Engine.
- The Diesel Engine Piston transmits the force of expanding gas in the cylinder via a connecting rod to the crankshaft.
- Piston converts the energies from one form to another. ( Chemical energy to mechanical energy)
- The sealing effect between the piston and the cylinder liner is provided with the help of piston rings. The economy and efficiency of the engine are due to the contribution of the piston in an engine.
- The small end of the connecting rod is guided by the piston. Hence, the piston bears the side thrust.
Diesel engine piston for the marine engine
Diesel engine piston Parts identification
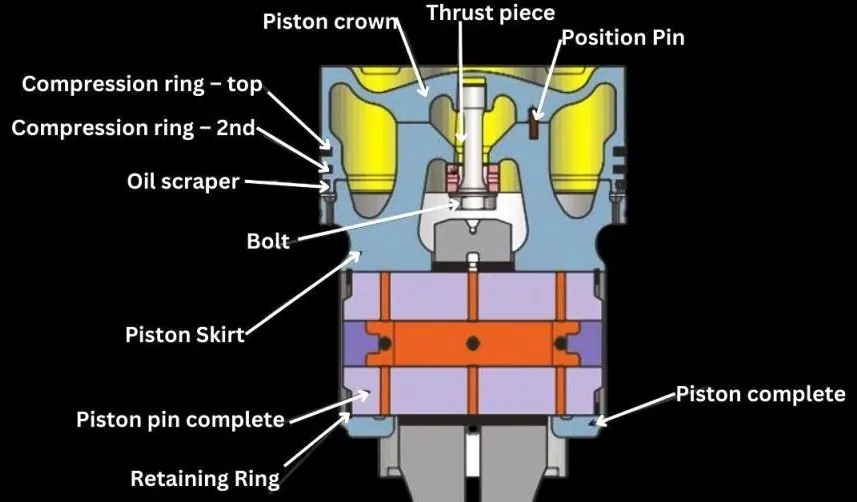
Detailed Description of Piston Components
Piston Complete
The piston is a critical component in an internal combustion engine. It moves up and down within the cylinder, converting the energy from the combustion process into mechanical motion. A complete piston assembly includes the piston crown, piston skirt, piston pin, and rings.
Piston Crown
The piston crown is the top part of the piston that comes into direct contact with the combustion gases. It is designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The shape of the crown can vary depending on the engine design and combustion requirements.
Piston Skirt
The piston skirt is the lower part of the piston that extends down into the cylinder. It helps to stabilize the piston as it moves up and down, reducing lateral movement and wear. The skirt is designed to minimize friction between the piston and the cylinder wall.
Bolt
Bolts are used to secure the piston components together. In some piston assemblies, bolts are used to attach the piston to the connecting rod. These bolts must be strong enough to handle the stresses of the engine operation.
Thrust Piece
The thrust piece is a component that helps to absorb the lateral forces exerted on the piston during its movement. It ensures that the piston remains properly aligned within the cylinder, reducing wear and tear.
Position Pin
The position pin, also known as the piston pin or gudgeon pin, connects the piston to the connecting rod. It allows the piston to pivot as the connecting rod moves up and down. The position pin is subjected to high stress and must be made of durable materials.
Piston Pin Complete
The complete piston pin assembly includes the position pin and any associated components such as bushings or retainers. This assembly ensures that the piston pin remains securely in place and can pivot smoothly within the piston and connecting rod.
Compression Ring – Top
The top compression ring is the first ring located closest to the piston crown. It creates a seal between the piston and the cylinder wall, preventing combustion gases from escaping into the crankcase. This ring also helps to transfer heat from the piston to the cylinder wall.
Compression Ring – 2nd
The second compression ring is located below the top compression ring. It provides an additional seal to prevent combustion gases from escaping. It also helps to control the amount of oil that reaches the piston skirt, reducing oil consumption and emissions.
Oil Scraper Ring
The oil scraper ring, also known as the oil control ring, is located below the compression rings. Its primary function is to scrape excess oil from the cylinder wall and return it to the crankcase. This ring helps to maintain proper lubrication while preventing oil from entering the combustion chamber.
Desired Qualities of Engine Piston
Designing the piston for an engine involves several important considerations:
Strength to Withstand Combustion Forces: The piston must be strong enough to handle the powerful forces generated during combustion. This durability prevents it from being harmed or deformed.
Reducing Weight: It’s crucial to minimize the weight of the piston. A lighter piston helps reduce the inertia caused by the engine’s moving parts. This makes the engine work better and use fuel more efficiently.
Heat Conductivity: The piston should be able to conduct heat effectively.
This helps spread out the heat created when the engine burns fuel, making it less likely for something harmful called “detonation” to happen and damage the engine.
Higher Compression Ratio: A well-designed piston allows for a higher compression ratio in the engine. This is essential for achieving better fuel efficiency and power output.
Low Thermal Expansion: The material used for the piston should have minimal thermal expansion. This means it shouldn’t change size significantly with temperature fluctuations. This quality ensures a proper fit with the cylinder block and other components, like aluminum pistons.
Uniform Bearing Effect: The design of the piston skirt should promote even contact and support under abnormal conditions. The piston’s uniform bearing effect keeps the engine stable and reliable
Types of diesel engine piston fitting arrangements
Listed below are type of pistons.
- Crosshead Piston
- Trunk type piston
Crosshead Piston

In the crosshead type piston, the piston connects with the crankshaft. The piston connects to the crosshead bearing through the connecting rod. and to the crankshaft by piston rod and crosshead guide. This method arrangement reduces the side thrust on the piston.
Trunk Design Piston

Trunk-design pistons are popularly used in four-stroke medium-speed engines. The skirt is long with trunk-type pistons. The piston connects to the connecting rod by a small end bearing. The piston pin is the axis of rotation for a small end-bearing
Difference in design of Crosshead type and trunk design piston
Trunk type Diesel engine piston
1. There is single connecting rod in trunk design piston.
2. Trunk design piston engines have no diaphragm.
3. In the trunk-type engine, the small end, connects with the piston through the gudgeon pin and small end bush assembly.
4. In the trunk-type engine, no separate lube oil is used for the cylinder liner.
5. The piston skirt takes the transverse thrust
6. Cross head assembly is not required to connect the connecting rod and piston.
7. High power is produced at medium and high speed.
8. Needs less space.
9. Reduced engine manufacturing cost
10. Engine height is less than the engine with the same speed and power.
11. Can use low-grade oil.
Crosshead Type Engine
1. Cross-head type engines use the connecting rod and piston rod
2. A diaphragm seprates Cylinder space and crankcase
3. In the crosshead type, the top part of the connecting rod connects to the crosshead, consisting of the block slipper. The lower part of the piston rod supports the assembly.
4. The lubrication system for the cylinder and crankcase is different.
6. Cross head assembly connects the connecting rod and piston rod
7. Crosshead type engine develops high torque at smallest speed.
8. Need of more Height and space for maintenance.
9. Manufacturing cost is high.
Advantages of Crosshead type Piston
1. At lower rotational speed will develop high power
2. Lube oil contamination by combustion products is less.
3. The lubricating oil cost is low in cross head type.
Lubrication of Trunk type pistons
Supply of lubricating oil from the crankshaft cools the piston. The shaking effect of lubricating oil cools the crown and flows out through the centre of the joint screw. After cooling, the piston crown oil scatters on the cylinder wall. Lubricating oil flows down to the sump after cooling down the cylinder liner wall.
Procedure for Inspection of Diesel engine piston
Overhauling Process of Piston
Pre-overhauling preparation
1. Close and lock the air starting system
2. Open the indicator cock
3. Cool down the engine.
4. Disconnect fuel and cooling water.
5. All the measuring and inspection tools should be ready with calibration, and working conditions
6. Check the availability, workability, and validity of lifting and strops and shackles.
7. Personnel involved in the maintenance should have the adequate knowledge of working procedures.
8. Place the safety symbols as per the manufacturer’s recommendations near the maintenance area.
9. Confirm the availability of spares.
10. Check the workability of hydraulic tools.
11. Ensure the mobilization permission.
12. Undertake the risk assessment.
13. Carry out the ventilation of the crankcase with permission to undertake the job.
14. Rope off the working vicinity.
Overhaul Procedure of Diesel engine piston
Carry out the below procedure for the liners with flame mounting (design of piston)
1. Clean the cylinder liner top of the coking as the piston may stick in the deposits
- Turn the piston to BDC
- Remove the flame ring after Inserting and mounting the tool above the piston.
- Put an old discarded piston ring above the flame ring removal tool.
- Install the liner holding tool on one of the cylinder head nut.
- Turn the engine slowly to push out the flame ring.
Important procedures
2. Dismount the crankcase cover for the cylinder section in question to dismount the platform to help access
3. Mount the supporting device on the crankcase cover frame.
4. Place the mandrel in the guide sleeve and push forward to rest the shoulder of mandrel in correct postion.
5. Turn the crankshaft till the center of the connecting rod screw is on a level to mandrel top
6. Bring the crank throw is in a position to loosen the both upper and lower connecting rod screw .
7. Install the piston lifting device after cleaning the threaded hole.
8. Mount the pipe for retaining of the cylinder liner
9. Grab the tackle in the lifting tool for the piston and tighten.
Before turning the crankshaft, loosen the rope.
Re-tighten the rope to suit the new position.
2nd Part of dismanteling procedures
10. Pull out the mandrel of the guide sleeve and dismount the supporting tool
11. Rotate the supporting tool to turn the position of torque exrension wrench.
12. Mount the supporting tool
13. Loosen and dismantle one of the upper connecting rod screws.
14. Fit the guiding pin in the threaded holeand tighten hard with tool
15. Mount the holding-up tool on the cover frame of the crank housing on the opposite side of the engine
16. Press the forked rod tool against the connecting rod and lock it in this position with the locking screw on the tool
17. Dismantle the remaining screws and the bearing cap.
Note:
Note: Guide pin is fitted to ensure the protection of any damage to the crank journal, joint faces and bearing surface.
18. Loosen the locking screw and release the forked rod tool, see fig. 8 for the connecting rod to swing free of the crank-pin for the proper dismanteling .
19Dismount the upper bearing shell with care.
20. Pull out the piston and the connecting rod throughout the cylinder liner and out of the engine.
21.Guide The connecting rod with care in order not to damage the cylinder liner skirt
Separation of Piston from connecting rod – Piston in Engine
1. Place the piston and connecting rod with care on wooden supports to avoid damage to the piston and rings
2. Mount the bearing cap with the screws forthe protection of threads in assembly.
3. Take out the shackle and piston lifting tool from the piston
4. Rest the connecting rod and piston in upright position with top face of the piston.
5 Arrest the connecting rod with wooden wedges for the swinging movement
7. Remove the securing ring, push out the piston gudgeon pin and lift away the con rod.
Removal of the Piston Ring ( Piston in Engine)
- Take out the piston rings with the help of piston ring expender tool
2.Clean and inspect the rings to ascertain for the acceptance of re-use.
3. Clean both sides of piston.
4. Carry out the inspection of piston ring grooves..
Important checks on Piston for Piston in Engine
2. Piston crown side wall and ring grooves for any wear marks
3. The top part of the piston for cracking caused due by the thermal ad mechanical stress
4. Entire piston for high-temperature corrosion. 5. for hot corrosion at the upper surface and acid (cold)corrosion at the lower part.
Piston Ring Grooves and Piston Rings ( Piston in Engine)
1. Make the piston rings free in the ring groove.
2. But clearance and radial clearance
3. Any wear, stepping, and scuffing at grooves.
Piston Skirt/ Sidewalls
Inspect the piston skirt for
1. Any rubbing marks
2. Wear of wear rings
Cooling Water section
1. Scaling by poor water quality
2. High-temperature congestion.
Condition for change of Piston for Marine Engines ( Piston in Engine
Abnormal conditions to change the piston.
- The wear limit on the testing mandrel has exceeded
2. Piston ring and piston groove clearance out of tolerance.
Blog Conclusion
We hope that you enjoyed our blog about Diesel engine pistons. A diesel engine piston is a vital component for the function of a diesel engine. The diesel piston is a rotating component connected to a crankshaft at the heart of the reciprocating motion. Our blog post is designed to help the readers understand the piston’s components and function. We would love to hear from you.
