Calculating Voltage Drop
Voltage drop refers to the reduction in voltage as electrical current travels through passive elements like wires and resistors in a circuit. This phenomenon is crucial to understand because it directly impacts the efficiency and safety of electrical systems. Efficiently managing voltage drop ensures that devices receive the correct voltage, minimizing energy loss and preventing overheating or equipment failure. Safety is another key aspect, as excessive voltage drop can lead to dangerous situations, including electrical fires. By comprehensively calculating and mitigating voltage drop, electrical systems can operate more reliably and efficiently, safeguarding both equipment and users from potential hazards.
Understanding Voltage Drop Calculation

Voltage drop refers to the reduction in voltage that occurs as electric current moves through passive elements of a circuit, such as wires and resistors. This phenomenon is significant because it affects both the efficiency and safety of electrical systems. Properly managing voltage drop ensures that devices receive the correct voltage, minimizing energy loss and preventing potential hazards like overheating or equipment failure.
Basic Concept of Voltage Drop
Voltage drop happens when the electrical current faces resistance in the circuit. This resistance causes a portion of the voltage to be “lost” as heat. Understanding and calculating this drop is essential for designing efficient and safe electrical systems.
Voltage Drop Calculation Formula
The formula to calculate voltage drop depends on the type of current in the circuit:


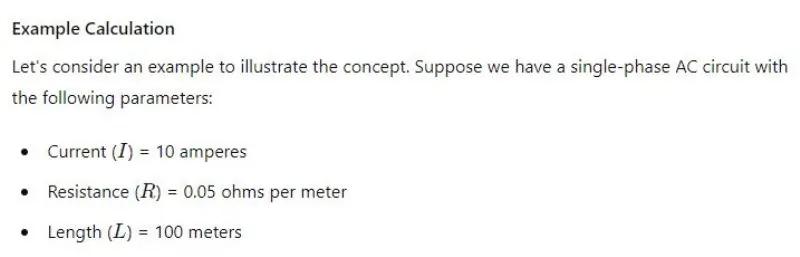
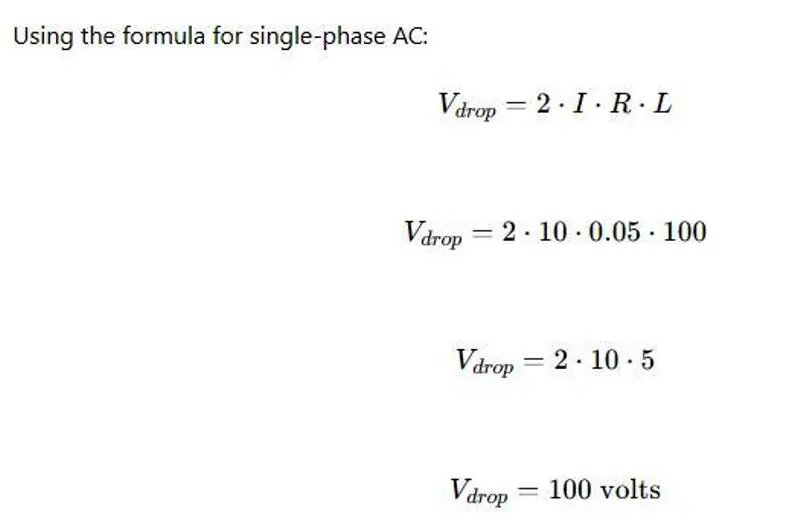
In this example, the voltage drop is 100 volts. This means that if the initial voltage was 220 volts, the voltage at the end of the circuit would be 120 volts. Understanding this drop is crucial for ensuring that the end devices receive adequate voltage for proper operation.
Key Factors Influencing Voltage Drop
| Factor | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Material | The type of material used for wiring affects the resistance and conductivity of the wire. | Copper vs. Other Materials: Copper has superior conductivity and lower resistance compared to aluminum and steel. Conductivity and Resistance: Copper’s low resistance makes it ideal for minimizing voltage drop in circuits. |
| Wire Size | The diameter of the wire influences its resistance and ability to carry current. | Diameter and Resistance: Thicker wires (larger diameter) have lower resistance, reducing voltage drop. Selecting Appropriate Gauge: Choosing the correct wire gauge ensures efficient current flow and minimizes voltage drop. Use the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system to determine the appropriate size. |
| Wire Length | Longer wires increase the total resistance in a circuit, leading to a higher voltage drop. | Resistance and Length: The longer the wire, the greater the resistance, resulting in increased voltage drop. Minimizing Length: Design circuits to use the shortest possible wire lengths to reduce resistance. Bundle cables appropriately to avoid excessive heat, which can increase resistance. |
| Load Current | The amount of current flowing through the wire affects the voltage drop. | Current and Voltage Drop: Higher currents lead to greater voltage drops due to increased resistance. Current Capacity: Ensure that wires can handle the expected load to prevent overheating and excessive voltage drop. Follow ampacity guidelines to match the wire size to the load current. |
Categorizing Voltage Drop
| Category | Definition | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Acceptable Voltage Drop | Less than 5% | Optimal Performance: Ensures that the electrical system operates efficiently, with minimal energy loss and no adverse effects on connected devices. |
| Marginal Voltage Drop | Between 5% and 10% | Potential Adjustments: Indicates that the system may require adjustments to improve efficiency. Voltage drop in this range could affect performance and longevity of electrical devices. |
| Unacceptable Voltage Drop | Greater than 10% | Immediate Action Required: Voltage drop in this range is considered hazardous and inefficient. It can lead to significant energy loss, overheating, and potential damage to electrical components. Immediate corrective measures are necessary to prevent system failures and ensure safety. |
Understanding these categories helps in maintaining the efficiency and safety of electrical systems. By keeping voltage drop within the acceptable range, you ensure optimal performance and longevity of your electrical components. In cases where voltage drop falls into the marginal or unacceptable categories, prompt action is required to mitigate potential risks and inefficiencies.
Practical Tips for Reducing Voltage Drop
| Tip | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Use High-Quality Materials | Advocate for the use of high-conductivity materials like copper. | High Conductivity: Copper has lower resistance compared to other materials, ensuring minimal voltage drop. |
| Optimize Wire Size and Length | Provide guidelines for selecting the appropriate wire gauge. Strategies for minimizing wire length in installations. | Wire Gauge Selection: Choose the correct wire gauge based on the current load to reduce resistance. Minimize Length: Design circuits to use the shortest possible wire lengths, reducing resistance and therefore voltage drop. |
| Calculate and Monitor Load Current | Importance of accurate current calculations. Regular monitoring and adjustments based on load changes. | Accurate Calculations: Properly calculate the expected load current to ensure wires can handle the load. Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor current loads and make necessary adjustments to prevent excessive voltage drop. |
| Regular Maintenance and Inspections | Tips for routine checks and maintenance to ensure optimal performance. | Routine Checks: Regularly inspect electrical systems for signs of wear and tear. Preventive Maintenance: Schedule periodic maintenance to address potential issues before they cause significant voltage drop. |
| Utilize Voltage Drop Calculators | Recommend reliable online tools for quick and accurate calculations (e.g., Calculator.net, Omni Calculator). | Online Tools: Use calculators like those on Calculator.net and Omni Calculator for precise voltage drop calculations. Easy Access: These tools simplify the process, ensuring accurate and efficient voltage drop management. |
These practical tips help in maintaining efficient and safe electrical systems by minimizing voltage drop. Using high-quality materials, optimizing wire size and length, accurately calculating and monitoring load current, performing regular maintenance, and utilizing reliable voltage drop calculators are essential practices for reducing voltage drop and enhancing system performance.
Advanced Considerations
Impact of Temperature on Voltage Drop
Temperature variations significantly affect the resistance of conductive materials. As temperature increases, the resistance of materials like copper also increases, leading to a higher voltage drop. For example, in a typical copper conductor, resistance can increase by approximately 0.4% for every degree Celsius rise in temperature. This increase in resistance causes more voltage to drop across the conductor for a given current.
To mitigate these effects, it’s essential to:
- Use materials with better temperature stability where possible.
- Ensure proper cooling and ventilation to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- Consider derating factors provided in electrical standards to account for temperature variations.
AC vs. DC Voltage Drop Calculations
The methods for calculating voltage drop differ between AC and DC circuits due to the nature of the current flow and the additional factors influencing AC circuits.


Additional Considerations for AC:
- Power Factor: AC circuits must consider the power factor, which affects the real power flowing through the system.
- Phase Angle: The phase difference between voltage and current can influence the voltage drop.
- Harmonic Distortion: Non-linear loads can introduce harmonics, complicating the voltage drop calculation.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Adhering to local electrical codes and standards is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical installations.
National Electrical Code (NEC):
- The NEC provides guidelines and tables for acceptable voltage drop limits and wire sizes. For example, the NEC recommends that the voltage drop for feeders and branch circuits should not exceed 3% for individual runs and 5% for the entire system.
- Compliance with these standards ensures that installations are safe, efficient, and reliable.
Local Regulations:
- In addition to national codes, local regulations may impose additional requirements.
- Regular updates to these codes mean that staying informed about the latest standards is essential for compliance.
- Failing to comply with these regulations can result in safety hazards and legal penalties.
By understanding these advanced considerations, you can design and maintain electrical systems that are both efficient and safe. Properly accounting for temperature impacts, differentiating between AC and DC calculations, and adhering to standards and regulations ensures the reliability and longevity of electrical installations.
Sources and Further Reading
| Source | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Calculator.net | Comprehensive online tool for calculating voltage drop, among other electrical calculations. | Provides precise calculations for voltage drop, taking into account wire material, size, length, and load current. Calculator.net |
| Omni Calculator | User-friendly platform offering a variety of calculators, including a detailed voltage drop calculator. | Offers easy-to-use calculators with explanations for voltage drop calculations in both DC and AC circuits. Omni Calculator |
| Electrical Engineering Portal | A resource-rich website providing technical articles, guides, and calculators related to electrical engineering. | Features in-depth articles and practical tools for electrical calculations, including voltage drop. Electrical Engineering Portal |
| Voltage Drop Calculation | Dedicated resource for understanding and calculating voltage drop in various types of electrical circuits. | Offers detailed explanations, formulas, and examples for accurately determining voltage drop. Voltage Drop Calculation |
These sources provide comprehensive tools and information for calculating voltage drop, ensuring you can design and maintain efficient and safe electrical systems. By leveraging these resources, you can enhance your understanding and application of voltage drop calculations in your projects.
FAQ on “Calculating Voltage Drop”
Q: What is voltage drop?
A: It’s the reduction in voltage as current flows through a circuit.
Q: How do you calculate voltage drop in DC circuits?
A: Use Vdrop=I⋅R
Q: What affects voltage drop?
A: Wire material, size, length, and load current.
Q: What is an acceptable voltage drop?
A: Less than 5%.
Conclusion
Understanding and calculating voltage drop is crucial for designing efficient and safe electrical systems. By comprehensively managing voltage drop, you can ensure that your electrical devices operate at optimal performance levels, reducing energy loss and preventing potential hazards such as overheating or equipment failure.
Implementing the tips provided—such as using high-quality materials, optimizing wire size and length, accurately calculating and monitoring load current, performing regular maintenance, and utilizing reliable voltage drop calculators—can significantly improve the efficiency and safety of your electrical systems.
We encourage you to integrate these strategies into your projects and share your experiences. Your feedback and questions are invaluable for building a knowledgeable and supportive community. Feel free to leave comments or reach out with any inquiries or insights. Together, we can enhance our understanding and application of voltage drop calculations, ensuring safer and more efficient electrical designs for everyone.
