Preparing for your marine engineering interview? From engine room operations to shipboard systems, centrifugal pump interview questions are a fundamental component of any technical assessment. Whether you’re a cadet facing your first placement or a seasoned engineer transitioning to a new vessel, a strong grasp of pump principles is essential. This guide breaks down the top 10 questions with clear, concise answers—tailored for marine applications and perfect for a quick revision to boost your confidence before the big day.
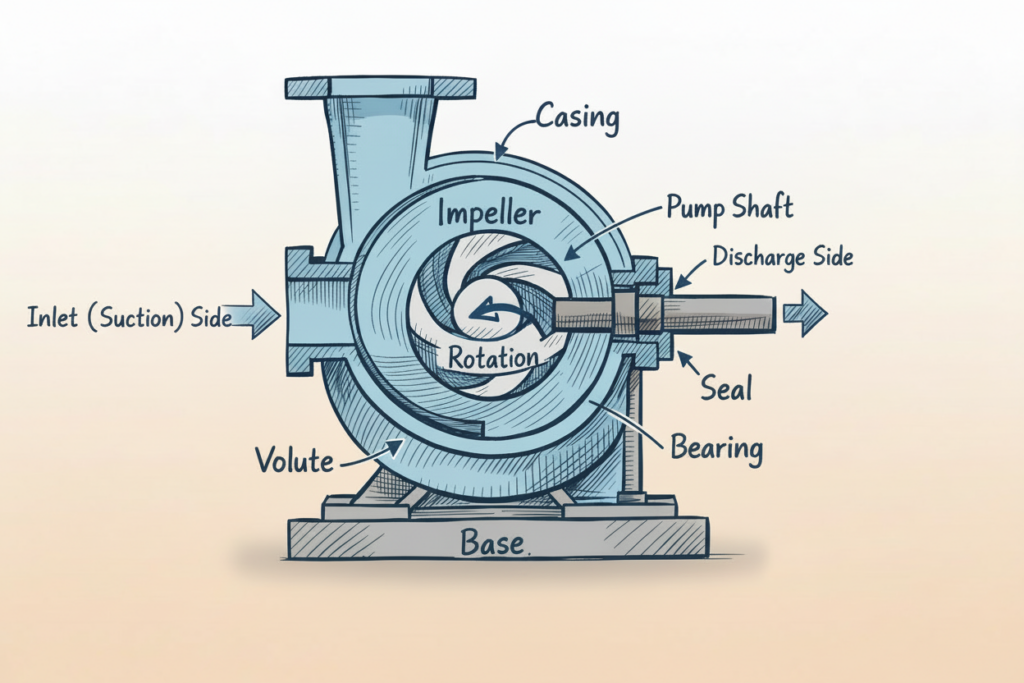
Centrifugal Pump Parts: Questions and Answers on Functions and Uses
Casing
Q: What is the function of the pump casing?
A: The casing forms the outer shell of the pump, enclosing the impeller and converting the high-velocity water leaving the impeller into pressure before discharge.
Q: Why is the casing important in operation?
A: It directs flow smoothly from suction to discharge, minimizes hydraulic losses, and contains the internal pressure safely to prevent leakage or structural failure.
Impeller
Q: What does the impeller do in a centrifugal pump?
A: The impeller imparts kinetic energy to the liquid by rotating at high speed, increasing the fluid’s velocity as it passes through the vanes.
Q: How does impeller design affect pump performance?
A: The impeller diameter, vane shape, and speed determine head, flow rate, and efficiency, so choosing the right impeller is crucial for the desired duty point.
Pump shaft
Q: What is the purpose of the pump shaft?
A: The shaft transmits mechanical power from the driver (motor/engine) to the impeller, allowing the impeller to rotate.
Q: Why must the pump shaft be accurately aligned?
A: Proper alignment reduces vibration, bearing load, and seal wear, improving reliability and extending service life.
Inlet / Suction side
Q: What happens at the suction side of the pump?
A: Liquid enters the pump at the suction nozzle and flows into the eye of the impeller at relatively low pressure.
Q: Why is suction condition critical for pump operation?
A: Poor suction (low NPSH, air ingress, high friction losses) can cause cavitation, noise, vibration, and loss of capacity.
Outlet / Discharge side
Q: What is the role of the discharge side?
A: The discharge side carries the pressurized liquid from the pump casing to the downstream piping or system.
Q: Why is a discharge valve used?
A: A discharge valve allows flow control, safe startup (by throttling), and isolation of the pump for maintenance.
Volute
Q: What is a volute in a centrifugal pump?
A: The volute is the spiral-shaped passage in the casing that collects high-velocity liquid from the impeller and gradually reduces its velocity.
Q: How does the volute improve efficiency?
A: By expanding the flow area, the volute converts kinetic energy into pressure energy with lower hydraulic losses, improving overall pump efficiency.
Seal
Q: What is the function of the shaft seal?
A: The seal prevents pumped liquid from leaking along the shaft where it exits the casing.
Q: When is a mechanical seal preferred over packing?
A: Mechanical seals are preferred for higher pressures, hazardous or expensive fluids, and when low leakage and reduced maintenance are required.
Bearing
Q: What do the bearings do in a centrifugal pump?
A: Bearings support the shaft radially (and sometimes axially), keeping it centered and allowing smooth rotation.
Q: Why is bearing lubrication important?
A: Proper lubrication minimizes friction and heat, preventing premature wear or failure of the bearings and shaft.
Base
Q: Why is the pump mounted on a base?
A: The base provides a rigid support for the pump and driver, maintaining alignment and distributing loads to the foundation.
Q: How does the base affect vibration?
A: A well-designed, grouted base with adequate rigidity reduces vibration, noise, and misalignment, improving pump reliability.
Top 10 Centrifugal Pump Interview Questions & Answers
1. What Is the Working Principle of a Centrifugal Pump?
A centrifugal pump converts mechanical energy from a motor into pressure energy (hydraulic energy) in a fluid. It works on the principle of centrifugal force: as the impeller rotates, it draws fluid into the center (eye) and flings it outward to the casing. This action increases the fluid’s velocity, which is then converted into pressure energy as it exits through the discharge nozzle.
2. Why Is Priming Essential in a Centrifugal Pump?
Priming involves filling the pump casing and suction line with the fluid to be pumped. It is necessary because centrifugal pumps cannot create a suction lift if air or vapor is present—they are not self-priming. Removing air ensures that the impeller can generate the required centrifugal force to move the fluid efficiently.
3. How Does a Centrifugal Pump Create Suction?
Suction is created by the rotation of the impeller. As the impeller spins, it reduces pressure at the pump’s inlet (eye). This pressure difference between the inlet and the fluid source pushes the fluid into the pump, following Bernoulli’s principle.
4. What Happens to Fluid When It Enters the Impeller?
When fluid enters the impeller eye, the rotating blades impart kinetic energy to it, accelerating the fluid radially outward. This increases the fluid’s velocity while building momentum, preparing it for pressure conversion in the casing.
5. How Does the Pump Casing Convert Velocity into Pressure?
The volute or diffuser casing gradually expands in cross-sectional area along the flow path. As the high-velocity fluid from the impeller enters this expanding space, its velocity decreases according to the principle of conservation of energy. This reduction in velocity is converted into an increase in static pressure.
6. What Is the Difference Between Suction and Delivery Pipes?
The suction pipe delivers fluid from the source to the pump inlet under a pressure lower than atmospheric pressure. The delivery pipe carries pressurized fluid from the pump discharge to the desired location. Suction pipes are typically larger to minimize friction losses and prevent cavitation.
7. What Is Cavitation, and Why Is It Harmful?
Cavitation occurs when the local pressure in the pump drops below the vapor pressure of the fluid, causing vapor bubbles to form. These bubbles collapse violently when they reach high-pressure regions, eroding impeller blades and internal surfaces. It reduces efficiency, causes noise/vibration, and can lead to catastrophic failure over time.
8. How Can Cavitation Be Prevented?
Cavitation is prevented by ensuring the Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSHa) exceeds the Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr) for the pump. Practical steps include:
- Keeping suction lines short and straight.
- Minimizing suction lift.
- Using a pump with a lower NPSHr if needed.
- Ensuring proper priming and avoiding air leaks.
9. What Is the Function of the Impeller?
The impeller is the rotating component with curved blades. Its primary functions are:
- Transferring energy from the motor to the fluid.
- Increasing the fluid’s kinetic energy and velocity.
- Determining the pump’s flow rate and head characteristics based on its design (open, semi-open, or closed).
10. What Is the Role of a Volute Casing?
The volute casing is a spiral-shaped enclosure that:
- Collects fluid discharged from the impeller.
- Converts kinetic energy (velocity) into pressure energy by gradually increasing its cross-sectional area.
- Guides the fluid to the discharge outlet with minimal losses.
Final Tips for Your Interview
- Relate Answers to Real Applications: Use examples from internships or projects.
- Practice Key Terminology: Terms like NPSH, priming, and volute casing show technical fluency.
- Stay Concise: Interviewers appreciate clear, direct answers—much like the format above.
Mastering these centrifugal pump interview questions not only prepares you for technical rounds but also builds a strong foundation for your role in design, maintenance, or operations. Good luck!
