Diesel Engine Maintenance
Maintaining a diesel engine is crucial for ensuring its longevity, performance, and reliability. Whether you’re operating a marine vessel, industrial machinery, or a commercial vehicle, regular maintenance of your diesel engine can prevent costly repairs, reduce downtime, and enhance efficiency. Diesel engines are known for their durability and robustness, but they require consistent care to operate at their best.
This blog post will guide you through essential diesel engine maintenance practices, covering vital aspects such as regular oil changes, fuel system upkeep, air filter replacement, cooling system checks, and proper lubrication. By adhering to these maintenance tips, you can keep your diesel engine running smoothly, maximize its lifespan, and ensure it delivers optimal performance under all conditions. Stay ahead of potential issues and maintain your engine’s health with our comprehensive guide to diesel engine maintenance.
Key Tests for Diesel Engine Maintenance
Key Tests for Diesel Engine Maintenance
To perform critical and complex tasks such as overhauling a ship’s diesel engine, a comprehensive understanding of engine components, their functions, and the necessary steps and tests for repairs is essential. As the lifeblood of ships, diesel engines require regular maintenance, including routine and major overhauls. As a Marine Engineer, you must be proficient in overhauling diesel engines during maintenance. A thorough knowledge of the diesel engine overhauling process is crucial at any level of marine engineering. Various tests are conducted on different tools and parts of the engine before and during the overhaul. Below are key tests performed during a ship engine overhaul.
1. Compression Test
A compression test measures the pressure in each cylinder to assess the condition of the piston rings, valves, and head gasket. Proper compression ensures efficient combustion and engine performance.
2. Cylinder Leakage Test
This test identifies leaks in the cylinders by pressurizing them and checking for air escaping through the valves, piston rings, or head gasket. It helps pinpoint the exact location of any leaks.
3. Injector Test
Injectors are tested for proper spray pattern, pressure, and atomization to ensure efficient fuel delivery and combustion. Faulty injectors can lead to poor engine performance and increased emissions.
4. Fuel Pump Test
The fuel pump is tested for adequate pressure and flow rate to ensure it delivers the correct amount of fuel to the injectors. A malfunctioning fuel pump can cause starting issues and engine misfires.
5. Oil Analysis
Oil analysis involves testing the engine oil for contamination, wear particles, and chemical composition. It provides insights into the engine’s internal condition and helps identify potential issues before they become severe.
6. Vibration Analysis
Vibration analysis detects imbalances, misalignments, and mechanical issues in the engine. By analyzing vibration patterns, you can identify problems such as worn bearings or misaligned components.
7. Exhaust Gas Analysis
Analyzing the exhaust gases helps determine the engine’s combustion efficiency and detect issues such as incomplete combustion or excessive emissions. It involves measuring the levels of various gases like CO, CO2, and NOx.
8. Coolant Analysis
Coolant analysis checks for contaminants, chemical composition, and pH levels in the engine’s cooling system. Proper coolant condition is essential for preventing overheating and corrosion.
9. Turbocharger Test
The turbocharger is tested for proper operation, including boost pressure and rotational speed. A malfunctioning turbocharger can significantly reduce engine power and efficiency.
10. Bearing Clearance Measurement
Measuring the clearance of engine bearings helps ensure they are within acceptable limits. Excessive clearance can lead to knocking and premature bearing failure, while insufficient clearance can cause overheating and seizure.
11. Bearing Cap Serration Test
Bearing cap serration testing ensures that the serrations on the bearing housing hold both caps tightly with the connecting rod bolts. This test helps reduce damage from excessive vibration during operation.
12. Hydraulic Jack Test
Hydraulic jacks are essential for various tasks when overhauling diesel engines. Testing these jacks ensures they have the strength and precision required to handle components like the main engine cover, cylinder head, bottom bolts, fuel pumps, and valves.
13. Cylinder Head Hydro Test
The cylinder head is tested for integrity and efficiency, involving a thorough inspection of valves, valve springs, valve guides, gaskets, and other parts. This ensures the cylinder head can be reused safely or identifies the need for replacement.
14. Connecting-Rod Bolts Test
Connecting rod bolts, exposed to high alternating loads, are tested frequently to ensure they can withstand the stresses and forces during engine operation.
15. Connecting Rod Bend Test
This test checks the straightness of the connecting rod by inserting a brass rod into the oil hole. Any slight bend in the connecting rod can be detected, ensuring it is straight and fit for use.
16. Fuel Valve Test
Fuel injectors are tested for proper pressure, timing, and atomization to ensure efficient combustion. This test is critical for the injector’s internal components – nozzle, needle, and valve – ensuring their proper function.
17. Starting Air Valve Testing
Starting air valves are tested for leaks and proper functioning before installation in the cylinder head, ensuring reliable engine starts.
18. Relief Valve Test
Cylinder head relief valves are pressure tested to ensure they function correctly, preventing overpressure and potential damage to the combustion chamber.
19. Turning Gear Test
After completing a major overhaul, the turning gear is activated to rotate the engine with the indicator tap open. Monitoring the current ensures there are no blockages or issues with the rotating shaft.
20. Alarm and Safety Trip Test
Generator alarms and safety trips, including lube shutdowns, high coolant temperature shutdowns, and overspeed shutdowns, are tested to verify their correct operation, ensuring the engine operates safely.
By conducting these comprehensive tests during a diesel engine overhaul, Marine Engineers can ensure the engine operates efficiently, reliably, and safely, extending its operational life and preventing costly breakdowns.
Note:- For the proper maintenance of Diesel generators, Engineers should understand the following.
- knowledge of design, construction
- Working of the machine.
- Overhauling Procedure and Maintenance works: There are standard procedures for the Diesel Generator Overhauling Procedure and maintenance of these machines, irrespective of their design and manufacturing.
Major Overhauling/De-carbonisation:
The process of dismantling, cleaning, and removing carbon deposits from the following parts.
- Piston
- Cylinder Liner
- Cylinder head
When Major Maintenance/Decarbonization is Needed
- Completion of running hours as per the planned maintenance program of OEM (Original equipment manufacturer).
- Accident/Breakdown.
- Before continuous surveys in which process of change of running parts like piston rings etc.
There are standard procedures for maintaining these machines, irrespective of their design and manufacturing.
Key Considerations for Maintenance Planning
- Makeshift arrangements for the emergency in the event of a Power failure
- Special Tools and tackles to be in proper operating condition.
- Measuring Instruments and Tools: All measuring tools, gauging, and measuring devices should be in suitable working conditions with a reasonable calibration period.
- Spare Parts: Check and ensure the availability of spares needed for maintenance.
- To ensure the working of Power Packs if available on board.
- Engineers/technicians involved in the care should know the procedure per the Operating manual.
- The maintenance team should have Knowledge of symbols and signs used to indicate the safety of machinery.
Real Life Incidences
- Onboard, the engineer in charge did not take a ship inventory of the spares. While the maintenance was on the way, during the inspection, it came to the light that the Con-rod bolts were elongated and needed replacement. The overhauling period was extended since the bolts were unavailable in the ship’s stock. Due to this delay, the company has to lose revenue for not taking the container with perishable goods because of lack of power.
- Before the hydraulic tool’s maintenance pump for loosening the Cylinder head, the Main Bearing and Con-rod nuts were not building pressure. During the maintenance, the engineer –in charge found out that the nuts were not getting loosened up, and hence dismantling work couldn’t be started. Ultimately it caused a delay in maintenance.
- Very often, it has been observed that due to the proper upkeep and maintenance of Measuring instruments/ calibration of the same in the stipulated period, many instruments fail to operate or lead to inaccurate measurements.
Getting Ready for an Overhaul
Essential Preparations Before Maintenance
- Quarantine
- Tagging Out
- Inspection of special tools supplied by the Manufacturer.
- Knowledge of functioning and procedure for operating the devices.
- Referring to the correct tightening torque and hydraulic pressure values.
- Complete understanding of parts assembly.
- Preparation of safety regulations for safe working.
Before maintenance begins, it’s crucial to quarantine the machine to prevent spills and accidents. This includes isolating both the prime mover and alternator for safety.
Steps to Isolate Electrical and Mechanical Systems
- Open the ACB ( Air Circuit Breaker) to cut off the alternate and bus bar links.
- The power supply of the Pre-Lube Oil Pump.
- Oil supply to Engine
- Cooling water supply
- Lube oil
- Fuel oil supply
- Air supply
A checklist of all the isolated areas is to be prepared, and the same is to be referred to before reopening the systems.
During the isolating process/opening procedure, a slow action with close observation must be followed to ensure other equipment is not affected.
Add on safety: While the maintenance work is in progress, additional tagging is to be carried out to prevent any opening up of Valves or Electrical breakers resulting in an accident of a serious nature.
Checking Engine Manufacturer’s Special Tools
- Injector and starting valve opening tool
- Spanners
- Cylinder head opening tool
- Cylinder Liner Removal Tools
- Cylinder Liner Holding Tool
- Cylinder head lifting tool
- Piston Lifting tool
- Bearing removal tool
- Cylinder Head and con rod nuts loosening and tightening hydraulic tool
- Valve grinding tool
- Valve seat grinding machine/tool
- Injector testing tool
- Rope and ceilings with proper size D shackles.
- Overhead cranes.
- Engine Barring arrangements
- Cylinder Liner Brushing tool
- Piston Ring removal tool
- Piston guide tool for inserting the piston.
- All the pressure and temperature calibration instruments.
- Electrical measuring instruments.
Assembly Guidelines to Follow
- The engineer in charge should know the assembly of parts and doubt the Instruction manual/Consult with the Senior Engineer.
- Store all the dismantled components in a separate box with the marking on significant parts. For each unit, a separate container is to be used.
- Mark all the bearings and con-rod bolts and wrap the threads with the cloth to avoid the threads’ damage.
Perform the Following Tasks
Cylinder Head Maintenance Checklist:
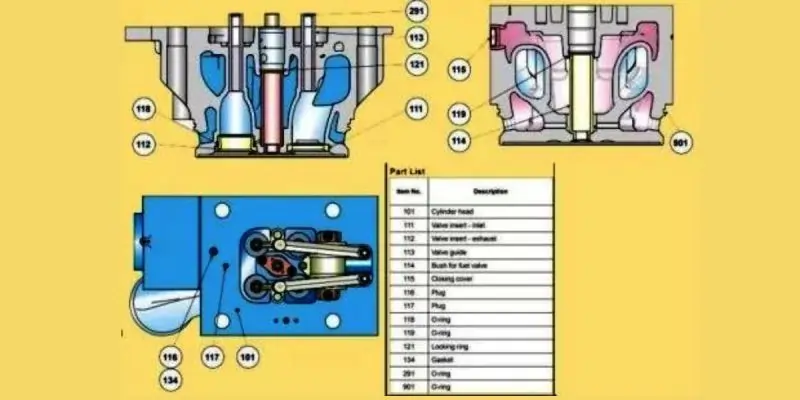
- Decarbonize all cylinder heads.
- Inspect cylinder heads for wear or damage.
- Examine valve spindles for proper functioning.
- Inspect Inlet and Exhaust valves, as well as Inlet valve guides, and record measurements.
- Replace corroded or worn-out valve guides with new ones.
- Inspect valve seats, rejecting excessively damaged ones and re-grinding accepted seats.
- Disassemble valve rotators for inspection, looking for deep markings on ball pocket surfaces.
- Inspect all Injector Sleeves and document observations.
- Verify and adjust safety valve operating pressure.
- Examine Indicator valves.
- Check cylinder head cooling water spaces.
- Lap cylinder head seating faces.
- Perform pressure testing on all cylinder heads.
- Conduct valve seat grinding for both old and new seats.
- Remove, clean, inspect, and reinstall Water guide jackets with new O rings.
- Properly tighten cylinder head nuts following OEM torque specifications.
Ensure thorough maintenance for optimal performance.
Cylinder Liner Maintenance Procedure:
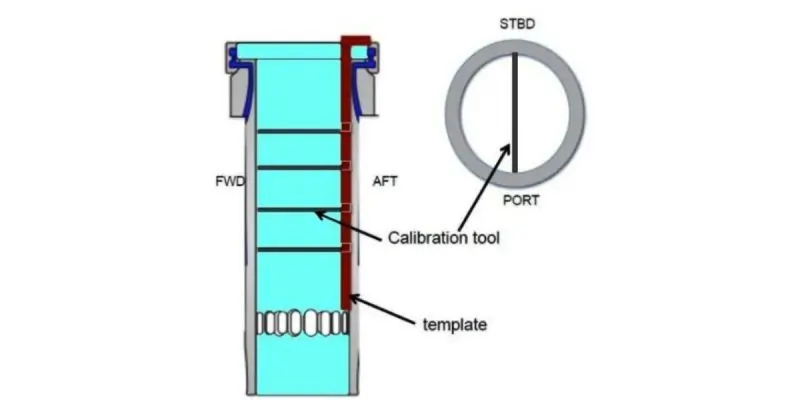
- Remove all cylinder liners for inspection.
- Conduct inspection, bore measurement, and honing at the workshop following OEM guidelines for Cylinder Liner Inspection and Honing.
- Record size measurements in the provided forms.
- Perform lapping on the upper face of the cylinder liner.
- Replace all flame rings with excessively worn-out working surfaces.
Follow these steps to ensure proper cylinder liner maintenance.
Piston Inspection and Overhauling Procedure

- Remove all pistons for inspection and overhaul.
- Perform decarbonization on all pistons, ensuring thorough cleaning both inside and outside.
- Clean all piston and oil scraper ring grooves, then inspect and measure them for wear using the groove measuring tool provided by the OEM. Record the measurements.
- Replace all piston rings with new ones.
- Ensure that the piston ring positions are offset 180 degrees from each other, and the spring joint of the scraper ring is also fitted with a 180-degree offset to the joint during piston installation.
- Verify the tightness of the piston plug at the specified torque.
Follow these steps for proper piston maintenance and overhaul.
Central Tools 6434 Sleeve Height and Counter Bore Gauge
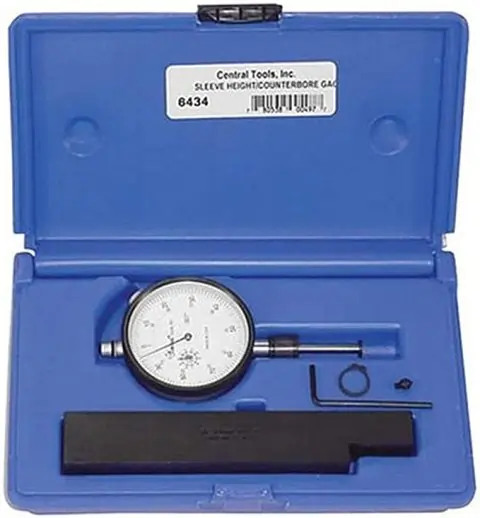

Quickly measures the cylinder sleeve height using pointed contact; Counter-bore depth using flat end contact; Top dead center; Piston-to-deck height; Valve protrusion; Easy readings around the entire bore. This is a compact and very versatile gauge.
Connecting Rod Inspection Steps
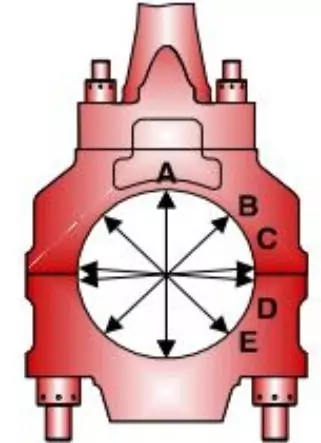
- Inspect all connecting rod big-end bearing shells. Replace any with deep grooves or excessive wear beyond accepted norms for shell thickness and free spread.
- Examine the connecting rod’s big end bore and document measurements.
- Check the small end bearings.
- Verify the clearance between the wrist pin and bush.
- Conduct an ultrasonic test on all piston pins to detect hairline cracks.
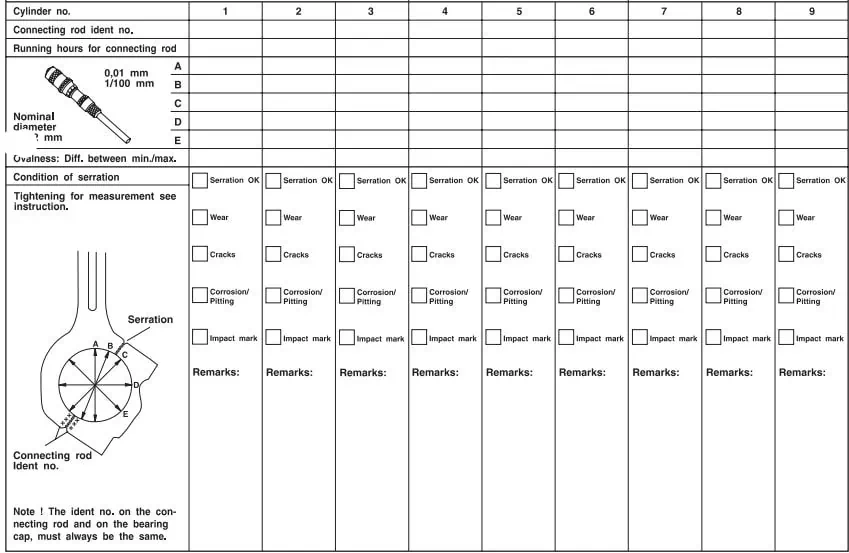
Follow these steps to inspect connecting rods to ensure proper maintenance thoroughly.
Connecting Rods Industrial Tools
Gear Wheel and Camshaft Inspection:
- Inspect all gear wheel bolts and connections following OEM instructions.
- Replace all camshaft bushes if worn out.
- Check the condition of the camshaft.
- Examine the lubrication of the camshaft, observing the flow of lube oil from all bearings and spray pipe nozzles. Ensure the oil jet hits the gear wheel precisely at the meshing point.
- Verify the tightness of locking devices and fasteners.
- Inspect all pushrods for straightness.
- Adjust inlet and exhaust valve clearances according to OEM recommendations.
Perform these checks to maintain the gear wheels’ and camshaft’s integrity and functionality.
Valve and Fuel Pump Mechanism Inspection
- Examine the Roller Guide for any marks.
- Check for deformation on the spherical stud.
- Inspect the surface of rollers for any marks or deformation.
- Verify the absence of free play between the rollers, the bush, and the pin.
- Inspect the Valve Gear, springs, and Pushrods.
- Examine all valve bridge springs, rocker arm brackets, and pushrods.
- Also, inspect the Roller Guide for fuel injection pumps.
- Ensure all roller guides are free of marks.
- Check the surface of rollers for defects and deformation.
- Confirm there is no free play between rollers, bush, and pin.
- Lastly, check the lubrication of all operating gears.
These inspections ensure the proper functioning of the inlet and exhaust valve mechanisms and fuel injection pumps.
Governor
- Overhaul the Governor.
- Change the Governor’s oil.
Crankshaft and Main Bearings Maintenance:
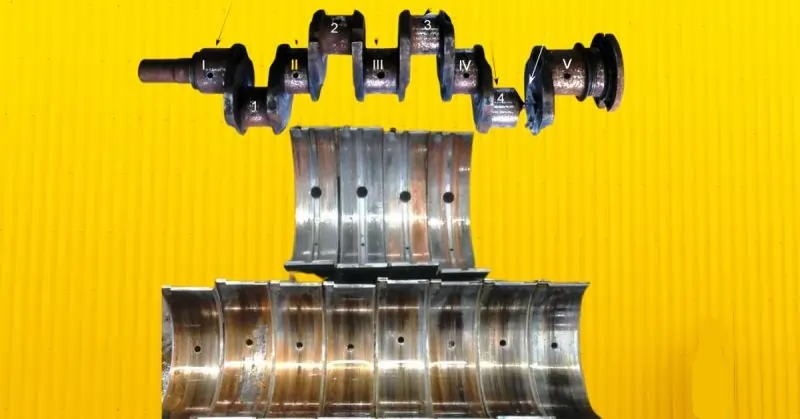

- Inspect all crankpins and polish all main and connecting rod pins with glossy paper.
- Examine thrust bearings and replace them if wear exceeds prescribed limits.
- Re-tighten counterweights to the specified torque.
- Disassemble all main bearings and polish all crankpins.
- Check for runout.
- Tighten the main and guide bearing caps to the prescribed torque.
- Inspect and replace any main bearings with abnormal wear.
Follow these steps for proper maintenance of the crankshaft and main bearings.
Turbocharger and Charge Air Cooler Maintenance:
- Remove the Turbocharger (TC) cartridge.
- Replace the nozzle ring.
- Dismantle the cartridge, inspect the bush and labyrinth ring, and replace if necessary.
- Re-assemble the cartridge.
- Check clearances following the procedure.
- Clean the Charge Air Cooler (CAC).
- Perform a pressure test on the Charge Air Cooler.
These steps ensure proper maintenance of the turbocharger and charge air cooler.
Engine Frame and Bed Plate Maintenance:
- Re-tighten the holding-down bolts.
- Re-tighten the bolts connecting the engine and base frame.
- Conduct a functional test of the safety cover.
- Inspect the AVM pad adjust screw clearance, and make adjustments if necessary.
These steps ensure the proper maintenance of the engine frame and bed plate.
Fuel Oil System Maintenance:
- Calibrate the fuel injection valves.
- Inspect all high-pressure fuel pipes and replace “O” rings.
- Examine the FIP roller and measure nominal height.
- Perform an overhaul of all fuel injection pumps, replacing the barrel, plunger, and ‘O’ ring kit as needed.
These steps are essential for the proper maintenance of the fuel oil system.
Lube Oil System Maintenance:
- Remove the engine-driven lube oil pump for inspection.
- Dismantle the entire pump and replace the bushes.
- Apply the correct torque to tighten the self-locking nut.
- Drain old oil from the engine and refill with new oil.
- Overhaul the pre-lube oil pump.
- Replace the lube oil filter cartridge.
- Clean and replace the Glacier bypass filter kit.
- Perform a chemical circulation cleaning of the lube oil Plate Heat Exchanger (PHE).
These steps are crucial for maintaining the lube oil system.
Water Pump and Thermostatic Valve Maintenance:
- Remove the LT (Low Temperature) and HT (High Temperature) water pumps from the engine.
- Perform a comprehensive overhaul of the pumps.
- Replace the rotating sealing and both ball bearings of the HT Water Pump.
- Replace the rotating sealing and both ball bearings of the LT Water Pump.
- Tighten the self-locking nuts of both pumps to the specified torque.
- Overhaul the HT water thermostatic valve.
- Clean the LT/HT Plate Heat Exchanger (PHE).
These steps are essential for maintaining the water pumps and thermostatic valve in optimal condition.
Mechanical Overspeed Device Maintenance:
- Perform an overhaul of the mechanical overspeed device.
This step ensures the proper maintenance of the mechanical overspeed safety mechanism.
Miscellaneous Procedures:
These are crucial steps in the Diesel Generator Overhauling Procedure:
- Record the Fuel pump index at Governor Index 0.
- Verify the integrity of the compressed air system.
- Inspect the fuel oil system and nozzle cooling system.
- Perform functional tests on safety shutdown switches and analog switches.
- Calibrate all safety switches.
- Consider replacing the alternator bearing if necessary.
- After completing maintenance, initiate the D.G. Set and follow the sequence for all moving parts per the standard Diesel Generator Overhauling Procedure.
- Conduct load trials of the D.G. Set according to the OEM protocol.
- Record the set’s performance during stage load sequences, ranging from 25% to the maximum available load, as specified in the manual.
- Continuously monitor parameters and log them in the logbook for reference.
These steps ensure a comprehensive and successful Diesel Generator Overhauling Procedure.
The thumb rule for oil clearance calculations
The reasonable starting point is 0.01905mm to 0.0254 mm. (Three quarters to 0.0254 of a millimeter) of clearance per mm of a shaft diameter.
For example, a 2 mm shaft diameter would require 0.0381mm to 0.0508mm (0.01905×2=0381 and 0.0254×2=0.0508mm)
For the super performance, engines add 0.0127 to the maximum calculated value. The recommendations for 2 mm shaft will be 0.0508 mm + 0.0127=0.0635mm.
(To maintain hydrodynamic lubrication between the shaft and bearing, the maximum ovality should not exceed the maximum oil clearance. If exceeded, there will be bearing failure due to boundary lubrication.)
