Expansion Valve in Refrigeration
An expansion valve plays a critical role in refrigeration systems by controlling the flow and pressure of refrigerant entering the evaporator. This ensures the refrigerant vaporizes efficiently, allowing the system to maintain optimal cooling performance. Understanding how expansion valves function is essential for achieving maximum energy efficiency, as improper valve operation can lead to temperature imbalances and increased power consumption.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about expansion valves—from the different types, such as thermostatic and electronic, to their working principles. We’ll also dive into common problems, troubleshooting tips, and practical advice for maintenance. Whether you’re managing a commercial refrigeration system or simply looking to improve energy savings, this guide will help you optimize your system’s performance through a proper understanding of expansion valves.
What is an Expansion Valve?
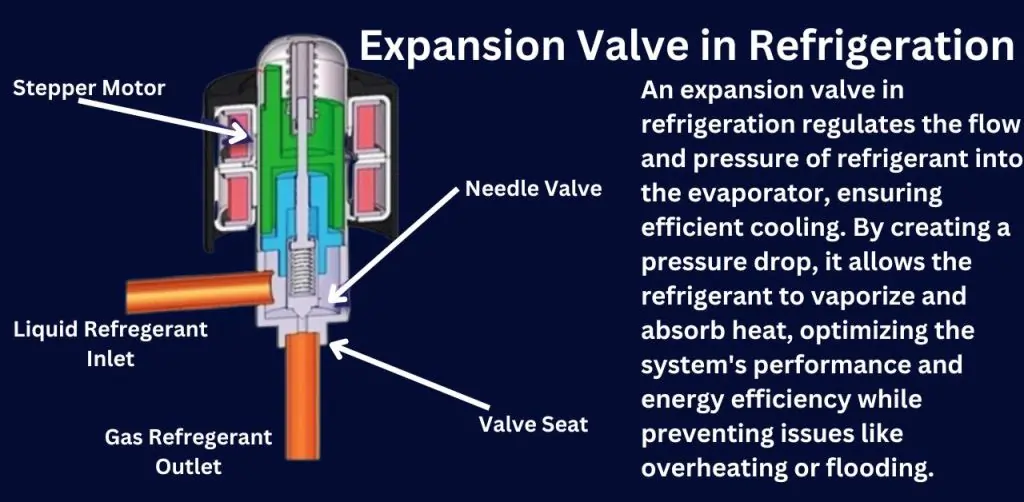
An expansion valve is a critical component in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, responsible for regulating the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It controls the amount of refrigerant released, ensuring a precise pressure drop, which allows the refrigerant to vaporize and absorb heat effectively.
The function of the expansion valve is to manage the refrigerant’s transition from high pressure in the condenser to low pressure in the evaporator, where cooling takes place. By doing so, it ensures that the refrigerant is in the correct state to absorb heat from the surrounding environment.
In regulating the refrigerant flow and pressure, the valve helps maintain the proper temperature inside the evaporator, which is essential for consistent cooling performance. Without accurate control, the system may become inefficient, leading to poor cooling and increased energy consumption. The expansion valve is key to balancing performance, energy use, and system longevity.
Types of Expansion Valves
- Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV)
The TXV is designed to regulate the refrigerant flow based on the temperature of the evaporator. It works by using a sensing bulb filled with refrigerant to measure the evaporator temperature, adjusting the valve accordingly to maintain proper superheat.- Where it’s used: Commonly found in larger, more complex refrigeration systems like commercial refrigerators and air conditioners.
- Advantages: Provides precise control of refrigerant flow, improving efficiency and preventing flooding in the evaporator.
- Limitations: More complex and expensive than simpler valves, and requires regular maintenance.
- Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV)
The EEV uses electronic sensors and a stepper motor to control refrigerant flow with high accuracy.- Key Features: Advanced controls, remote monitoring capabilities, and precise adjustments in real-time.
- Use cases: Ideal for modern, energy-efficient systems that demand tight control, such as industrial refrigeration.
- Efficiency Benefits: Enhanced control leads to higher efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and longer equipment life.
- Automatic Expansion Valve (AXV)
The AXV maintains constant pressure in the evaporator by adjusting the refrigerant flow automatically.- Functionality: It responds to pressure changes in the evaporator, maintaining a stable flow rate regardless of the system load.
- Typical Applications: Used in smaller, less dynamic systems where load variation is minimal, such as small coolers and freezers.
- Capillary Tube
The capillary tube is the simplest type of expansion device, consisting of a long, narrow tube that restricts refrigerant flow, causing a pressure drop.- Mechanism: The refrigerant’s pressure and temperature drop as it passes through the tube, entering the evaporator.
- Cost and Use: This inexpensive option is widely used in smaller, low-cost systems like domestic refrigerators and window air conditioners. It is easy to install but lacks precision.
Working Principle of an Expansion Valve
An expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant by regulating its pressure as it moves from the condenser to the evaporator. The valve reduces the high-pressure liquid refrigerant coming from the condenser to a lower pressure, allowing it to vaporize in the evaporator. This pressure drop is crucial for refrigerant vaporization, enabling the refrigerant to absorb heat from the surrounding environment and provide the necessary cooling effect.
Key components that make this process possible include the sensing bulb, diaphragm, orifice, and valve body.
- The sensing bulb monitors the temperature at the evaporator outlet and adjusts the valve opening based on the refrigerant’s superheat.
- The diaphragm moves in response to pressure changes, controlling the orifice’s size.
- The orifice restricts the refrigerant flow, creating the necessary pressure drop.
- The valve body houses these components and facilitates refrigerant flow control.
The thermodynamic process inside the valve involves converting the refrigerant from a high-pressure liquid to a low-pressure mixture of liquid and vapor. As the refrigerant exits the valve into the evaporator, the low pressure causes it to expand and vaporize, absorbing heat and creating the cooling effect essential for refrigeration.
Essential Formulas for Expansion Valves
Refrigerant Mass Flow Rate (ṁ)
The mass flow rate of refrigerant passing through the expansion valve can be calculated using:
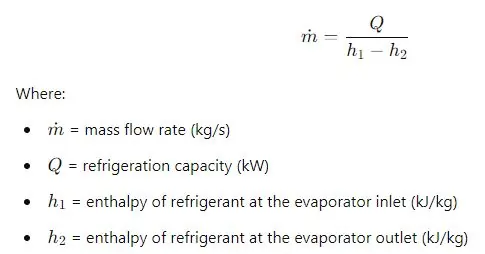
Superheat (SH)
The degree of superheat can be measured to ensure proper expansion valve operation:
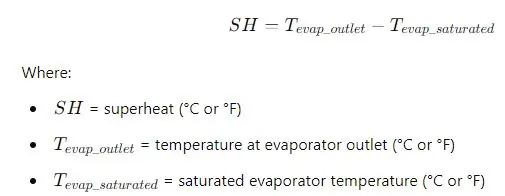
Pressure Drop Across Expansion Valve (ΔP)
The pressure drop is a key factor that determines refrigerant vaporization:

Refrigerant Enthalpy Difference (Δh)
The enthalpy difference across the expansion valve shows the energy extracted by the refrigerant:
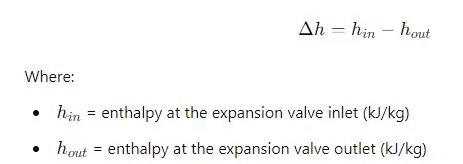
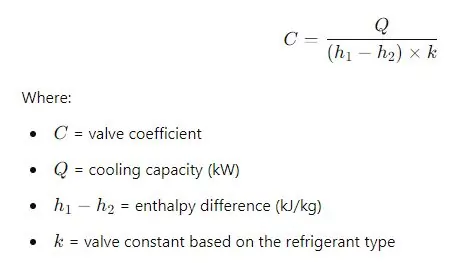
Valve Sizing Formula (Simplified for TXV)
Valve sizing can be estimated using this simplified approach for thermostatic expansion valves:
How to Choose the Right Expansion Valve for Your System
Selecting the right expansion valve is critical for the efficiency and performance of your refrigeration system. Several factors must be considered to ensure optimal functioning:
- System Size
The size of your refrigeration or air conditioning system plays a major role in determining the appropriate expansion valve. Larger systems typically require more advanced valves like thermostatic or electronic expansion valves (TXV or EEV) for precise control, while smaller systems may use simpler options like capillary tubes or automatic expansion valves (AXV). - Refrigerant Type
Different refrigerants have varying pressure and temperature characteristics, and the valve you choose must be compatible with the refrigerant used in your system. Some valves are optimized for specific refrigerants, ensuring better performance and preventing inefficiencies. - Load Variation
If your system experiences frequent load variations, such as changing cooling demands, valves like TXV or EEV are ideal due to their ability to adjust flow in real-time. Systems with minimal load changes may benefit from AXV, which maintains constant evaporator pressure. - Performance and Control Accuracy
Expansion valves vary in their ability to control refrigerant flow accurately. TXV and EEV offer higher control precision, making them suitable for applications that require consistent temperature control. AXV and capillary tubes are less precise but are cost-effective for smaller, simpler systems. - Energy Efficiency
Matching the expansion valve with other system components, such as the compressor and evaporator, is essential for maximizing energy efficiency. EEVs provide the best energy savings in modern systems with variable loads, while TXVs offer balanced control and efficiency for most commercial applications. Selecting the right valve ensures reduced energy consumption and prolonged system life.
Common Problems & Troubleshooting Tips for Expansion Valves
| Problem | Causes | Symptoms | Troubleshooting & Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valve Blockage | Contaminants or moisture inside the refrigerant line | Frosting on valve, high superheat, poor cooling | – Inspect and clean the valve – Replace filters and driers – Evacuate moisture from the system |
| Valve Oversizing or Undersizing | Incorrect valve selection for system size | Reduced cooling efficiency, high or low superheat | – Check valve sizing and refrigerant type – Replace with correctly sized valve |
| Thermostatic Malfunctions | Malfunctioning TXV sensing bulb or diaphragm | Inconsistent refrigerant flow, erratic superheat | – Check the sensing bulb for damage – Replace faulty diaphragm – Verify superheat settings |
| Valve Seat Leakage | Worn or damaged valve seat | System unable to maintain pressure, refrigerant leaks | – Inspect the valve seat for wear – Replace the valve if necessary to restore proper sealing |
Maintenance Tips for Expansion Valves
Proper maintenance of expansion valves is essential to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and system longevity. Here are key tips to keep your expansion valve functioning smoothly:
- Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Conduct regular inspections of the expansion valve to check for any signs of blockage, corrosion, or wear. Cleaning the valve components, such as the orifice and filter, helps prevent contaminants from clogging the valve. It’s recommended to inspect the valve at least every 6 to 12 months as part of routine system maintenance. - Monitoring Superheat Levels
Keeping an eye on the superheat levels is crucial in maintaining the efficiency of your refrigeration system. Incorrect superheat settings can cause the valve to either underfeed or overfeed the evaporator, leading to poor cooling and potential damage to the compressor. Regularly measure and adjust superheat to ensure the valve operates within optimal parameters. - Preventative Maintenance
Preventative measures, such as replacing worn-out parts, checking for refrigerant leaks, and ensuring the valve’s sensing bulb is securely attached, can help avoid sudden system breakdowns. Addressing small issues early on helps maintain system efficiency, reduces the risk of costly repairs, and prolongs the life of both the expansion valve and the refrigeration system.
Expansion Valve in Modern Refrigeration Systems
As refrigeration technology evolves, expansion valves have seen significant advancements to meet the demands for efficiency, precision, and environmental sustainability. Modern refrigeration systems now incorporate innovative valve technologies that enhance performance and reduce energy consumption.
- Latest Innovations in Expansion Valve Technology
Smart expansion valves and adaptive control systems represent the latest breakthroughs in refrigeration technology. These valves are equipped with sensors and electronic controls that automatically adjust refrigerant flow based on real-time system conditions. This ensures optimal efficiency even under varying load conditions. Smart valves can also integrate with centralized control systems, allowing remote monitoring and diagnostics to detect issues before they impact performance. - Integration with Energy-Efficient Systems and Sustainable Refrigerants
Modern expansion valves are designed to work seamlessly with energy-efficient refrigeration systems that use sustainable refrigerants, such as natural refrigerants (CO2, ammonia) and low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) alternatives. These valves help maximize energy savings by precisely controlling refrigerant flow and minimizing system losses, making them crucial in reducing the carbon footprint of refrigeration systems. - Future Trends in Refrigeration Valve Technology
The future of expansion valves is focused on further enhancing energy efficiency and system automation. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies are expected to be integrated into valve control systems, enabling predictive adjustments for maximum efficiency. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing valves that are compatible with new, eco-friendly refrigerants, supporting the global shift toward more sustainable refrigeration solutions.
Conclusion
In summary, the expansion valve plays a crucial role in regulating refrigerant flow and maintaining optimal pressure, directly impacting the performance and energy efficiency of refrigeration systems. Without proper control from the expansion valve, systems can become inefficient, leading to poor cooling and increased energy consumption.
When selecting the right expansion valve, it’s essential to consider factors like system size, refrigerant type, and load variation to ensure you choose a valve that suits your system’s needs. Regular maintenance, including monitoring superheat levels and performing routine inspections, will help prevent breakdowns and maximize the valve’s lifespan.
By choosing and maintaining the correct expansion valve, you not only improve energy efficiency but also ensure long-term reliability and performance for your refrigeration system. Investing in the right valve and its upkeep will pay off through reduced energy costs and extended system life.
FAQ on Expansion Valve
Q- What are the symptoms of a faulty expansion valve?
A- Inconsistent cooling, high superheat, frosting, or refrigerant leaks.
Q- How do I know if my expansion valve is too large or too small?
A- Oversized valves reduce efficiency; undersized valves cause poor cooling and high superheat.
Q- Can a malfunctioning expansion valve affect energy consumption?
A- Yes, it makes the system work harder, increasing energy use.
Q- How often should an expansion valve be inspected or serviced?
A- Inspect it every 6 to 12 months during routine mainte