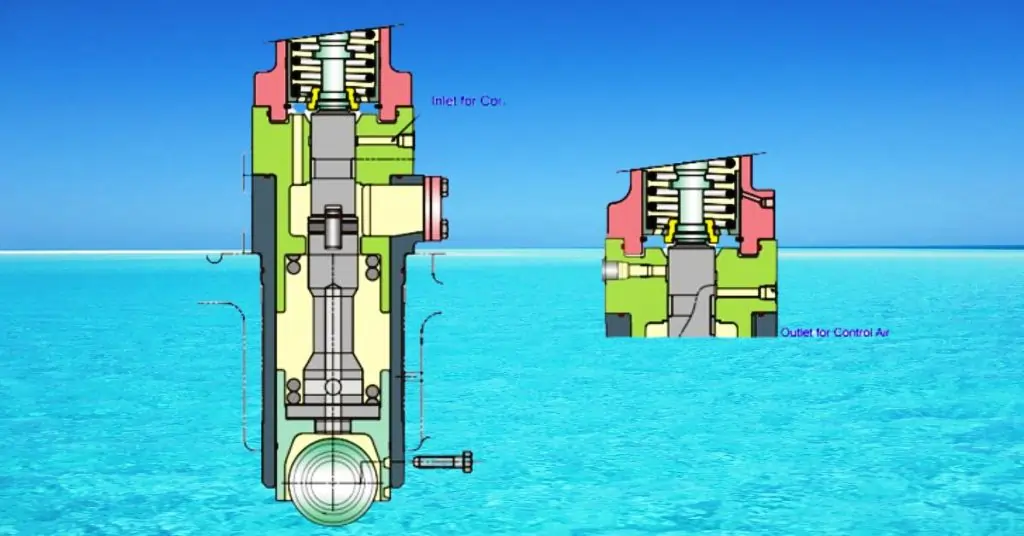
Fuel Injection Pump
The fuel injection pump is the heart of a marine diesel engine, ensuring it runs smoothly and efficiently. Onboard maintenance of this critical component is vital for any marine engineer aiming to prevent costly downtime and engine failures at sea. By maintaining the fuel injection pump, you ensure optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity of the engine. In the unforgiving marine environment, neglecting this essential task can lead to significant operational issues and safety risks.
This blog post will provide you with key maintenance tips to keep your fuel injection pump in top shape. From routine visual inspections and cleaning techniques to monitoring fuel quality and adjusting injection timing, these actionable tips are designed to help you perform necessary upkeep directly onboard. By following these guidelines, you can ensure your marine diesel engine remains reliable and efficient, no matter the challenges you face at sea.
The overhauling of a fuel pump
1. Preparation and Safety
- Ensure the engine is shut down and all safety precautions are followed.
- Gather necessary tools, spare parts, and manuals specific to the fuel pump model.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and eye protection.
- Clean the surrounding area and the fuel pump exterior to prevent contaminants from entering the system.
2. Removal of the Fuel Pump
- Isolate the fuel supply by shutting off fuel lines and draining the system to prevent leakage.
- Disconnect the fuel lines and any electrical connections (if applicable).
- Mark the alignment of the fuel pump to ensure correct reassembly.
- Carefully remove the fuel pump from the engine.
3. Dismantling the Fuel Pump
- Place the pump on a clean workbench.
- Disassemble the pump by removing external parts like the fuel delivery valves, springs, plungers, and camshaft (if applicable).
- Keep track of small parts, organize and label them to avoid confusion during reassembly.
- Use special tools as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent damaging precision parts.
- Carefully remove the plungers and delivery valves, noting their orientation and condition.
4. Inspection of Components
- Clean all components using an appropriate cleaning solution (usually diesel or a manufacturer-recommended solvent).
- Inspect each part for wear, corrosion, or damage. Key components to check include:
- Plungers: Check for scoring, wear, or damage that could affect fuel delivery.
- Barrel: Inspect for internal damage or wear.
- Delivery Valves: Check the seating surface for pitting or wear.
- O-rings and Seals: Ensure all sealing components are intact.
- Camshaft: Check for wear or damage on the cam lobes.
- Springs: Check for loss of tension or any deformation.
5. Replacement of Worn Parts
- Replace any worn or damaged components, such as plungers, delivery valves, seals, gaskets, and springs.
- Always use genuine parts as recommended by the manufacturer.
6. Reassembly
- Reassemble the fuel pump in the reverse order of dismantling, paying attention to:
- Correct orientation of plungers and barrels.
- Proper torque settings for bolts and nuts, as per the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Ensuring all seals and gaskets are properly seated to prevent leaks.
- Apply lubrication to parts where necessary to ensure smooth operation.
7. Calibration
- Calibrate the fuel pump to the manufacturer’s specifications. This step ensures that the fuel delivery timing, quantity, and pressure are accurate.
- Use a test bench or a specialized calibration machine to check the pump’s performance and adjust if needed.
- Calibration involves adjusting the fuel delivery stroke, maximum fuel delivery, and injection pressure.
8. Reinstallation
- Reinstall the fuel pump onto the engine, ensuring it is aligned according to the markings made during removal.
- Reconnect the fuel lines and any electrical connections.
- Bleed the fuel system to remove any air pockets that may have entered during the overhaul process.
9. Testing
- Start the engine and test for proper operation.
- Check for any leaks and ensure that the fuel pump is delivering fuel correctly by observing engine performance.
- Conduct load tests if necessary to ensure the fuel pump is working efficiently under operational conditions.
10. Final Checks
- Once the engine is running smoothly, check the fuel pump for any abnormal noise, leaks, or signs of overheating.
- Monitor the engine performance for any irregularities related to fuel delivery, such as power loss or excessive smoke.
By following this procedure, the fuel pump will be overhauled and restored to its optimal working condition, ensuring efficient engine operation and extended service life. Regular fuel pump maintenance helps prevent breakdowns and reduces fuel consumption.
Fuel Injection Pump Common Onboard Issues
| Common Problems | Possible Causes | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Won’t Start | Battery issues Fuel supply problems Air in the fuel system Faulty ignition components | Check battery connections and charge level Ensure adequate fuel and open fuel valves Bleed the fuel system Inspect ignition system (spark plugs, wiring) |
| Loss of Power | Clogged fuel filters Dirty air filters Fuel quality issues Injector problems | Replace/clean fuel filters Check/clean air filters Verify fuel quality, add additives Inspect/clean/replace injectors |
| Excessive Smoke | Incorrect fuel injection timing Poor fuel quality Clogged air filters Worn engine components | Adjust fuel injection timing Ensure clean fuel Replace/clean air filters Check/repair worn components |
| Overheating | Low coolant levels Blocked cooling passages Faulty thermostat Water pump issues | Check/top up coolant Clean cooling passages Test/replace thermostat Inspect/replace water pump |
| Fuel Leaks | Damaged fuel lines Loose connections Faulty seals | Inspect/replace damaged lines Tighten connections Replace worn seals |
| Actionable Steps | Details |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Conduct a thorough inspection Use a flashlight for hard-to-see areas |
| Basic Tools Kit | Keep a well-stocked tools kit Familiarize with tools and their uses |
| Check Connections | Regularly check electrical and fuel connections Clean and secure loose/corroded connections |
| Fluid Levels | Routinely check fluid levels (oil, coolant, fuel) Top up fluids and check for leaks |
| Bleed the Fuel System | Learn to bleed the fuel system to remove air Follow manufacturer’s bleeding procedure |
| Carry Spare Parts | Keep essential spare parts onboard (filters, belts, gaskets, seals) |
| Record and Monitor | Maintain a log of issues and resolutions Monitor engine performance for recurring problems |
FAQ on “Fuel Injection Pump”
Q: How often should I inspect the fuel injection pump?
A: Inspect the fuel injection pump every 100 operating hours or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Q: What are the signs of a failing fuel injection pump?
A: Signs include difficulty starting, engine misfires, loss of power, and excessive smoke from the exhaust.
Q: Can I clean the fuel injection pump without removing it?
A: Yes, regular surface cleaning and using fuel additives can help maintain cleanliness without remova
Q: How do I know if the fuel pressure is correct?
A: Use a fuel pressure gauge to check the pressure against the manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring it falls within the recommended range.
Conclusion
Maintaining the fuel injection pump is essential for the optimal performance and longevity of marine diesel engines. By following these seven powerful maintenance tips, marine engineers can effectively ensure smooth operation, prevent common issues, and enhance engine efficiency directly onboard. Regular inspections, clean fuel practices, timely filter replacements, correct injection timing, and vigilant troubleshooting are key to keeping your engine reliable at sea. Implement these strategies to maintain peak performance and avoid costly downtime, ensuring your marine engine operates at its best under all conditions.