Fuel Injector Cleaning
Maintaining clean fuel injectors is crucial for the optimal performance of marine diesel engines. Dirty or clogged injectors can lead to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and costly repairs. As a critical component in the fuel delivery system, fuel injectors ensure that the engine receives the right amount of fuel at the right time, contributing significantly to engine efficiency and reliability.
For qualified marine engineers looking to enhance their injector cleaning techniques, understanding the intricate process of maintaining these vital components is essential. This guide will delve into the seven best steps for cleaning fuel injectors, providing detailed, advanced methods to ensure your engines run smoothly and efficiently. By following these steps, you can extend the lifespan of your injectors, improve overall engine performance, and reduce maintenance costs. Let’s dive into the comprehensive process of keeping your fuel injectors in top condition.
Preparation and Safety Measures
Essential Tools and Equipment
Proper preparation is crucial for effectively and safely cleaning fuel injectors in marine diesel engines. Here’s a list of necessary tools and equipment, along with their descriptions:
- Injector Removal Tool: A specialized tool designed to remove injectors without causing damage to the surrounding components.
- Cleaning Kit: Includes brushes, picks, and other small tools specifically designed for cleaning the intricate parts of fuel injectors.
- Ultrasonic Cleaner: A device that uses ultrasonic waves to thoroughly clean injectors, removing carbon deposits and other contaminants.
- Fuel Pressure Tester: Used to check the fuel pressure before and after cleaning to ensure proper injector function.
- Safety Gloves: Protect hands from harmful chemicals and sharp edges.
- Safety Goggles: Protect eyes from debris, fuel, and cleaning solutions.
- Protective Clothing: Overalls or lab coats to protect skin and regular clothing from spills and stains.
- Fire Extinguisher: Essential for dealing with potential fires, especially when working with flammable substances like diesel fuel.
Safety Gear and Precautions
Working with fuel injectors involves handling potentially hazardous materials and tools. Proper safety gear and precautions are vital:
- Safety Gloves: Always wear chemical-resistant gloves to protect your hands from fuel and cleaning solvents.
- Safety Goggles: Protect your eyes from splashes and airborne particles.
- Protective Clothing: Wear overalls or other protective clothing to prevent skin exposure to harmful substances.
- Fire Extinguisher: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby to quickly address any fire hazards.
- Ventilation: Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling harmful fumes from fuel and cleaning agents.
Safety Protocols
To maintain a safe working environment, follow these step-by-step safety protocols:
- Preparation:
- Gather all necessary tools and safety gear.
- Ensure the workspace is clean, well-lit, and well-ventilated.
- Place a fire extinguisher within easy reach.
- Engine Shutdown:
- Turn off the engine and allow it to cool completely to avoid burns and other injuries.
- Disconnect the battery to prevent accidental starts.
- Fuel System Depressurization:
- Relieve the fuel system pressure by following the manufacturer’s guidelines. This step is crucial to avoid fuel spray injuries.
- Work Area Organization:
- Arrange tools and parts in an orderly manner to prevent accidents and ensure efficiency.
- Use trays or containers to keep small parts and tools organized.
- Personal Protection:
- Wear all required safety gear, including gloves, goggles, and protective clothing.
- Avoid loose clothing and jewelry that could get caught in moving parts.
- Handling Chemicals:
- Use chemicals and cleaning agents in a well-ventilated area.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper handling and disposal of chemicals.
- Injector Removal and Cleaning:
- Use the injector removal tool carefully to avoid damaging the injectors or surrounding components.
- Follow proper cleaning procedures, using the ultrasonic cleaner if available, to ensure thorough cleaning without damaging the injectors.
- Reassembly and Testing:
- Reinstall the injectors carefully, ensuring all connections are secure.
- Test the fuel system for leaks and proper pressure before starting the engine.
- Post-Work Cleanup:
- Clean the workspace and dispose of any hazardous materials according to local regulations.
- Store tools and equipment properly for future use.
Step 1 – Diagnosing Injector Issues
Initial Inspection
Before diving into the intricate process of cleaning fuel injectors, it is crucial to accurately diagnose the issues they might have. An initial inspection helps identify the root cause of performance problems and determines the necessary steps for cleaning or repairs.
Visual Inspection Techniques
- External Examination: Start by visually inspecting the injectors for any external damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or fuel leaks. Look for signs of wear and tear on the injector body and nozzle.
- Connector and Wiring Check: Examine the electrical connectors and wiring for any signs of fraying, corrosion, or loose connections. Ensuring a solid electrical connection is vital for proper injector operation.
- Fuel Line Inspection: Check the fuel lines connected to the injectors for any leaks, cracks, or blockages. Ensure the lines are securely connected and free from obstructions.
Using Diagnostic Tools for Accurate Assessment
To complement the visual inspection, employ diagnostic tools for a more precise assessment of injector performance:
- OBD-II Scanner: For engines equipped with an onboard diagnostics system, use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve error codes that may indicate injector issues. This tool can provide valuable information about injector performance and potential faults.
- Multimeter: Use a multimeter to check the resistance and continuity of the injector’s electrical connections. This helps ensure the injectors are receiving the correct voltage and signal from the engine control unit (ECU).
Common Diagnostic Methods
Once the initial inspection is complete, proceed with more detailed diagnostic methods to thoroughly assess the condition of the fuel injectors.
Pressure Testing
Pressure testing is a critical method to evaluate the injectors’ ability to maintain the correct fuel pressure:
- Connect a Fuel Pressure Gauge: Attach a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail or the injector line, following the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific engine model.
- Start the Engine: With the gauge connected, start the engine and observe the fuel pressure reading. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specified pressure range.
- Monitor Pressure Drop: Turn off the engine and observe the fuel pressure gauge for any rapid drops in pressure, which could indicate a leaking injector or a problem within the fuel system.
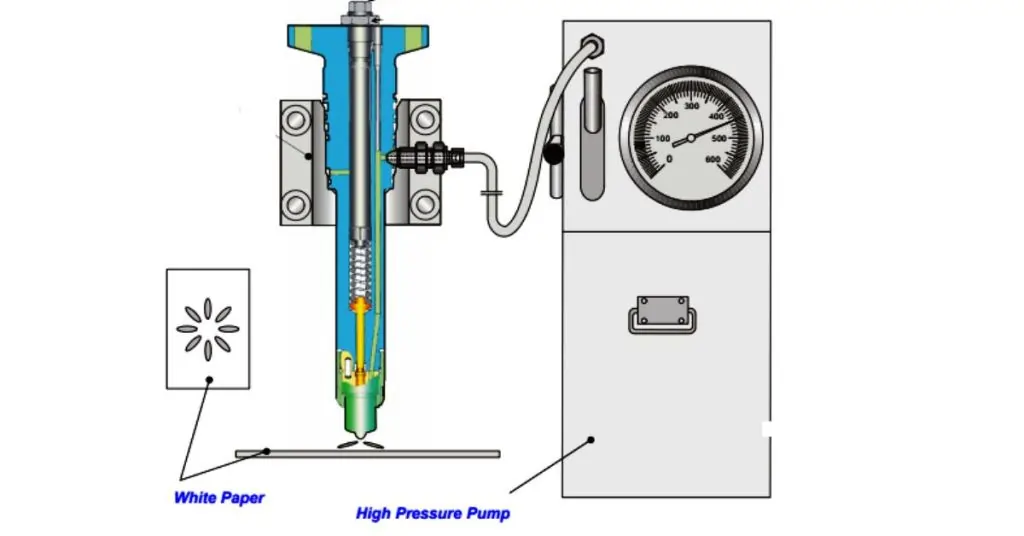
Spray Pattern Analysis

Analyzing the spray pattern helps ensure that the injectors are atomizing fuel correctly, which is essential for efficient combustion:
- Injector Testing Machine: Use an injector testing machine equipped with a spray pattern viewing chamber.
- Remove and Install Injectors: Remove the injectors from the engine and install them into the testing machine.
- Observe Spray Pattern: Activate the injectors using the testing machine and observe the spray pattern through the viewing chamber. A healthy injector should produce a fine, even mist with a consistent spray pattern.
- Check for Anomalies: Look for signs of improper atomization, such as dribbling, uneven spray, or blockage. These issues can indicate clogged or damaged injector nozzles.
Step 2 – Removing the Injectors
Engine Shutdown Procedures
Before removing fuel injectors, it’s essential to ensure the engine is safely shut down to prevent accidents and damage. Follow these steps for a safe shutdown:
- Cool Down the Engine: Allow the engine to cool completely. Working on a hot engine can cause burns and make parts difficult to handle.
- Turn Off the Engine from the Control Panel: Switch off the engine using the control panel. Ensure the engine is completely off and not in standby mode.
- Shut Off the Air Starting Valve: As a safety measure, close the air starting valve to prevent accidental engine start-up from the compressed air system.
- Disconnect the Battery: Remove the negative terminal of the battery to prevent any electrical accidents or unintentional engine starts. This step is crucial for ensuring your safety.
- Shut Off the Fuel Inlet Valve: Close the fuel inlet valve to isolate the fuel system and prevent fuel from entering the engine during maintenance.
- Relieve Fuel System Pressure: Use the manufacturer’s guidelines to depressurize the fuel system. This typically involves releasing a pressure valve or using a special tool. Relieving the pressure prevents fuel spray, which can be hazardous.
Injector Removal Process
The process of removing injectors can vary depending on the engine type. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to remove injectors from common marine diesel engines:
- Gather Necessary Tools:
- Injector removal tool
- Wrenches and sockets
- Screwdrivers
- Fuel line disconnect tool
- Clean rags and containers
- Access the Injectors:
- Remove Engine Covers: Take off any engine covers or shrouds that obstruct access to the injectors. Use the appropriate tools to avoid damaging bolts or clips.
- Clear Fuel Lines and Connectors: Disconnect any fuel lines, electrical connectors, and hoses connected to the injectors. Label the lines and connectors for easy reassembly.
- Remove Fuel Rail (if applicable):
- Unbolt the Fuel Rail: Use a wrench or socket to carefully unbolt the fuel rail. Gently lift the fuel rail off the injectors, ensuring you do not bend or damage it.
- Place the Fuel Rail Aside: Set the fuel rail in a clean, safe location to prevent contamination.
- Remove the Injectors:
- Detach Retaining Clips: If the injectors are held in place by retaining clips, carefully remove them using a screwdriver or pliers. Be cautious not to lose the clips.
- Use Injector Removal Tool: Insert the injector removal tool around the injector. Apply even pressure to extract the injector from its seating. If the injector is stuck, gently wiggle it free to avoid damage.
- Inspect and Store Injectors: Once removed, inspect the injectors for any visible damage or wear. Place the injectors in a clean container to prevent contamination.
Tips for Avoiding Damage to Injectors and Surrounding Components
Removing injectors requires precision and care to avoid damaging the injectors and surrounding engine components. Here are some tips to ensure a safe and damage-free removal process:
- Use the Correct Tools: Always use tools specifically designed for injector removal. Improvised tools can cause damage to the injectors or engine components.
- Apply Even Pressure: When using the injector removal tool, apply even and steady pressure. Avoid sudden jerks or excessive force, as this can damage the injector or its seating.
- Keep the Area Clean: Ensure the workspace is clean and free of debris. Contaminants can enter the injector ports or engine, leading to potential issues during reassembly.
- Label Components: Label all disconnected fuel lines, electrical connectors, and other components. This practice helps ensure correct reassembly and prevents mistakes.
- Handle Injectors with Care: Fuel injectors are delicate and precise components. Handle them gently, avoiding any impact or rough handling that could affect their performance.
- Inspect O-Rings and Seals: Check the O-rings and seals on the injectors for wear or damage. Replace any damaged seals to ensure a proper fit and prevent leaks during reinstallation.
Step 3 – Cleaning the Injectors
Cleaning Solutions and Methods
Cleaning fuel injectors in marine diesel engines requires specific solutions and methods to ensure effectiveness without causing damage. Here’s an overview of suitable cleaning solutions and a comparison of ultrasonic and manual cleaning methods:
Overview of Cleaning Solutions Suitable for Marine Diesel Injectors
- Commercial Injector Cleaner: Formulated specifically for fuel injectors, these cleaners effectively dissolve carbon deposits and other contaminants.
- Ultrasonic Cleaning Solution: Designed for use in ultrasonic cleaners, this solution helps break down and remove stubborn residues through ultrasonic waves.
- Solvent-Based Cleaners: These cleaners use powerful solvents to dissolve deposits and grime. While effective, they must be used with caution to avoid damaging injector components.
- DIY Cleaning Solutions: A mixture of isopropyl alcohol and acetone can serve as an alternative cleaning solution. However, it’s essential to ensure compatibility with the injector materials to prevent damage.
Ultrasonic Cleaning vs. Manual Cleaning
- Ultrasonic Cleaning: Uses high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic bubbles in the cleaning solution, which implode and remove contaminants from the injectors. This method is highly effective for deep cleaning without disassembling the injectors.
- Advantages: Thorough and uniform cleaning, less labor-intensive, minimizes risk of damaging injectors.
- Disadvantages: Requires specialized equipment, higher initial cost.
- Manual Cleaning: Involves physically scrubbing and cleaning the injectors using brushes, picks, and cleaning solutions. This method allows for detailed attention to specific areas but requires more time and effort.
- Advantages: Lower cost, no need for specialized equipment, can target specific areas with precision.
- Disadvantages: Labor-intensive, higher risk of damaging injectors if not done carefully.
Step-by-Step Cleaning Process
Detailed Instructions for Ultrasonic Cleaning
- Prepare the Ultrasonic Cleaner:
- Fill the ultrasonic cleaner tank with the appropriate ultrasonic cleaning solution.
- Set the cleaner’s temperature and timer according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Pre-Clean the Injectors:
- Remove any large debris or deposits from the injectors using a soft brush.
- Rinse the injectors with a solvent-based cleaner to remove initial surface grime.
- Place Injectors in the Ultrasonic Cleaner:
- Submerge the injectors in the ultrasonic cleaner, ensuring they are fully covered by the cleaning solution.
- Activate the ultrasonic cleaner and let it run for the recommended duration, typically 20-30 minutes.
- Rinse and Inspect:
- After cleaning, remove the injectors from the ultrasonic cleaner and rinse them with clean water or a solvent to remove any residual cleaning solution.
- Inspect the injectors to ensure all contaminants have been removed.
- Dry and Lubricate:
- Allow the injectors to air dry completely or use compressed air to speed up the drying process.
- Apply a light coating of lubricant to the O-rings and seals to prevent damage during reinstallation.
Detailed Instructions for Manual Cleaning
- Pre-Clean the Injectors:
- Use a soft brush to remove any loose debris or deposits from the injectors.
- Rinse the injectors with a solvent-based cleaner to remove initial surface grime.
- Disassemble the Injectors (if applicable):
- If possible, disassemble the injectors to access all internal components. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe disassembly.
- Clean the Injector Components:
- Soak the injector components in a commercial injector cleaner or DIY cleaning solution.
- Use small brushes, picks, and pipe cleaners to scrub away carbon deposits and contaminants from all surfaces and orifices.
- Pay special attention to the injector nozzles and spray holes to ensure they are free of blockages.
- Rinse and Inspect:
- After cleaning, rinse all components with clean water or a solvent to remove any residual cleaning solution.
- Inspect each component carefully to ensure thorough cleaning.
- Reassemble and Dry:
- Reassemble the injectors according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Allow the injectors to air dry completely or use compressed air to speed up the drying process.
- Lubricate and Protect:
- Apply a light coating of lubricant to the O-rings and seals to prevent damage during reinstallation.
Tips for Ensuring Thorough Cleaning Without Damaging Injectors
- Use Appropriate Tools: Always use tools specifically designed for cleaning injectors to avoid causing damage.
- Avoid Abrasive Materials: Do not use abrasive brushes or materials that can scratch or damage injector surfaces.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for cleaning solutions and procedures.
- Inspect Thoroughly: After cleaning, inspect the injectors carefully to ensure no contaminants remain.
- Handle with Care: Fuel injectors are delicate components; handle them gently to avoid damage during cleaning and reassembly.
Step 4 – Inspecting and Testing Clean Injectors
Post-Cleaning Inspection
After cleaning the fuel injectors, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough inspection to ensure they are free of contaminants and in good working condition. This step involves both visual and microscopic inspection techniques.
Visual Inspection Techniques
- Surface Examination:
- Carefully inspect the injector’s external surfaces for any remaining deposits, corrosion, or damage.
- Ensure the nozzle tips are clean and free of obstructions.
- Seal and O-Ring Check:
- Examine the seals and O-rings for any signs of wear, cracks, or deformation. Replace any damaged components to ensure proper sealing and prevent fuel leaks.
- Connector and Wiring Inspection:
- Check the electrical connectors and wiring for signs of corrosion, wear, or damage. Ensure the connectors are clean and fit securely.
Microscopic Inspection Techniques
- Nozzle Examination:
- Use a magnifying glass or microscope to inspect the injector nozzles closely.
- Look for any microscopic cracks, erosion, or remaining deposits that could affect fuel spray patterns.
- Spray Hole Inspection:
- Inspect the spray holes under magnification to ensure they are clean and unobstructed.
- Any blockages or irregularities can significantly impact injector performance and fuel atomization.
Common Issues to Look for After Cleaning
- Residual Deposits: Check for any stubborn carbon deposits or residues that may not have been removed during cleaning.
- Corrosion or Pitting: Look for signs of corrosion or pitting on the injector surfaces, especially around the nozzle and sealing areas.
- Wear and Tear: Identify any wear and tear on moving parts or seals that could compromise injector performance.
- Cracks or Damage: Look for any cracks or physical damage that could cause injector failure or fuel leaks.
Testing Injectors
After a thorough inspection, it’s time to test the injectors to ensure they are functioning correctly. This step includes pressure testing and verifying spray patterns.
Pressure Testing Post-Cleaning
- Set Up the Pressure Tester:
- Connect the fuel injector to a pressure testing machine or a bench tester designed for injectors.
- Ensure the connections are secure and leak-free.
- Apply Test Pressure:
- Gradually apply the specified test pressure according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Monitor the pressure gauge to ensure it remains within the recommended range.
- Check for Leaks:
- Observe the injector for any signs of fuel leakage. Leaks indicate faulty seals or damage that needs to be addressed.
- A properly functioning injector should maintain the set pressure without any drop for a specified period.
Verifying Spray Patterns and Injector Performance
- Injector Testing Machine:
- Place the injector in an injector testing machine equipped with a spray pattern viewing chamber.
- Activate the injector to simulate its operation under normal conditions.
- Observe Spray Pattern:
- Observe the fuel spray pattern through the viewing chamber. A healthy injector should produce a fine, even mist with a consistent and symmetrical spray pattern.
- Look for any irregularities, such as uneven spray, dribbling, or blockages.
- Performance Testing:
- Perform multiple cycles of injection to test the consistency of the spray pattern.
- Ensure the injector delivers fuel at the correct volume and pressure for each cycle, as specified by the manufacturer.
Common Issues to Address During Testing
- Inconsistent Spray Patterns: Irregular spray patterns can indicate blockages or damage to the nozzle.
- Fuel Leaks: Any signs of leaking during pressure testing suggest problems with seals or cracks in the injector body.
- Uneven Fuel Delivery: Variations in fuel delivery volume or pressure may point to internal wear or damage.
Step 5 – Reinstalling the Injectors
Preparation for Reinstallation
Before reinstalling the fuel injectors, it’s crucial to ensure they are in optimal condition and all necessary preparations are made. This step involves thoroughly checking for debris, lubricating necessary parts, and making sure all components are ready for reassembly.
Ensuring Injectors are Free from Debris and Contaminants
- Final Cleaning:
- Give the injectors a final rinse with clean solvent or compressed air to ensure all cleaning residues and contaminants are removed.
- Pay special attention to the nozzle tips and spray holes, ensuring they are completely clear of debris.
- Inspect Seals and O-Rings:
- Check the seals and O-rings for any damage or wear. Replace any that are not in perfect condition to ensure a proper seal during reinstallation.
- Clean Installation Area:
- Thoroughly clean the injector ports and surrounding areas on the engine to prevent any dirt or debris from entering the combustion chamber during reinstallation.
Lubricating Necessary Parts
- Apply Lubricant to Seals and O-Rings:
- Lightly coat the seals and O-rings with a suitable lubricant, such as engine oil or a specific O-ring lubricant. This helps prevent damage during installation and ensures a proper seal.
- Lubricate Injector Ports:
- Apply a small amount of lubricant to the injector ports to facilitate smooth insertion and proper seating of the injectors.
Reinstallation Process
With the injectors cleaned and prepared, follow this detailed guide to reinstall them correctly, ensuring they are aligned and torqued to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Detailed Guide on Correctly Reinstalling Injectors
- Position the Injectors:
- Carefully place each injector into its respective port, ensuring it is aligned correctly. The injector should fit snugly without any force.
- Secure the Injectors:
- If the injectors use retaining clips, reattach them securely. Ensure they are properly seated and not damaged.
- For injectors held by bolts or screws, insert them loosely by hand to ensure proper alignment before tightening.
- Connect the Fuel Rail:
- Align the fuel rail with the injectors and gently press it into place, ensuring all injectors are properly seated in the rail.
- Secure the fuel rail with bolts or screws, tightening them gradually and evenly to avoid misalignment.
- Reconnect Fuel Lines and Electrical Connectors:
- Reconnect any fuel lines, ensuring they are securely fastened and free of leaks.
- Attach the electrical connectors to the injectors, ensuring they click into place and form a secure connection.
Torque Specifications and Alignment Tips
- Consult Manufacturer’s Specifications:
- Refer to the engine manufacturer’s manual for the specific torque settings for the injector bolts or screws. Using the correct torque is critical to avoid damaging the injectors or the engine.
- Use a Torque Wrench:
- Use a calibrated torque wrench to tighten the injector bolts or screws to the specified torque. This ensures uniform pressure and prevents over-tightening.
- Gradual Tightening:
- Tighten the bolts or screws in stages, gradually increasing the torque. This helps maintain proper alignment and seating of the injectors.
- Use a crisscross pattern if applicable to distribute the pressure evenly and prevent warping.
- Final Check:
- After securing the injectors, perform a final inspection to ensure all components are properly aligned and torqued.
- Check that the fuel lines and electrical connectors are securely attached and free from any signs of leakage or damage.
Step 6 – Engine Testing and Calibration
Initial Engine Start-Up Procedures
After reinstalling the fuel injectors, it’s crucial to follow a systematic approach to safely start the engine and ensure everything is functioning correctly. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Steps to Safely Start the Engine After Injector Reinstallation
- Reconnect the Battery:
- Reattach the negative terminal of the battery that was previously disconnected to prevent electrical accidents.
- Open Fuel Inlet Valve:
- Reopen the fuel inlet valve to allow fuel to flow into the system.
- Prime the Fuel System:
- Prime the fuel system to eliminate any air pockets that may have formed during the injector removal and reinstallation. This may involve using a manual priming pump or following the manufacturer’s specific priming procedure.
- Check for Leaks:
- Before starting the engine, inspect the fuel injectors, fuel lines, and connections for any signs of leaks. Tighten any loose connections if necessary.
- Activate the Air Starting Valve:
- Reopen the air starting valve to enable the engine’s air start system if it was closed during the shutdown procedures.
- Initial Crank:
- Perform an initial crank of the engine without starting it fully to build up oil pressure and ensure fuel is properly delivered to the injectors. This can be done by briefly engaging the starter for a few seconds.
- Start the Engine:
- Start the engine and let it idle at a low RPM. Observe the engine for any unusual noises, vibrations, or warning lights. Pay close attention to the exhaust for signs of unburned fuel or excessive smoke.
- Warm-Up Period:
- Allow the engine to warm up gradually to its normal operating temperature. This helps ensure that the injectors and other components are functioning correctly under typical operating conditions.
Performance Calibration
Once the engine is running smoothly, calibrating the injectors for optimal performance is essential. This involves adjusting the injectors to ensure precise fuel delivery and using diagnostic tools to verify proper calibration.
Calibrating Injectors for Optimal Performance
- Set Baseline Parameters:
- Refer to the engine’s service manual to set the baseline parameters for injector timing and fuel delivery rates. These specifications are crucial for achieving optimal engine performance.
- Adjust Injector Timing:
- Use the manufacturer’s guidelines to adjust the timing of the injectors. Proper timing ensures that fuel is injected at the correct moment in the combustion cycle for efficient combustion.
- Fine-Tune Fuel Delivery:
- Adjust the fuel delivery rates for each injector to ensure even distribution of fuel. This may involve adjusting the fuel pressure regulator or using specialized tools provided by the manufacturer.
Using Diagnostic Tools to Ensure Proper Calibration
- Engine Diagnostic Software:
- Connect an engine diagnostic software tool to the engine’s ECU. This software provides real-time data on injector performance, fuel pressure, and other critical parameters.
- Monitor Injector Performance:
- Use the diagnostic software to monitor the performance of each injector. Look for any inconsistencies or deviations from the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Perform Injector Balancing:
- Injector balancing ensures that all injectors deliver the same amount of fuel. The diagnostic tool can help identify any discrepancies, and adjustments can be made to balance the injectors accordingly.
- Check Exhaust Emissions:
- Analyze the exhaust emissions using an exhaust gas analyzer. Properly calibrated injectors should produce minimal emissions and indicate complete combustion.
- Test Under Load:
- Run the engine under various loads and operating conditions to ensure the injectors maintain proper performance. This involves conducting sea trials or load tests to simulate real-world conditions.
- Final Adjustments:
- Based on the diagnostic data and performance observations, make any final adjustments to the injectors. Ensure all settings are within the manufacturer’s recommended ranges.
Conclusion
Maintaining clean and properly functioning fuel injectors is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of marine diesel engines. By following the detailed steps of diagnosing issues, safely removing and cleaning the injectors, conducting thorough inspections, and carefully reinstalling and calibrating them, marine engineers can ensure their engines run efficiently and reliably. Adhering to these best practices not only enhances engine performance but also helps prevent costly repairs and downtime. Regular maintenance and attention to detail are key to keeping your marine diesel engine in top condition, ensuring smooth sailing for your maritime operations.
FAQ on How to Clean Fuel Injectors
Q: How often should I clean my fuel injectors?
A: Clean your fuel injectors every 15,000 to 30,000 miles to maintain optimal engine performance.
Q: What do I need to clean my fuel injectors?
A: You need a cleaning kit, safety gear, solution, and compressed air to clean your fuel injectors.
Q: Can I clean fuel injectors myself?
A: Yes, you can clean fuel injectors yourself by following the engine’s manual and using a proper injector cleaning kit.
Q: How do I know if my fuel injectors need cleaning?
A: If your engine misfires, idles roughly, or you notice a drop in fuel efficiency, it might be time to clean your fuel injectors.
Read our related posts:-
Fuel injection system of diesel engine | 22-23 The best-updated tutorial on
Fuel Injector and How it Works | 23-24 The best tutorial for Engnrs