Fuel Shut Off Solenoid
In the world of marine engineering, the fuel shut off solenoid and its related components are crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. These small yet powerful devices control the fuel flow to the engine, playing a pivotal role in preventing accidents and maintaining optimal performance. A malfunctioning solenoid can lead to severe engine issues or even catastrophic failures at sea, making regular maintenance and proper understanding essential.
To help marine engineers and enthusiasts keep their engines running smoothly and safely, we’ve compiled seven powerful tips. These insights cover everything from basic functionality to advanced maintenance techniques, providing a comprehensive guide to mastering fuel shut off solenoids. Dive into our expert advice to enhance your marine engine’s performance and safeguard your voyages against unexpected breakdowns.
Understand the Basics of Fuel Shut Off Solenoids
Definition and Function
A fuel shut off solenoid is an electromechanical device that controls the flow of fuel to an engine. It operates by receiving an electrical signal, which either opens or closes a valve to start or stop the fuel supply. In marine engines, this solenoid is vital for controlling the engine’s fuel intake, ensuring that the engine can be quickly and safely shut down in case of an emergency or when the engine is turned off. The precision of the fuel shut off solenoid ensures that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel, preventing overfueling or fuel starvation.
Importance in Marine Engines
The fuel shut off solenoid is crucial for both the safety and performance of marine engines. In emergency situations, such as an engine fire or fuel leak, the solenoid allows for an immediate cessation of fuel flow, thereby minimizing potential damage and hazards. Additionally, a well-functioning solenoid ensures optimal engine performance by regulating the fuel supply accurately, which is essential for maintaining engine efficiency and longevity. Without a reliable fuel shut off solenoid, marine engines are at a higher risk of malfunctioning, which can lead to costly repairs and dangerous situations at sea.
Understanding and Maintaining Key Components
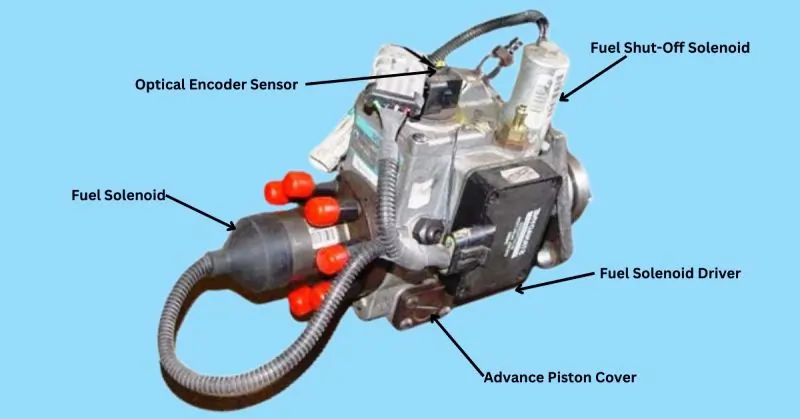
Fuel Shut-Off Solenoid
Function:
The fuel shut-off solenoid is a critical component that regulates the flow of fuel to the engine. It functions by opening or closing a valve based on electrical signals, enabling or disabling the fuel supply as needed. This control ensures that the engine can be promptly stopped or started, which is vital for both routine operations and emergency situations.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check the solenoid for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Cleaning: Keep the solenoid clean from dirt and debris to prevent blockages and ensure smooth operation.
- Testing: Regularly test the solenoid’s functionality by verifying the electrical signals and valve movements.
- Replacement: Replace the solenoid if it shows signs of malfunction or deterioration to maintain engine reliability.
Optical Encoder Sensor
Function:
The optical encoder sensor provides precise feedback on the position and speed of engine components. This feedback is essential for accurate control and synchronization of various engine functions, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Maintenance Tips:
- Cleanliness: Keep the sensor and its surroundings clean from dust and oil to prevent interference with its optical components.
- Regular Checks: Inspect the sensor regularly for any signs of wear or damage.
- Alignment: Ensure the sensor is correctly aligned to accurately read the positions and speeds of engine components.
Fuel Solenoid
Function:
The fuel solenoid acts as an on/off valve for the fuel supply to the engine. It manages the fuel flow, ensuring that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel for optimal operation.
Maintenance Tips:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the solenoid for any wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Electrical Connections: Check the electrical connections to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
- Functionality Test: Periodically test the solenoid to confirm it is operating correctly and replace it if necessary.
Fuel Solenoid Driver
Function:
The fuel solenoid driver is responsible for controlling the operation of the fuel solenoid. It ensures accurate fuel delivery by managing the electrical signals that activate the solenoid.
Maintenance Tips:
- Signal Check: Regularly check for proper electrical signals to the solenoid.
- Inspection: Inspect the driver for any signs of malfunction or wear.
- Replacement: Replace the driver if it fails to provide consistent and accurate signals to the fuel solenoid.
Advance Piston Cover
Function:
The advance piston cover protects the pistons and helps maintain optimal compression and engine performance. It ensures that the pistons operate efficiently by preventing debris and contaminants from affecting their movement.
Maintenance Tips:
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the piston cover for cracks, damage, or wear.
- Cleaning: Keep the piston cover clean to prevent any debris from entering the engine.
- Replacement: Replace the piston cover if it shows signs of significant wear or damage to maintain engine integrity and performance.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Inspection Checklist
| Component | Inspection Task |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Check for visible signs of wear, corrosion, or damage on all engine components. Inspect hoses and connections for leaks or cracks. Ensure all bolts and fasteners are tight and secure. |
| Fuel System | Examine the fuel shut-off solenoid for any signs of wear or corrosion.Inspect fuel lines for leaks, cracks, or blockages. Verify that the fuel solenoid operates correctly and that its connections are secure. |
| Electrical System | Check electrical connections for corrosion or loose wires. Test the optical encoder sensor for accurate feedback on engine component positions. Ensure the fuel solenoid driver is functioning correctly by verifying signal integrity. |
| Lubrication System | Check oil levels and quality. Inspect lubrication points and apply oil or grease as needed. |
| Cooling System | Inspect coolant levels and top up if necessary. Check for leaks or blockages in the cooling system. |
| Piston and Cylinder | Inspect the advance piston cover for cracks or damage. Ensure the pistons move freely and are free from debris. |
Maintenance Routine
| Frequency | Maintenance Task |
|---|---|
| Daily Maintenance | Pre-Operation Check: Inspect fuel levels, oil levels, and coolant levels. Ensure all gauges and meters are working correctly. Post-Operation Check: After each use, visually inspect the engine for any signs of leaks or abnormalities. Clean off any saltwater or debris from the engine. |
| Weekly Maintenance | Cleaning: Clean the exterior of the engine to remove salt, dirt, and grime. Pay special attention to electrical connections and moving parts. Lubrication: Apply lubrication to moving parts, such as the throttle and steering mechanisms, to ensure smooth operation. |
| Monthly Maintenance | Detailed Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection using the comprehensive checklist. Address any issues or potential problems immediately. Fuel System Maintenance: Check and clean the fuel filters. Inspect the fuel shut-off solenoid and fuel solenoid for proper operation. |
| Quarterly Maintenance | Electrical System Check: Inspect all electrical components, including the optical encoder sensor and fuel solenoid driver. Ensure they are free from corrosion and functioning correctly. Oil and Filter Change: Change the engine oil and replace the oil filter to maintain lubrication quality. |
| Bi-Annual Maintenance | Cooling System Flush: Flush the cooling system to remove any buildup or contaminants. Refill with fresh coolant. Advance Piston Cover Inspection: Remove and inspect the advance piston cover and pistons for wear or damage. Replace if necessary. |
| Annual Maintenance | Comprehensive Overhaul: Conduct a full engine overhaul, including inspecting and replacing worn-out parts. This should include all major components like the fuel shut-off solenoid, optical encoder sensor, fuel solenoid, fuel solenoid driver, and advance piston cover. Professional Service: Consider having a professional marine engineer perform a detailed service and inspection to catch any issues you might have missed. |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Symptoms of Problems | Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide |
|---|---|
| Engine Not Starting | 1. Check Electrical Connections: Ensure all wires to the solenoid are secure and corrosion-free. 2. Test Voltage: Use a multimeter to verify that the solenoid is receiving the correct voltage. 3. Inspect Solenoid Valve: Remove and inspect the solenoid valve for blockages or damage. 4. Replace if Necessary: If the solenoid is faulty, replace it with a new one. |
| Engine Stalls Unexpectedly | 1. Check Fuel Supply: Ensure there is no interruption in the fuel supply. 2. Inspect Fuel Lines: Look for leaks or blockages in the fuel lines. 3. Test Solenoid Operation: Activate the solenoid manually to see if it opens and closes correctly. 4. Examine Electrical Signals: Ensure the signal from the engine control unit (ECU) to the solenoid is consistent. |
| Solenoid Overheating | 1. Check for Proper Ventilation: Ensure the solenoid is not obstructed and has proper airflow. 2. Inspect for Electrical Overload: Verify that the electrical system is not supplying too much current to the solenoid. 3. Test for Internal Short Circuit: Use a multimeter to check for internal shorts within the solenoid. 4. Replace if Faulty: If overheating persists, replace the solenoid. |
| No Fuel Flow | 1. Verify Fuel Tank Level: Ensure the fuel tank is not empty. 2. Inspect Fuel Filter: Check and replace a clogged fuel filter. 3. Test Solenoid Valve: Ensure the solenoid valve is opening fully when activated. 4. Check Fuel Pump: Verify that the fuel pump is functioning properly. |
| Intermittent Operation | 1. Inspect Wiring for Loose Connections: Ensure all wiring to the solenoid is secure and free from corrosion. 2. Test Solenoid Coil: Use an ohmmeter to check the solenoid coil for continuity. 3. Monitor ECU Signals: Verify that the ECU is sending consistent signals to the solenoid. 4. Replace Solenoid if Inconsistent: If the solenoid operation is inconsistent, replace it. |
| Unusual Noises | 1. Listen for Clicking or Humming: Identify the type of noise the solenoid is making. 2. Check for Obstructions: Ensure there are no physical obstructions causing the noise.3. Inspect Mounting: Ensure the solenoid is mounted securely and not vibrating. 4. Replace if Damaged: If the solenoid is damaged, replace it. |
Ensuring Proper Installation
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation of a fuel shut off solenoid is critical for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of marine engines. Follow this detailed guide to ensure a correct and secure installation:
- Preparation:
- Gather Tools and Materials: Ensure you have all necessary tools, such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and a multimeter, as well as the solenoid, mounting hardware, and wiring.
- Safety First: Disconnect the battery and ensure the engine is off and cool before starting the installation process.
- Positioning the Solenoid:
- Identify Mounting Location: Choose a location close to the fuel line and engine, ensuring it is accessible for maintenance but protected from excessive heat and vibrations.
- Secure Mounting: Use the provided mounting hardware to securely attach the solenoid to a stable surface. Ensure it is firmly fixed and does not move.
- Connecting Fuel Lines:
- Attach Fuel Lines: Connect the fuel lines to the solenoid’s inlet and outlet ports. Use appropriate fittings and clamps to ensure a leak-free connection.
- Check Alignment: Ensure that the fuel lines are properly aligned and not kinked or twisted, which could restrict fuel flow.
- Electrical Connections:
- Wire the Solenoid: Connect the solenoid to the electrical system using the manufacturer’s wiring diagram. Ensure that the wires are properly insulated and secured.
- Verify Voltage: Use a multimeter to check that the solenoid is receiving the correct voltage according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Testing the Installation:
- Initial Test: Reconnect the battery and turn on the engine. Activate the solenoid to ensure it opens and closes correctly.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect all connections for fuel leaks and tighten fittings as necessary.
- Final Verification: Test the solenoid under different operating conditions to ensure it functions reliably.
Common Installation Mistakes
Avoid these frequent mistakes to ensure a successful and trouble-free installation:
- Incorrect Positioning:
- Mistake: Placing the solenoid in an area exposed to excessive heat or vibration.
- Solution: Mount the solenoid in a location that is stable and protected from harsh conditions, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Improper Fuel Line Connections:
- Mistake: Using incorrect fittings or failing to secure fuel lines properly.
- Solution: Ensure all fuel line connections are tight and use appropriate clamps and fittings to prevent leaks.
- Faulty Electrical Connections:
- Mistake: Incorrectly wiring the solenoid or using inadequate insulation on electrical connections.
- Solution: Follow the wiring diagram carefully, use proper insulation, and secure all connections to prevent electrical issues.
- Ignoring Voltage Requirements:
- Mistake: Not verifying the voltage requirements of the solenoid, leading to improper operation.
- Solution: Use a multimeter to ensure the solenoid receives the correct voltage as specified by the manufacturer.
- Skipping Testing:
- Mistake: Failing to thoroughly test the solenoid after installation.
- Solution: Conduct comprehensive tests under various conditions to confirm the solenoid operates correctly and there are no leaks or electrical issues.
Staying Updated with Technological Advances
Latest Innovations
Recent advancements in fuel shut off solenoid technology and related components have significantly enhanced the efficiency, reliability, and safety of marine engines. Here are some of the most notable innovations:
- Smart Solenoids:
- Integration with IoT: Modern fuel shut off solenoids are increasingly being integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) technology. These smart solenoids can communicate with central control systems, providing real-time data on their status and performance.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Operators can monitor and control smart solenoids remotely, which allows for immediate response to any issues and reduces the need for manual inspections.
- Enhanced Materials and Coatings:
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials: New solenoids are being manufactured with advanced materials that offer superior resistance to corrosion, which is crucial in harsh marine environments.
- Protective Coatings: Innovative coatings are being applied to solenoid components to extend their lifespan and enhance their performance under extreme conditions.
- Energy-Efficient Designs:
- Low Power Consumption: Advances in solenoid design have led to more energy-efficient models that require less power to operate, reducing the overall energy consumption of marine engines.
- Improved Magnetic Efficiency: Enhancements in the magnetic components of solenoids have increased their efficiency, allowing for quicker and more reliable operation.
- Advanced Diagnostic Features:
- Self-Diagnosing Solenoids: Some modern solenoids come with built-in diagnostic capabilities that can detect issues such as electrical faults or mechanical wear, alerting operators to potential problems before they cause significant damage.
- Predictive Maintenance: These diagnostic features support predictive maintenance strategies, enabling more proactive and efficient upkeep of marine engines.
Future Trends
The future of fuel shut off solenoid technology in marine applications looks promising, with several trends likely to shape the industry:
- Increased Automation:
- Autonomous Vessels: As the development of autonomous vessels progresses, the need for highly reliable and automated solenoid systems will grow. These systems will need to function flawlessly without human intervention, making reliability and advanced diagnostics even more critical.
- Integrated Control Systems: Future solenoids will likely be part of more comprehensive, integrated control systems that manage multiple aspects of engine operation, further enhancing automation and efficiency.
- Enhanced Connectivity:
- 5G and Beyond: With the advent of 5G technology, the connectivity of smart solenoids will improve, allowing for even faster and more reliable communication with control systems. This will enable more precise control and quicker response times to any issues.
- Blockchain for Security: Blockchain technology may be used to secure communication between solenoids and control systems, ensuring that the data is tamper-proof and enhancing the overall security of marine operations.
- Sustainability Focus:
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Future solenoid designs will increasingly focus on sustainability, with materials and manufacturing processes that minimize environmental impact.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solenoids that can integrate with renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, will become more common, supporting the shift towards greener marine operations.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques:
- 3D Printing: The use of 3D printing technology in manufacturing solenoids will allow for more customized and complex designs, improving performance and reducing production costs.
- Nanotechnology: Nanotechnology may lead to the development of solenoids with even greater efficiency and durability, utilizing materials with superior properties at the nanoscale.
FAQ on “Fuel Shut Off Solenoid”
Q: What is the primary function of a fuel shut off solenoid in marine engines?
A: It controls the fuel flow to the engine.
Q: How can I tell if my fuel shut off solenoid is malfunctioning?
A: Look for engine starting issues or unexpected stalling.
Q: What are some common maintenance tips for a fuel shut off solenoid?
A: Inspect regularly, keep it clean, and check connections.
Q: Why is proper installation of the fuel shut off solenoid important?
A: It ensures reliable operation and prevents fuel leaks.
Conclusion
Staying updated with the latest advancements in fuel shut off solenoid technology is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of marine engines. From smart solenoids with IoT integration to energy-efficient designs and enhanced materials, these innovations are transforming marine operations. By understanding these advancements and anticipating future trends, marine engineers and operators can maintain optimal engine performance and stay ahead in the ever-evolving maritime industry. Implementing these powerful tips will not only enhance your engine’s functionality but also contribute to safer and more sustainable marine practices.
