Gas Solenoid Valve
Gas solenoid valves play a crucial role in various marine applications, ensuring the safe and efficient control of gas flow within complex systems. These valves operate by using an electromagnetic solenoid to open and close, allowing precise regulation of gas. Their reliability and precision make them indispensable in maintaining the safety and functionality of marine vessels.
In this blog post, we will explore the seven most powerful uses of gas solenoid valves in the marine industry. From gas detection systems and LNG handling to fuel supply and heating systems, we’ll delve into how these valves enhance safety and operational efficiency. This comprehensive overview is designed to provide marine engineers with valuable insights into the critical applications of gas solenoid valves, highlighting their significance in modern marine engineering. Whether you’re involved in designing, operating, or maintaining marine systems, understanding the versatile uses of gas solenoid valves is essential for optimizing performance and safety
Understanding Gas Solenoid Valves
Definition and Basic Concept of Gas Solenoid Valves
Gas solenoid valves are electromechanical devices designed to control the flow of gas within a system. These valves operate by using an electromagnetic solenoid coil that, when energized, moves a plunger to open or close the valve. This precise mechanism allows for accurate regulation of gas flow, making solenoid valves essential in various applications where gas control is critical.
Importance of Gas Solenoid Valves in Marine Settings
In marine environments, the role of gas solenoid valves is paramount. They ensure the safe and efficient operation of essential systems on board vessels, such as gas detection, LNG handling, fuel supply, and heating systems. The ability to precisely control gas flow helps in preventing leaks, optimizing fuel combustion, and maintaining overall safety standards. Their reliability and responsiveness are crucial in marine applications where conditions can be harsh and the stakes high. Understanding and utilizing gas solenoid valves effectively can significantly enhance the safety and performance of marine operations.
Working Mechanism of Gas Solenoid Valve
Detailed Explanation of How Gas Solenoid Valves Operate
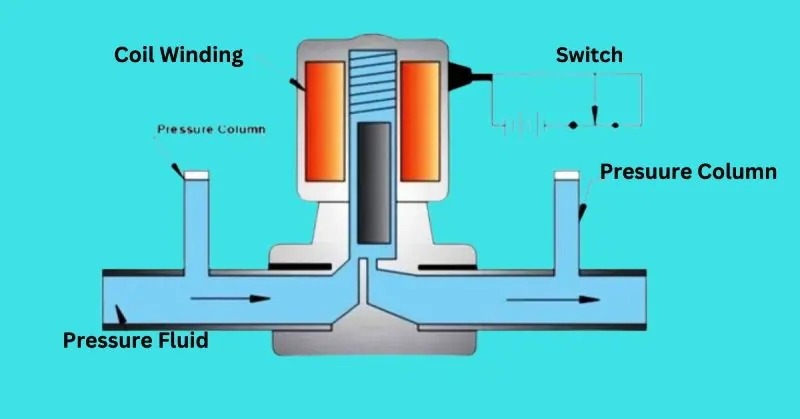
Gas solenoid valves function through the interaction of electrical and mechanical components to control the flow of gas. When an electric current passes through the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field exerts a force on a plunger or armature, causing it to move. Depending on the valve’s design, this movement either opens or closes the valve, allowing or blocking the gas flow. This operation can be finely controlled by adjusting the electrical input, providing precise gas flow regulation.
Key Components Involved in the Working Mechanism
- Solenoid Coil: The electromagnetic coil that generates a magnetic field when energized.
- Plunger/Armature: The moving part that responds to the magnetic field, opening or closing the valve.
- Valve Body: The outer casing that houses the internal components and channels the gas flow.
- Spring: A component that returns the plunger to its original position when the solenoid is de-energized.
- Orifice: The passage through which gas flows, controlled by the plunger’s position.
Safety Features of Gas Solenoid Valves
Overview of Essential Safety Features Integrated into Gas Solenoid Valves
Gas solenoid valves are equipped with numerous safety features designed to prevent accidents and ensure reliable operation in demanding marine environments. Key safety features include fail-safe mechanisms, pressure relief systems, and leak detection capabilities. These features are critical in maintaining the integrity of gas control systems and protecting both the vessel and crew from potential hazards.
How These Safety Features Contribute to Safe Marine Operations
- Fail-Safe Mechanisms: In the event of power loss or system failure, fail-safe solenoid valves automatically return to their default position (open or closed) to prevent uncontrolled gas flow. This feature is vital for averting dangerous situations during electrical or mechanical malfunctions.
- Pressure Relief Systems: Integrated pressure relief valves help manage excessive pressure within the system, preventing potential explosions or system damage. This is especially important in marine environments where pressure fluctuations can be common.
- Leak Detection: Advanced gas solenoid valves are equipped with sensors that detect leaks and trigger automatic shutoff. This early detection system minimizes the risk of gas leaks, which can lead to fires or toxic exposures.
- Corrosion Resistance: Marine environments are harsh, with high humidity and saltwater exposure. Gas solenoid valves are often constructed with corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring long-term durability and safety.
Real-World Examples of Safety Features in Action
- Emergency Shutdown Systems (ESD): On oil tankers and LNG carriers, gas solenoid valves with fail-safe features are integral to the ESD systems. In the event of a detected hazard, these valves automatically shut down fuel lines, preventing potential fires or explosions.
- Engine Room Safety: In marine engine rooms, pressure relief systems in gas solenoid valves protect the engines and crew by managing overpressure conditions, ensuring that the gas supply remains within safe operating limits.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Onboard fire suppression systems utilize gas solenoid valves with leak detection to ensure that in the event of a gas leak, the supply is immediately cut off, preventing the gas from feeding a fire.
- HVAC Systems: Corrosion-resistant gas solenoid valves in HVAC systems maintain safe and efficient operation, crucial for the comfort and safety of the crew on long voyages.
Critical Marine Applications of Gas Solenoid Valves
Introduction to the Critical Roles of Gas Solenoid Valves in Marine Environments
Gas solenoid valves are indispensable components in the maritime industry, playing pivotal roles in various critical applications. These valves are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of gas-related systems on board ships. Their ability to precisely control gas flow and provide rapid shutoff capabilities makes them vital in maintaining the integrity of marine systems, enhancing safety, and improving operational efficiency.
Case Studies or Scenarios Showcasing Their Importance
- Gas Detection Systems: Ensuring Immediate Response to Leaks
- Scenario: On a modern LNG carrier, gas detection systems equipped with gas solenoid valves are in place to monitor and control gas levels. During a routine voyage, a minor leak is detected in the cargo hold.
- Importance: The gas solenoid valve immediately shuts off the gas supply to the affected area, preventing a potential hazardous situation. This quick response is crucial in averting a fire or explosion, showcasing the valve’s role in enhancing onboard safety.
- LNG Handling: Safe Management of Liquefied Natural Gas
- Scenario: During the loading and unloading of LNG at a port, gas solenoid valves are used to control the flow of gas. A sudden pressure spike is detected in the pipeline.
- Importance: The solenoid valve’s pressure relief feature activates, safely venting the excess pressure and maintaining stable operations. This incident highlights the valve’s critical role in managing LNG safely, preventing equipment damage and ensuring smooth operations.
- Fuel Supply Systems: Efficient Combustion in Marine Engines
- Scenario: On a commercial vessel, gas solenoid valves regulate the flow of gaseous fuels to the marine engines. During a long voyage, the crew notices a fluctuation in engine performance.
- Importance: The crew adjusts the solenoid valves to optimize the fuel-air mixture, restoring efficient combustion and improving engine performance. This scenario demonstrates the valve’s importance in maintaining engine efficiency and reliability.
- Heating Systems: Maintaining Safe and Efficient Operation
- Scenario: A research vessel operates in Arctic conditions, relying on gas-powered heating systems controlled by solenoid valves. A malfunction in the heating system could pose a significant risk to the crew.
- Importance: The solenoid valves ensure a consistent and safe flow of gas to the heaters, maintaining optimal temperatures and ensuring the crew’s safety and comfort. This example underscores the valve’s role in critical onboard systems, particularly in extreme environments.
Critical Marine Applications Include:
Gas Detection Systems
Gas solenoid valves play an integral role in gas detection systems aboard marine vessels. These systems are designed to monitor and control gas levels in real-time, ensuring the immediate shutoff of gas flow in case of leaks. The precise operation of solenoid valves is crucial in preventing potential hazards such as fires, explosions, and toxic gas exposure. By swiftly responding to abnormal gas levels, these valves enhance onboard safety, protecting both the crew and the vessel.
LNG Handling
In the context of liquefied natural gas (LNG) handling, gas solenoid valves are essential for controlling the flow of gas during loading, unloading, and storage operations. These valves ensure the safe handling and distribution of LNG by maintaining precise control over gas flow rates and pressure levels. This control is vital in preventing accidents and ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations. The reliability and precision of solenoid valves make them indispensable in the efficient and safe management of LNG on marine vessels.
Fuel Supply Systems
Gas solenoid valves are critical components in fuel supply systems for marine engines. They regulate the flow of gaseous fuels, ensuring efficient and safe combustion processes. By controlling the fuel supply, solenoid valves help optimize engine performance, reduce emissions, and improve fuel efficiency. Their ability to provide consistent and accurate fuel flow is essential for maintaining the reliability and longevity of marine engines, especially during extended voyages.
Heating Systems
In marine heating systems, gas solenoid valves control the flow of gas to boilers and heaters. These systems are crucial for maintaining safe and efficient operation, particularly in harsh maritime environments. Solenoid valves ensure that the gas supply to heating equipment is precisely regulated, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance. This control is vital for maintaining the comfort and safety of the crew, as well as for protecting the vessel’s heating infrastructure from potential damage.
Choosing the Right Gas Solenoid Valve for Marine Use
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Gas Solenoid Valve for Marine Applications
- Material and Corrosion Resistance
- Marine environments are harsh, with exposure to saltwater, humidity, and varying temperatures. It’s crucial to select gas solenoid valves made from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or marine-grade alloys. These materials ensure long-term durability and reliable performance under challenging conditions.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings
- Assess the pressure and temperature specifications of the valve to ensure they match the operational requirements of your marine application. High-pressure and high-temperature ratings are often necessary for marine engines, LNG handling, and heating systems to withstand the demanding conditions.
- Response Time
- The response time of a gas solenoid valve is critical for applications requiring quick shutoff or precise control. Fast-acting valves are essential in gas detection systems and emergency shutdown scenarios to prevent accidents and ensure safety.
- Seal Material Compatibility
- The compatibility of the valve’s seal material with the type of gas used is crucial. For instance, different gases may require specific seal materials to prevent degradation and ensure a tight seal. Selecting the appropriate seal material enhances the valve’s longevity and performance.
- Certification and Compliance
- Ensure the gas solenoid valve meets industry standards and certifications relevant to marine applications, such as ABS, DNV, or Lloyd’s Register. Compliance with these standards guarantees that the valve adheres to safety and performance criteria essential for marine use.
Tips for Ensuring the Best Fit for Specific Marine Requirements
- Conduct a Thorough Needs Assessment
- Analyze the specific requirements of your marine application, including the type of gas, operating environment, and system demands. This assessment helps in identifying the exact specifications needed for the gas solenoid valve, ensuring optimal performance.
- Consult with Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Engage with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who specialize in marine-grade gas solenoid valves. Their expertise can guide you in selecting the right valve, considering factors such as material compatibility, performance ratings, and certification requirements.
- Consider Customization Options
- In some cases, off-the-shelf solutions may not fully meet your needs. Explore customization options where manufacturers can tailor the gas solenoid valve to your specific requirements. Custom valves can provide better performance, longevity, and safety for unique marine applications.
- Evaluate Maintenance and Serviceability
- Choose gas solenoid valves that are easy to maintain and service. Valves with modular designs and accessible components simplify routine maintenance, reducing downtime and ensuring continuous operation. Consider the availability of spare parts and support services.
- Perform Rigorous Testing
- Before full-scale implementation, conduct rigorous testing of the selected gas solenoid valves in real-world conditions. This step helps verify the valve’s performance, reliability, and compatibility with your marine system, ensuring it meets all operational requirements.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Routine Maintenance Practices for Gas Solenoid Valves in Marine Environments
- Regular Inspection
- Conduct regular visual inspections to check for signs of wear, corrosion, and damage. Inspect the valve body, seals, and connections for leaks or deformities that might indicate potential issues.
- Frequency: Monthly
- Cleaning and Lubrication
- Clean the solenoid valve components to remove salt, debris, and other contaminants that can accumulate in marine environments. Use appropriate cleaning solutions that do not damage the valve materials.
- Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation and prevent wear. Use lubricants compatible with the valve materials and the gas being controlled.
- Frequency: Quarterly
- Seal and Gasket Replacement
- Replace seals and gaskets periodically to prevent leaks and maintain a tight seal. This is especially important in marine environments where salt and humidity can degrade these components faster.
- Frequency: Annually or as needed based on inspection results
- Electrical Connections
- Check the electrical connections to ensure they are secure and free of corrosion. Clean and tighten any loose connections to maintain reliable operation.
- Frequency: Quarterly
- Functional Testing
- Perform functional tests to verify that the solenoid valve operates correctly. This includes checking the response time, ensuring the valve opens and closes properly, and confirming that it holds pressure without leaks.
- Frequency: Semi-annually
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips to Ensure Optimal Performance
- Valve Fails to Open or Close
- Cause: Electrical fault, debris blockage, or damaged solenoid coil.
- Solution: Check the electrical supply and connections. Clean any debris obstructing the valve. Test and replace the solenoid coil if necessary.
- Leaks at Connections
- Cause: Worn seals or gaskets, loose fittings.
- Solution: Replace seals and gaskets as needed. Tighten fittings and connections. Ensure that the materials used are compatible with the marine environment.
- Corrosion on Valve Components
- Cause: Exposure to saltwater and harsh marine conditions.
- Solution: Use corrosion-resistant materials for valve components. Apply protective coatings if necessary. Regularly clean and inspect the valve to prevent corrosion buildup.
- Slow Response Time
- Cause: Build-up of debris, lack of lubrication, or aging components.
- Solution: Clean the valve and ensure all moving parts are properly lubricated. Replace any worn or aging components that may be causing friction.
- Intermittent Operation
- Cause: Electrical issues such as loose connections or damaged wiring.
- Solution: Inspect and secure all electrical connections. Replace any damaged wiring or components. Ensure the power supply is stable and meets the valve’s specifications.
- Pressure Regulation Issues
- Cause: Malfunctioning pressure relief valve, incorrect pressure settings, or blockage.
- Solution: Inspect and test the pressure relief valve. Adjust pressure settings to the recommended levels. Clear any blockages that might be affecting pressure regulation.
FAQ on “Gas Solenoid Valve”
Q: What is a gas solenoid valve?
A: It’s a device that controls gas flow using an electromagnetic solenoid.
Q: Why are gas solenoid valves important in marine applications?
A: They ensure safety and precise control in critical marine systems.
Q: How often should gas solenoid valves be maintained in marine environments?
A: Monthly inspections and annual seal replacements.
Q: What are common issues with gas solenoid valves and their solutions?
A: Issues include electrical faults and leaks, resolved by regular maintenance.
Conclusion
Gas solenoid valves are vital components in the marine industry, playing crucial roles in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of various systems on board. From gas detection and LNG handling to fuel supply and heating systems, these valves provide precise control and rapid response capabilities, significantly enhancing maritime safety and performance. By understanding their working mechanisms, selecting the right valves for specific applications, and adhering to proper maintenance practices, marine engineers can optimize the functionality and reliability of these essential devices. Embracing the advanced features and applications of gas solenoid valves will undoubtedly lead to safer and more efficient marine operations.