Generator Starting Procedure
Starting a generator on a marine vessel or in an industrial setting requires precision and care. Following the correct procedure ensures reliable performance and avoids unexpected issues. In this guide, we’ll outline the 5 essential steps to start your generator safely and efficiently, whether for emergency use or regular operation. From initial inspections to final checks, these steps are designed to keep your generator running smoothly. Whether you’re managing a marine vessel or an industrial site, knowing how to start your generator correctly is crucial. Let’s dive into these steps to ensure trouble-free operation every time.
Preparation of Cooling Water System
1. Check the Cooling Water Tank Level
- Inspect the cooling water tank to ensure it has the appropriate water level.
- If the water level is low, fill the tank with the required coolant mixture to prevent overheating during operation.
2. Prepare the Cooling Water System for Starting
- Ensure all components of the cooling water system are in good condition and ready for operation.
- Verify that hoses, clamps, and connections are secure and free from wear and tear.
3. Change the Position of the Valve from Stop to Operation
- Locate the valve that controls the flow of cooling water.
- Turn the valve from the “stop” position to the “operation” position to allow water to circulate through the system.
4. Stop the System Water Leakages
- Inspect the entire cooling system for any signs of water leaks.
- Tighten any loose connections and replace faulty components to prevent leaks during operation.
5. Check the Cooling Water System for Proper Venting
- Ensure the cooling water system is properly vented to avoid air locks.
- Open any vent valves and allow trapped air to escape, ensuring a steady flow of coolant.
6. Check the Operating Parameters
- Before starting the generator, verify all critical operating parameters such as temperature, pressure, and fluid levels.
- Adjust settings as necessary to match the manufacturer’s specifications and operational requirements.
7. Check the Cleanliness Around the Engine
- Inspect the area around the engine for any debris, oil spills, or other contaminants.
- Clean the surroundings to prevent any potential hazards or obstructions during the generator’s operation.
Starting Air system

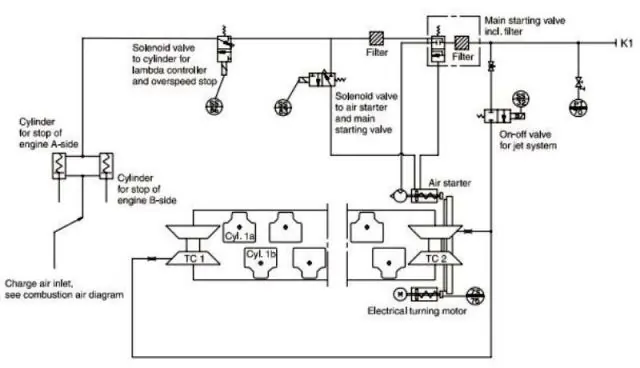
1. Inspect the Starting Air System
- Begin by thoroughly inspecting the entire starting air system. Look for any visible damage, wear, or loose connections.
- Ensure that all components, such as hoses, valves, and fittings, are in good condition and ready for operation.
2. Check the Air Pressure Levels
- Verify that the air pressure in the starting air reservoir is within the specified range.
- Ensure that the pressure is adequate for starting the generator, as insufficient pressure can prevent a successful start.
3. Check the Pressure Reducing Valve (PRV)
- Inspect the Pressure Reducing Valve (PRV) to ensure it is set to the correct pressure for starting the generator.
- Adjust the PRV if necessary to maintain the proper pressure required for the air start system.
4. Drain Moisture from the Air System
- Open the drain valve to release any accumulated moisture from the air system.
- Ensure all moisture is drained to prevent water damage and ensure efficient operation of the air start system.
5. Open the Air Supply Valve
- Locate the main air supply valve for the starting air system.
- Turn the valve to the open position to allow compressed air to flow from the reservoir to the starter motor.
6. Test the Air Start System
- Conduct a test of the air start system by briefly engaging the starter motor without fully starting the engine.
- Listen for any unusual noises and ensure the air flows correctly to the starter motor.
7. Ensure Proper Venting
- Check for proper venting in the air start system to prevent air locks.
- Open any vent valves as needed to release trapped air, ensuring a smooth flow of air to the starter motor.
8. Verify Safety Precautions
- Confirm that all safety precautions are in place before proceeding.
- Ensure that the generator is in a safe condition to start and that all personnel are aware of the starting procedure.
9. Engage the Air Start System
- With all checks complete, engage the air start system by pressing the start button or turning the start switch.
- Monitor the system to ensure the engine begins to turn over and starts as expected.
10. Observe Initial Operation
- Once the engine starts, closely observe its initial operation.
- Check for any abnormal sounds, vibrations, or signs of malfunction, and be prepared to shut down the system if necessary.
11. Close the Air Supply Valve
- After the engine has started successfully, close the main air supply valve to prevent unnecessary air consumption.
- Ensure the starting air system is ready for the next start sequence.
12. Conduct a Final Inspection
- Perform a final inspection of the starting air system and the generator.
- Verify that everything is operating correctly and there are no leaks or issues that need to be addressed.
Pre-heating of the Engine
1. Carry out the Preheating of the engine to protect the engine from abnormal thermal expansions.
2. Ensure the proper circulation of lubricating oil and fuel oil systems
3. Operate a cooling water heating system is installed.
To bring the operating parameters of the engine, it is required to heat the engine by circulation of cooling fluid at least one to two hours.
Make sure that the rotating parts of the Engine are free from obstacles.
Preparation of Fuel System
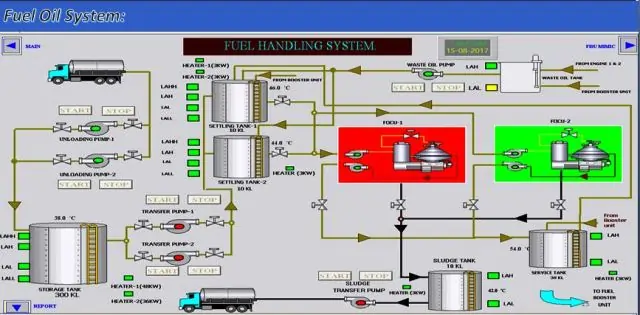
1. Drain the Water from the Fuel System
- Begin by locating the drain valves in the fuel system.
- Open the drain valves to release any accumulated water from the fuel tanks and filters.
- Ensure all water is completely drained to prevent contamination and potential engine issues.
2. Check and Top Up the Fuel Tank
- Inspect the fuel level in the tank to ensure it has sufficient fuel for the operation.
- Top up the fuel tank with the appropriate grade of diesel if the level is low.
- Use clean fuel to avoid introducing impurities into the system.
3. Check the Diesel Cooling System
- Examine the diesel cooling system to ensure it is functioning properly.
- Verify that the coolant levels are adequate and there are no signs of leaks.
- Refill the coolant if necessary and tighten any loose connections.
4. Check the Fuel System if Stopped
- Inspect the entire fuel system to ensure it is in good condition if it has been previously stopped.
- Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or any potential issues that might affect performance.
5. Operate the Fuel System if Stopped
- If the fuel system was previously stopped, operate it to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Turn on the fuel pumps and allow the fuel to circulate through the system.
- Monitor for any irregularities in fuel flow or pressure.
6. Change the Position of Valves from Stop to Operating Position
- Locate the fuel system valves that control the flow of diesel.
- Change the position of these valves from “stop” to “operating” to allow fuel to flow to the engine.
- Ensure the valves are securely positioned to prevent accidental closure.
7. Check for Any Leakage and Correct It
- Inspect the fuel system for any signs of leaks.
- Look at hoses, connections, and fittings for drips or wet spots.
- Tighten connections and replace damaged parts to stop any leaks.
8. Check Air Venting in the System
- Ensure proper air venting in the fuel system to prevent airlocks.
- Open any vent valves and allow trapped air to escape from the system.
- Verify that fuel is flowing smoothly without any air bubbles.
Preparation of Lubricating Oil System
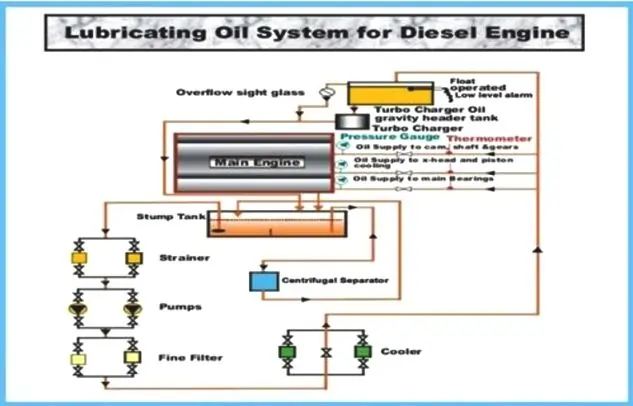
1. Verify the Date of the Last Sample Taken for Quality Check
- Locate the maintenance records to verify the date when the last lubricating oil sample was taken for quality analysis.
- Ensure the oil quality meets the required standards. If the sample date is outdated, consider taking a new sample for testing to ensure the oil is still within acceptable limits.
2. Replace the Oil Filters
- If the engine was recently overhauled or has been idle for an extended period, replace the oil filters to ensure they are clean and functioning properly.
- Remove the old filters and install new ones, making sure they are the correct type and size for your engine.
3. Check Oil Sump Tank Level and Fill if Necessary
- Inspect the oil sump tank to check the current oil level.
- If the oil level is below the recommended level, add the appropriate type and grade of lubricating oil until the correct level is reached.
- Ensure the oil used is compatible with the engine’s specifications.
4. Change the Position of the Valve to Operations
- Locate the valves in the lubricating oil system that control the flow of oil.
- Change the position of these valves from any non-operational state to the “operations” position to allow the flow of oil throughout the system.
5. Inspect the Oil Piping and Connections
- Perform a thorough inspection of the oil piping and connections to ensure there are no leaks or damage.
- Tighten any loose fittings and replace any damaged sections of piping to prevent oil leaks during operation.
6. Check for Proper Venting in the Oil System
- Ensure the lubricating oil system is properly vented to prevent air locks.
- Open any vent valves to allow trapped air to escape, ensuring a smooth flow of oil.
7. Verify Oil Pressure and Temperature Sensors
- Check that all oil pressure and temperature sensors are functioning correctly.
- Ensure that the sensors are calibrated and providing accurate readings to monitor the engine’s performance during operation.
8. Conduct a Preliminary Oil Circulation Test
- Before starting the engine, conduct a preliminary oil circulation test.
- Engage the oil pump manually (if possible) to circulate oil through the system without starting the engine.
- Check for consistent oil flow and proper pressure levels, ensuring there are no obstructions or issues.
Pre-Lubrication of the Engine
1. Heat the Lubricating Oil Temperature to 40⁰C by Heater
- Begin by using the onboard heater to raise the temperature of the lubricating oil to approximately 40⁰C.
- This helps ensure the oil is at an optimal viscosity for effective lubrication.
2. Operate Pre-Lubricating Oil Pump if Stopped
- Engage the pre-lubricating oil pump to start circulating oil through the engine.
- If the pump was previously stopped, ensure it is operating correctly to distribute the oil evenly.
3. Check and Correct Any System Leakage
- Inspect the entire lubricating oil system for any signs of leaks.
- Tighten any loose connections and replace any damaged components to prevent oil leaks during pre-lubrication.
4. Check Oil Pressure Rise and Pre-Lubricating Oil Condition
- Monitor the oil pressure gauge to ensure there is a proper rise in pressure as the oil circulates.
- Observe the condition of the oil, checking for any contaminants or abnormalities that might indicate issues within the system.
5. Pre-Lubricate the Engine for 5 to 10 Minutes Prior to Operation
- Continue to operate the pre-lubricating oil pump for at least 5 to 10 minutes before starting the engine.
- This ensures that all critical components are adequately lubricated, reducing wear and preventing damage during initial startup.
6. Ensure Oil Flows to Critical Points if Engine Has Been Standstill or Overhauled
- If the engine has been idle for a long time or has undergone maintenance, verify that oil is reaching the following critical points:
- Bearings: Ensure that all engine bearings are receiving sufficient oil to prevent dry starts and reduce friction.
- Pump and Valve Operating Rollers: Check that oil is lubricating the pump and valve operating rollers to ensure smooth operation.
7. Remove the Tapes Attached During Maintenance
- If any protective tapes or covers were used during maintenance, remove them to allow unrestricted oil flow.
- Double-check that all maintenance tapes and covers are removed to prevent blockages.
8. Verify Proper Functioning of the Oil Pump and System
- Confirm that the pre-lubricating oil pump and the entire lubricating system are functioning correctly.
- Listen for any unusual noises and check for smooth operation, ensuring that oil is being delivered consistently.
9. Check Oil Filters and Strainers
- Inspect the oil filters and strainers for any clogs or debris.
- Clean or replace them as necessary to maintain proper oil flow and filtration.
10. Ensure Proper Venting of the Lubricating System
- Open any vent valves to release trapped air from the lubricating system.
- Ensure a smooth and continuous flow of oil without air pockets.
Intake Air and Exhaust system

1. Inspect the Air Intake System
- Check Air Filters:
- Inspect air filters for any dirt, debris, or obstructions.
- Clean or replace air filters as necessary to ensure optimal airflow and prevent engine damage.
- Inspect Air Ducts:
- Examine the air intake ducts and hoses for any signs of wear, cracks, or leaks.
- Ensure all connections are secure and free from damage.
2. Verify the Operation of Turbochargers (if applicable)
- Check Turbocharger Condition:
- Inspect the turbocharger for any signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure the turbocharger spins freely and is free from obstructions.
- Check Turbocharger Lube Oil Flow:
- Verify that the turbocharger is receiving adequate lubrication through the pressure lubrication system.
- Check the oil flow to the turbocharger and ensure it is within the specified levels.
- Inspect the oil supply lines and connections for any leaks or blockages to ensure consistent oil delivery.
- Lubricate Turbocharger:
- Ensure that the turbocharger bearings are properly lubricated.
- Check the oil level and pressure in the lubrication system to maintain optimal performance.
3. Inspect the Exhaust System
- Check Exhaust Manifold:
- Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks, leaks, or damage.
- Ensure all bolts and connections are tight and secure.
- Inspect Exhaust Piping:
- Examine the exhaust piping for any signs of corrosion, leaks, or blockages.
- Ensure that the exhaust piping is properly routed and free from obstructions.
- Check Mufflers and Silencers:
- Inspect mufflers and silencers for any signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure they are securely mounted and functioning correctly to reduce noise levels.
- Check Exhaust Dampers:
- Inspect the exhaust damper to ensure it is properly positioned and functioning.
- Verify whether the exhaust is routed directly from the engine or through a waste heat recovery boiler.
- Adjust the damper as needed to ensure the correct exhaust flow path.
4. Check and Clean Air Intake and Exhaust Vents
- Air Intake Vents:
- Ensure that air intake vents are clear of any obstructions.
- Clean the vents to allow unrestricted airflow into the engine.
- Exhaust Vents:
- Verify that exhaust vents are free from blockages.
- Clean the vents to ensure efficient expulsion of exhaust gases.
5. Inspect and Test the Intercooler (if applicable)
- Check Intercooler Condition:
- Inspect the intercooler for any signs of damage, leaks, or blockages.
- Clean the intercooler to ensure optimal cooling of the intake air.
- Test Intercooler Function:
- Verify that the intercooler is functioning correctly and effectively reducing the temperature of the intake air.
6. Ensure Proper Operation of the Air Intake Preheaters (if applicable)
- Inspect Preheaters:
- Check the condition of the air intake preheaters and ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Verify that the preheaters are heating the intake air to the required temperature.
- Test Preheater Operation:
- Operate the preheaters to ensure they are working as intended, especially in cold weather conditions.
7. Verify the Integrity of Gaskets and Seals
- Inspect Gaskets and Seals:
- Check all gaskets and seals in the air intake and exhaust systems for any signs of wear or damage.
- Replace any faulty gaskets or seals to prevent air or exhaust leaks.
Other Important Checks in Generator Starting Procedure
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Open the Indicator Valves | Begin by opening the indicator valves on each cylinder. This allows you to check for any escaping fluids and lubricate the cylinder liners. |
| Lubricate the Dry Surface of Liners | Pour Oil Through Indicator Cocks: Pour approximately 50 CC of lubricating oil through each indicator cock. Spray Oil Under the Piston: Use a suitable tool to spray oil under the piston. This ensures that the dry surfaces of the liners are adequately lubricated. Turn the Engine: Manually turn the engine a few revolutions to distribute the oil evenly across the liners and pistons. |
| Rotate the Engine with a Shaft-Barring Arrangement | Setup: Engage the shaft-barring arrangement to rotate the engine. Initial Rotations: Rotate the engine for a few revolutions to check the smoothness and freshness of the moving parts. Ensure that all components are moving freely without any abnormal resistance or noise. Check for Trapped Fluids: Continue turning the engine to ensure no fluids are trapped in the combustion chambers. This step is critical to prevent hydraulic locks, which can cause severe engine damage. |
| Observe for Escaping Fluids | Check Indicator Cocks: If you notice any fluid escaping through the indicator cocks, it is a sign of potential issues. Wrap the Indicator Cock: Wrap the indicator cock to prevent fluid from spraying out uncontrollably. Clean Up: Use waste cloth to clean any scattered fluid around the indicator cocks to maintain a clean working area. |
| Rotate the Crankshaft for Further Observation | Crankshaft Rotation: Rotate the crankshaft by 2 to 3 complete revolutions. Check for Emerging Fluids: Observe each cylinder for any fluid emerging during these rotations. If fluid is observed, identify the source and take corrective action before starting the engine. |
Disengaging from Turning Gear
1. Ensure the Turning Gear is in the Correct Position
- Check the position of the turning gear and ensure it is in a safe and neutral position to disengage.
- Verify that the turning gear is not engaged with the crankshaft to avoid any mechanical damage.
2. Disengage the Turning Gear
- Follow the specific procedure for your engine model to disengage the turning gear.
- Typically, this involves manually or automatically moving the turning gear away from the crankshaft.
- Ensure the turning gear is fully retracted and secured in its disengaged position.
3. Verify the Turning Gear is Fully Disengaged
- Physically inspect the turning gear to confirm that it is fully disengaged and not in contact with the crankshaft.
- Check any indicators or gauges that confirm the turning gear’s position to ensure it is safely retracted.
4. Secure the Turning Gear
- Lock the turning gear in its disengaged position if applicable.
- Ensure that all securing mechanisms are properly engaged to prevent accidental re-engagement during engine startup.
5. Final Safety Check
- Conduct a final safety check around the engine to ensure there are no tools, equipment, or personnel in unsafe positions.
- Verify that all guards and covers are in place and secured.
6. Notify Control Room
- Inform the control room or relevant supervisory personnel that the turning gear has been disengaged and the engine is ready for startup.
- Confirm that all safety protocols have been followed and the engine is clear to start.
7. Record the Procedure
- Document the disengagement of the turning gear in the engine logbook.
- Include details such as the time, personnel involved, and any observations or issues encountered during the procedure.
Fuel regulating System preparedness
1. Check the Regulating Rod
- Inspect for Smooth and Free Movement:
- Ensure the regulating rod moves smoothly and freely from the governor to all the fuel racks of the high-pressure fuel injection pumps.
- Any resistance or sticking should be addressed to ensure proper operation during startup.
2. Check and Reset the Operation of the Emergency Stop Button
- Operate the Emergency Stop Button:
- With the fuel control rod in the maximum position, activate the emergency stop button.
- Observe Fuel Rack Movement:
- During this operation, ensure all the fuel racks move to the maximum zero position.
- This check is crucial to confirm that the engine can be stopped in the event of an abnormality.
3. Check the Flexibility of Each Fuel Injection Pump Rack
- Manual Movement:
- Manually pull each fuel rack from one position to the other to check its flexibility.
- Return to Original Position:
- Ensure each fuel rack returns to its original position smoothly without sticking or resistance.
4. Check the Mechanical Fuel Limiter for Overload
- Set to 110% Load:
- Verify that the mechanical fuel limiter is set correctly to 110% load.
- Importance:
- This setting is critical to prevent engine overload and potential damage.
5. NOTICE: Correct Setting of Mechanical Fuel Limiter
- Potential Damage:
- If the mechanical fuel limiter is not set correctly, the engine may be seriously damaged.
- Importance of Accurate Setting:
- Ensure precise adjustments to avoid operational issues.
6. Set the Mechanical Fuel Limiter on Governor
- Initial Load Limit Setting:
- Set the mechanical fuel limiter on the governor to a load limit of 30-50%.
- Adjustment for Safe Operation:
- This initial setting allows for safe startup and operation, preventing excessive load during the initial running period.
FAQs on Generator Starting Procedure
Q: What is the first step in starting a generator?
A: Check fuel and oil levels.
Q: Why is pre-lubrication important?
A: It prevents engine damage.
Q: How do you ensure proper air intake?
A: Clean air filters and vents.
Q: What to do if fluid escapes from indicator valves?
A: Wrap the cock, clean, and identify the source.
Conclusion
Properly starting a generator involves a series of meticulous steps to ensure safety and efficiency. By following the outlined procedures for checking fuel levels, lubricating the engine, inspecting air intake and exhaust systems, and ensuring smooth operation of the fuel regulating system, you can prevent potential issues and extend the lifespan of your generator. Regular maintenance and adherence to these guidelines are crucial for reliable performance, especially in critical situations. Stay diligent with your pre-start checks, and your generator will be ready to provide power whenever you need it.
