GFCI Outlets
Did you know that electrical accidents in homes cause thousands of injuries worldwide each year? GFCI outlets, or Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters, are critical devices designed to protect against these electrical hazards. By detecting imbalances in electrical currents and shutting off power immediately, GFCI outlets can prevent serious injuries and even save lives. In this post, we’ll explore the seven essential safety features of GFCI outlets, highlighting their importance and how they enhance electrical safety in your home.
Instantaneous Ground Fault Detection
Explanation
GFCI outlets are designed to detect ground faults, which occur when the electrical current strays outside its intended path, such as through water or a person. This feature is crucial because ground faults can lead to electric shocks or even fatal injuries. GFCI outlets protect by quickly identifying these faults and cutting off the power supply, thereby preventing harm.
Mechanism
The internal workings of a GFCI outlet involve a sophisticated detection system. Inside the outlet are sensing coils that monitor the current flowing through the hot (live) and neutral wires. These coils constantly compare the amount of current entering and exiting the outlet. Under normal circumstances, the current should be balanced. However, if there is any discrepancy, even as small as 4-5 milliamps, the GFCI outlet detects this imbalance. This imbalance indicates that current is leaking somewhere, potentially through a human body, causing a ground fault. When such a fault is detected, the GFCI outlet’s internal circuit trips, cutting off the electrical supply almost instantaneously—typically within 1/40th of a second.
Example Scenario
Consider a scenario in a household kitchen where a person accidentally drops a hairdryer into a sink full of water. Without a GFCI outlet, the electrical current from the hairdryer could flow through the water, creating a serious risk of electric shock to anyone who touches the water. However, with a GFCI outlet installed, the outlet detects the imbalance in the current flow as soon as the hairdryer hits the water. It immediately trips the circuit, cutting off the power supply and preventing the electrical current from causing any harm. This quick action significantly reduces the risk of injury or even death, demonstrating the vital role of ground fault detection in enhancing home safety.
Detailed Working of Key Components
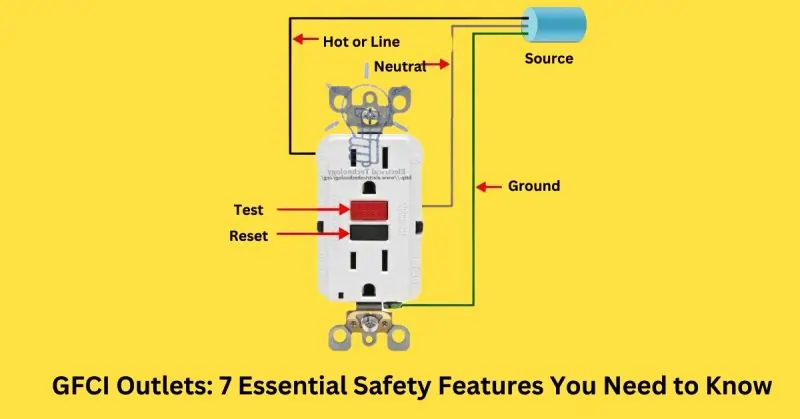
Hot or Line
- Function: The hot or line wire carries the electrical current to the outlet, supplying power to connected devices.
- Connection: This wire is connected to the brass terminal of the GFCI outlet. Properly securing the hot wire to this terminal ensures that the current flows correctly through the outlet.
- Safety Note: Ensuring a secure connection of the hot wire is crucial to prevent electrical hazards such as short circuits or overheating. Loose connections can lead to arcing, which may cause fires or electrical shocks.
Source
- Function: The source provides the electrical power to the GFCI outlet, ensuring it can deliver electricity to connected devices.
- Connection: The source connects to both the line and neutral terminals. The line (hot) wire connects to the brass terminal, while the neutral wire connects to the silver terminal.
- Importance: A reliable power source is essential for the effective operation of a GFCI outlet. Consistent power ensures that the outlet can properly monitor and detect any ground faults, maintaining safety.
Neutral
- Function: The neutral wire completes the electrical circuit by carrying the current back to the power source, ensuring a continuous flow of electricity.
- Connection: The neutral wire is connected to the silver terminal of the GFCI outlet.
- Role in Safety: The neutral wire helps maintain the current balance that the GFCI outlet monitors. Any imbalance between the hot and neutral wires signals a potential ground fault, prompting the GFCI to trip and cut off the power.
Ground
- Function: The ground wire provides a path to ground for any fault current, enhancing the overall safety of the electrical system.
- Connection: The ground wire connects to the green terminal of the GFCI outlet.
- Importance: Grounding is critical in preventing electrical shocks. In the event of a fault, the ground wire directs the stray current away from users and toward the ground, reducing the risk of injury or fire.
Test
- Function: The test button allows users to simulate a fault condition to ensure the GFCI outlet is functioning correctly.
- Operation: To use the test button, press it to create a small imbalance in the current flow, which should trip the outlet and cut off power. This verifies that the GFCI outlet can detect faults and respond appropriately.
- Frequency: It is recommended to test the GFCI outlet at least once a month to ensure it remains in proper working condition. Regular testing helps maintain safety by ensuring the outlet will respond correctly in a real fault situation.
Reset
- Function: The reset button restores power to the outlet after it has tripped due to a detected fault.
- Operation: After the GFCI outlet trips, inspect the area for any potential hazards or reasons for the trip. Once resolved, press the reset button to restore power to the outlet.
- Importance: The reset button is essential for maintaining the functionality of the outlet. It allows users to safely restore power after addressing any detected faults, ensuring continuous protection and operation.
Quick Response Time
Feature Breakdown
GFCI outlets are renowned for their rapid response time when detecting electrical faults. These devices are engineered to monitor the current flow through the hot and neutral wires continuously. The moment an imbalance is detected, indicating a potential ground fault, the GFCI outlet trips and cuts off the power supply almost instantaneously. This swift action is crucial in preventing electrical shocks and other hazards.
Importance
The quick response time of GFCI outlets is critical in preventing serious injuries or even fatalities. Electrical faults can occur suddenly and without warning, often within environments where water is present, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor areas. The human body’s reaction to an electric shock can be immediate, leading to involuntary muscle contractions, severe injuries, or drowning if the person is in water. By tripping the circuit almost instantaneously, GFCI outlets minimize the duration of exposure to the electric current, significantly reducing the risk of severe harm.
Technical Insight
GFCI outlets are designed to trip within an incredibly short timeframe, typically within 1/40th of a second (approximately 25 milliseconds). This rapid response is made possible by the outlet’s internal circuitry, which continuously monitors the current balance between the hot and neutral wires. Any deviation from the expected current flow triggers the GFCI to cut off power immediately. The sensitivity of GFCI outlets is also noteworthy; they can detect current imbalances as small as 4-5 milliamps, a level that is sufficient to cause a potentially dangerous electric shock but not enough to trip conventional circuit breakers. This high sensitivity, combined with the rapid response time, makes GFCI outlets exceptionally effective at preventing electrical injuries.
Manual Test and Reset Buttons
Description
The manual test and reset buttons on a GFCI outlet are essential features that ensure the outlet is functioning correctly and providing continuous protection against electrical hazards. The test button allows users to simulate a ground fault, verifying that the GFCI mechanism trips and cuts off power as it should. The reset button restores power to the outlet after it has tripped, ensuring that the outlet is ready to function again once any issues have been addressed.
Usage Instructions
Using the Test Button:
- Locate the Test Button: On the face of the GFCI outlet, find the test button, usually marked “Test.”
- Press the Test Button: Press the test button firmly. This action simulates a ground fault by creating a small current imbalance.
- Observe the Reaction: The outlet should trip immediately, cutting off power to the connected devices. You may hear a clicking sound, and the indicator light (if present) will turn off.
- Verify Power Cutoff: Check the connected device or use a voltage tester to ensure the outlet is no longer providing power.
Using the Reset Button:
- Inspect for Issues: Before resetting, ensure there is no ongoing electrical hazard or fault in the area.
- Locate the Reset Button: The reset button is typically located near the test button and is marked “Reset.”
- Press the Reset Button: Press the reset button firmly until you hear a click. This action restores power to the outlet.
- Confirm Power Restoration: Check that power has been restored by testing the connected device or using a voltage tester.
Wide Range of Applications
Indoor and Outdoor Use
GFCI outlets are essential in various locations to ensure safety in environments where electrical hazards are more likely to occur. Here are the key areas where GFCI outlets are particularly important:
- Bathrooms: The presence of water and electrical appliances makes bathrooms high-risk areas for electric shock. GFCI outlets are required near sinks, bathtubs, and showers.
- Kitchens: With multiple appliances and potential for water spills, GFCI outlets should be installed near countertops, sinks, and kitchen islands.
- Garages: Tools and equipment in garages can pose electrical risks, especially in damp or wet conditions. GFCI outlets protect users from potential shocks.
- Basements and Crawlspaces: These areas are prone to moisture, increasing the risk of electrical hazards. Installing GFCI outlets provides an additional layer of safety.
- Outdoor Areas: GFCI outlets are necessary for any outdoor receptacles, including those near pools, hot tubs, and garden areas, where exposure to the elements and water is common.
- Laundry Rooms: Near washing machines and utility sinks, GFCI outlets help prevent shocks in areas where water and electricity meet.
- Wet Bars: In-home bars where drinks are prepared and spills are likely, GFCI outlets are critical for safety.
Regulatory Requirements
The National Electrical Code (NEC) mandates the installation of GFCI outlets in specific locations to enhance safety. Key requirements include:
- Bathrooms: All receptacles must be GFCI-protected.
- Kitchens: GFCI outlets are required for all countertop receptacles.
- Garages: All outlets must be GFCI-protected.
- Outdoor Areas: All outdoor receptacles must be GFCI-protected.
- Basements and Crawlspaces: GFCI protection is required for all outlets.
- Laundry Areas: Outlets within six feet of a sink must have GFCI protection.
- Wet Bars: Outlets within six feet of the bar sink must have GFCI protection.
These regulations ensure that GFCI outlets are installed in areas with high risk of electrical shock, providing a standardized level of safety.
Installation Guide
Installing a GFCI outlet is straightforward, but it requires caution and attention to detail to ensure safety and compliance with electrical codes. Here is a basic overview of the installation process:
- Turn Off Power: Locate the circuit breaker that controls the outlet you are replacing and turn it off. Use a voltage tester to ensure the power is off before proceeding.
- Remove the Old Outlet: Unscrew the faceplate and the existing outlet from the electrical box. Carefully disconnect the wires from the old outlet.
- Identify the Wires: Identify the line (hot) and neutral wires. The line wires supply power from the breaker panel, while the load wires supply power to additional outlets downstream.
- Connect the Wires to the GFCI Outlet:
- Attach the line (hot) wire to the brass terminal marked “Line.”
- Connect the neutral wire to the silver terminal marked “Line.”
- If there are load wires, connect the hot load wire to the brass terminal marked “Load” and the neutral load wire to the silver terminal marked “Load.”
- Attach the ground wire to the green terminal.
- Secure the Outlet: Carefully push the wires back into the electrical box and secure the GFCI outlet with screws.
- Attach the Faceplate: Screw on the faceplate, ensuring it fits snugly and securely.
- Turn On Power: Turn the circuit breaker back on and test the GFCI outlet by pressing the “Test” button. The outlet should trip, cutting off power. Press the “Reset” button to restore power.
Enhanced Fire Prevention
Risk Reduction
GFCI outlets play a critical role in reducing the risk of electrical fires by quickly detecting ground faults and shutting off the power supply. Electrical fires often start when faulty wiring or damaged electrical devices cause unintended currents to flow to ground, potentially igniting surrounding materials. GFCI outlets prevent this by monitoring the current balance between the hot and neutral wires. When an imbalance is detected, indicating a ground fault, the GFCI outlet trips and cuts off the power almost instantly, preventing the fault from escalating into an electrical fire.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Kitchen Safety In a residential kitchen, a homeowner plugged in an old toaster that had a frayed cord. As the toaster was used, the frayed cord caused a ground fault. The GFCI outlet detected the fault and immediately shut off the power, preventing the frayed cord from overheating and starting a fire. The quick response of the GFCI outlet likely prevented a serious kitchen fire, protecting the home and its occupants.
Case Study 2: Outdoor Holiday Lights During the holiday season, a homeowner set up decorative lights in the garden. Unknown to them, one of the light strands had a damaged section that was exposed to moisture. When it rained, the water caused a ground fault. The GFCI outlet tripped as soon as the fault was detected, cutting off power to the lights. This action prevented the damaged lights from causing an electrical fire in the wet conditions, ensuring the safety of the outdoor decorations.
Comparative Analysis
GFCI Outlets vs. Standard Outlets
| Feature | GFCI Outlets | Standard Outlets |
|---|---|---|
| Ground Fault Detection | Yes, detects ground faults and shuts off power within milliseconds. | No, does not detect ground faults. |
| Fire Prevention | High, significantly reduces risk by cutting off power during faults. | Low, higher risk of faults leading to fires. |
| User Safety | High, protects against electrical shocks and fires. | Moderate, only protects against circuit overloads. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Required in high-risk areas (bathrooms, kitchens, etc.) per electrical codes. | Not required to detect ground faults, only to handle current loads. |
| Response Time | Extremely fast, typically within 1/40th of a second. | No response to ground faults, only to overcurrent situations. |
User-Friendly Features
Accessibility
GFCI outlets are designed with user accessibility in mind, making them easy to use and maintain. One of the most user-friendly aspects is the straightforward testing and resetting process, which can be done with the push of a button. The “Test” and “Reset” buttons are clearly labeled and accessible, allowing users to ensure the outlet is functioning correctly without needing specialized tools or knowledge. Additionally, the outlets are compatible with standard electrical systems, meaning they can be installed in place of regular outlets without requiring significant modifications to existing wiring.
Design Elements
GFCI outlets incorporate several design features that enhance their usability:
- LED Indicators: Many GFCI outlets come equipped with LED indicators that provide visual confirmation of the outlet’s status. A green light typically indicates normal operation, while a red light or absence of light can signal a trip or fault condition. This immediate visual feedback helps users quickly identify and address issues.
- Clear Labeling: The “Test” and “Reset” buttons are prominently labeled and color-coded, usually with contrasting colors to ensure they stand out. This design makes it easy for users to understand the functions and operate the outlet correctly.
- Tamper-Resistant Shutters: Some GFCI outlets include tamper-resistant shutters that prevent the insertion of foreign objects into the outlet slots, enhancing safety, especially in homes with children.
- Weather-Resistant Models: For outdoor use, weather-resistant GFCI outlets are available. These models are designed to withstand exposure to moisture and extreme temperatures, providing reliable protection in harsh environments.
FAQ on “GFCI Outlets”
Q: What does a GFCI outlet do?
A: It protects against electrical shocks by cutting power during faults.
Q: Where should GFCI outlets be installed?
A: In bathrooms, kitchens, garages, and outdoor areas.
Q: How often should I test my GFCI outlet?
A: Test monthly with the built-in button.
Q: What happens if my GFCI outlet keeps tripping?
A: Frequent trips indicate a fault; consult an electrician.
Conclusion
Incorporating GFCI outlets into your home or workplace is a crucial step towards enhancing electrical safety. These outlets provide vital protection by detecting ground faults, reducing the risk of electrical fires, and preventing serious injuries from electric shocks. From their rapid response time and user-friendly features to compliance with modern safety standards, GFCI outlets are essential in safeguarding your environment. By understanding and utilizing the seven essential safety features discussed, you can ensure a safer, more secure space for you and your loved ones. Don’t wait—upgrade to GFCI outlets today and experience the peace of mind that comes with superior electrical protection.
