Marine engines are the heart of any vessel, and their smooth operation is paramount for safety, efficiency, and longevity. However, these powerful machines are constantly subjected to immense forces, leading to vibrations that, if left unchecked, can cause significant damage and costly downtime. Understanding how to measure vibrations in marine engines is not just a best practice; it’s a critical component of modern predictive maintenance strategies. This blog post delves into the latest techniques for vibration measurement and how advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence are transforming the prediction and interpretation of these vital readings.
The Critical Importance of Marine Engine Vibration Monitoring

Vibration monitoring in marine engines is far more than just a diagnostic tool; it’s a proactive approach to maintaining the health and operational integrity of a vessel’s propulsion system. Excessive or unusual vibrations can be early indicators of underlying issues such as bearing wear, shaft misalignment, propeller imbalance, or even structural fatigue. Ignoring these signs can lead to catastrophic failures, resulting in expensive repairs, extended downtime, and potential safety hazards at sea. By continuously monitoring vibration levels, marine operators can:
•Detect Faults Early: Identify developing problems before they escalate into major failures.
•Optimize Maintenance Schedules: Transition from reactive or time-based maintenance to condition-based maintenance, reducing unnecessary interventions and maximizing operational uptime.
•Extend Equipment Lifespan: Address issues promptly, preventing further damage and prolonging the life of critical components.
•Enhance Safety: Mitigate risks associated with unexpected machinery breakdowns.
•Improve Fuel Efficiency: Ensure optimal engine performance, which can directly impact fuel consumption.
In essence, effective vibration monitoring translates directly into improved reliability, reduced operational costs, and enhanced safety for marine vessels of all types.
Understanding the Different Types of Marine Engine Vibrations
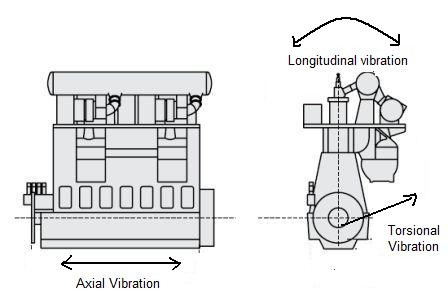
To effectively measure and interpret marine engine vibrations, it’s crucial to understand the different types that can occur. Each type provides unique insights into the engine’s operational health and potential issues:
•Longitudinal Vibration: This refers to vibrations that occur along the length of the engine or shafting system. It is often associated with issues like thrust bearing wear or problems with the coupling between the engine and the propeller shaft. [7]
•Axial Vibration: Axial vibrations are those that occur along the axis of rotation. These can be caused by imbalances in rotating components or issues with the alignment of the shaft. [7]
•Torsional Vibration: Perhaps one of the most critical and complex types, torsional vibration involves rotational oscillations around the axis of rotation. This type of vibration is particularly dangerous as it can lead to fatigue failures in crankshafts, propeller shafts, and gearing. Sources of torsional vibration include engine firing impulses, propeller forces, and resonant frequencies within the propulsion system. [7]
Understanding these distinct vibration modes is fundamental for accurate diagnosis and effective mitigation strategies. Modern measurement techniques are designed to capture and differentiate these various types of vibrations, providing a holistic view of the engine’s dynamic behavior.
Modern Techniques for Measuring Marine Engine Vibrations
The evolution of technology has brought forth sophisticated tools and methodologies for accurately measuring marine engine vibrations. These techniques go beyond simple visual inspections, providing precise data for in-depth analysis:
1. Advanced Sensor Technology

At the forefront of modern vibration measurement are advanced sensors designed for the harsh marine environment. These include:
•Accelerometers: These are the most common type of vibration sensor, measuring acceleration, which can then be integrated to determine velocity and displacement. They are typically mounted directly onto engine components, bearings, and structural elements. [4]
•Proximity Probes: Used to measure the displacement of rotating shafts relative to their bearings, providing critical data for identifying shaft runout, unbalance, and misalignment. [5]
•Magnetic Vibration Sensors: These non-contact sensors offer advantages in certain applications, providing accurate data without direct physical contact, which can be beneficial for monitoring components in challenging locations. [6]
•In-Cylinder Gas Pressure Sensors: While not directly vibration sensors, integrating data from these sensors with vibration data can provide a more comprehensive diagnostic picture, especially for combustion-related issues that manifest as vibrations. [1]
2. Data Acquisition Systems

Modern vibration measurement relies on robust data acquisition systems that can handle high-frequency data streams from multiple sensors simultaneously. These systems are capable of:
•Real-time Monitoring: Providing immediate feedback on engine health, allowing operators to react quickly to anomalies. [10]
•High Sampling Rates: Capturing the nuances of complex vibration patterns, including transient events.
•Wireless Connectivity: Enabling easier installation and data transmission, reducing the need for extensive cabling in confined engine rooms. [12]
3. Advanced Analysis Methods
Raw vibration data is only useful if it can be effectively analyzed and interpreted. Modern techniques employ sophisticated algorithms and software for:
•Frequency Analysis (FFT – Fast Fourier Transform): This is a cornerstone of vibration analysis, transforming time-domain signals into the frequency domain. This allows for the identification of specific frequencies associated with different engine components (e.g., shaft speeds, gear mesh frequencies, blade pass frequencies), making it easier to pinpoint the source of a vibration. [8]
•Time Waveform Analysis: Examining the raw vibration signal in the time domain can reveal impacts, looseness, and other non-linear behaviors that might be missed in frequency analysis alone.
•Orbital Analysis: For rotating machinery, orbital plots (plotting shaft displacement in X and Y directions) can provide insights into shaft centerline movement, preloads, and oil whirl/whip phenomena.
•Phase Analysis: Comparing the phase of vibration signals from different locations can help determine the type of unbalance or misalignment present.
•Torsional Vibration Analysis (TVA): Dedicated systems and software are used to measure and analyze torsional vibrations, often involving specialized encoders or laser vibrometers. Data-driven TVA is becoming increasingly important for real-time monitoring and pattern identification. [6]
These advanced techniques, when combined, provide a powerful toolkit for understanding the complex vibrational behavior of marine engines, moving beyond simple detection to precise diagnosis and prediction.
Predicting Vibration Readings: The Power of AI and Data Analytics
The true revolution in marine engine vibration monitoring lies in the ability to not just measure, but to predict. This is where the synergy of artificial intelligence (AI) and comprehensive data analytics comes into play, transforming reactive maintenance into proactive, predictive strategies.
1. Data-Driven Models for Predictive Insights
Modern marine engines are equipped with an array of sensors that continuously generate vast amounts of operational data, including vibration data. This rich dataset forms the foundation for building sophisticated data-driven models. These models, often based on machine learning algorithms, can learn the normal operating patterns of an engine and identify deviations that indicate impending issues. By analyzing historical data, these models can:
•Establish Baselines: Define what constitutes ‘normal’ vibration behavior under various operating conditions (e.g., different RPMs, loads, temperatures).
•Identify Anomalies: Flag unusual vibration patterns that fall outside the established baselines, even subtle ones that might be missed by human inspection or simpler threshold-based alarms. [9]
•Forecast Degradation: Predict the rate of wear or degradation of components based on trending vibration data, allowing for scheduled maintenance before failure occurs. [10]
2. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML algorithms are at the heart of advanced vibration prediction. They enable systems to learn from complex, multi-dimensional data and make intelligent inferences:
•Supervised Learning: Algorithms trained on labeled datasets (e.g., ‘normal operation’ vs. ‘bearing fault’) can classify new, unseen vibration patterns into known fault categories. This helps in automating the diagnostic process.
•Unsupervised Learning: Clustering algorithms can identify previously unknown patterns or anomalies in vibration data, potentially uncovering novel failure modes or operational inefficiencies.
•Deep Learning: Neural networks, particularly recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), are increasingly used for analyzing time-series vibration data. They excel at recognizing intricate patterns and dependencies that might be too complex for traditional methods. [11]
•Predictive Analytics: AI-powered systems can analyze real-time vibration data alongside other operational parameters (e.g., engine speed, fuel consumption, exhaust gas temperature) to predict remaining useful life (RUL) of components, enabling highly optimized maintenance scheduling. [12]
While the potential of AI in marine engine monitoring is immense, it’s important to note that some experts advocate for a balanced approach, emphasizing that AI should augment, rather than entirely replace, human expertise and traditional condition monitoring techniques. [13]
3. Comprehensive Data Analytics Platforms
Beyond individual algorithms, integrated data analytics platforms are crucial for harnessing the full power of vibration data. These platforms provide:
•Data Visualization: Intuitive dashboards and graphical representations of vibration trends, frequency spectra, and alarm states, making complex data accessible to operators and engineers.
•Trend Analysis: The ability to track changes in vibration levels over time, identifying gradual degradation or sudden shifts that indicate a problem. This is particularly effective for monitoring overall operating conditions and propeller performance. [14]
•Correlation with Other Parameters: Analyzing vibration data in conjunction with other engine parameters (e.g., load, RPM, pressure) to understand how operational conditions influence vibration and to differentiate between normal operational variations and actual faults. [15]
•Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics: Cloud-based platforms allow for vibration data to be transmitted from vessels at sea to onshore analysis centers, enabling expert diagnosis and support regardless of location. [16]
By leveraging these advanced techniques, marine operators can move towards a truly predictive maintenance paradigm, minimizing unexpected breakdowns, optimizing operational efficiency, and ensuring the long-term reliability of their marine engines.
Conclusion: Navigating Towards a Future of Predictive Reliability
How to measure vibrations in marine engines has evolved from a simple diagnostic task into a sophisticated science, driven by advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and artificial intelligence. The ability to accurately measure, analyze, and predict vibration readings is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern marine operations. By embracing these cutting-edge techniques, the maritime industry can achieve unprecedented levels of operational efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Predictive maintenance, powered by intelligent vibration monitoring, ensures that marine engines – the very heart of our vessels – continue to beat strong, propelling us towards a future of uninterrupted and reliable voyages.
You may love to read our amazing post on : Vibration In Engine: 5 Best Tips to End Marine Engine Vibration
References
[1] R Varbanets, O Shumylo, A Marchenko… – Polish Maritime …, 2022 – sciendo.com. Concept of vibroacoustic diagnostics of the fuel injection and electronic cylinder lubrication systems of marine diesel engines. Available at: https://sciendo.com/pdf/10.2478/pomr-2022-0046
[2] Vibromera.eu. Vibration Diagnostics of Marine Equipment. Available at: https://vibromera.eu/content/technical-diagnostics-vibration-monitoring-marine-equipment/
[3] ScienceDirect. Review of noise and vibration reduction technologies in marine …. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S014111872400316X
[4] Dieselservicesofamerica.com. Diesel Engine Vibration Analysis: Top 3 Expert Tips 2025. Available at: https://www.dieselservicesofamerica.com/vibration-nation-understanding-diesel-engine-diagnostics/
[5] Marineinsight.com. Understanding Vibrations in Marine Engines. Available at: https://www.marineinsight.com/main-engine/understanding-vibrations-in-marine-propulsion-engines/
[6] MAN-ES.com. Synchrophasing. Available at: https://www.man-es.com/docs/default-source/marine/tools/synchrophasing.pdf
[7] Marineinsight.com. Understanding Vibrations in Marine Engines. Available at: https://www.marineinsight.com/main-engine/understanding-vibrations-in-marine-propulsion-engines/
[8] Binsfeld.com. A Beginner’s Guide to Torsional Vibration Analysis & Testing. Available at: https://binsfeld.com/torsional-vibration-analysis-guide/
[9] Maintwiz.com. The Future of Vibration Analysis: Transforming Equipment …. Available at: https://www.maintwiz.com/blog/future-vibration-analysis-transforming-equipment-maintenance/
[10] Iconresearch.co.uk. The Future of Machinery Health: Vibration Monitoring and Industry …. Available at: https://iconresearch.co.uk/the-future-of-machinery-health-vibration-monitoring-and-industry-trends/?srsltid=AfmBOorVU81sVlfsCQVrGNMmOGQE-1w4prTOwSjAUiLNm2mYayGCo8rd
[11] MDPI.com. Application of Machine Learning to Classify the Technical Condition of Marine Engine Injectors Based on Experimental Vibration Displacement Parameters. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/16/19/6898
[12] Solutelabs.com. AI is Changing the Marine Industry – Solute Labs. Available at: https://www.solutelabs.com/blog/ai-and-marine-industry
[13] Shipmanagementinternational.com. AI not ready for engine monitoring and diagnostics, says CMT. Available at: https://www.shipmanagementinternational.com/news/ai-not-ready-for-engine-monitoring-and-diagnostics-says-cmt
[14] Amesolutions.com. Condition Monitoring & Vibration Analysis Increases Efficiency and Performance of Yacht Propellers. Available at: https://www.amesolutions.com/blog/condition-monitoring-vibration-analysis-increases-efficiency-and-performance-of-yacht-propellers/15089
[15] E-learning.info-marine.com. trend analysis – Info Marine. Available at: https://e-learning.info-marine.com/article-list/trend-analysis
[16] Marinelog.com. Vibration sensor data can help prevent major equipment problems …. Available at: https://www.marinelog.com/news/vibration-sensor-data-can-help-prevent-major-equipment-problems-at-sea/
