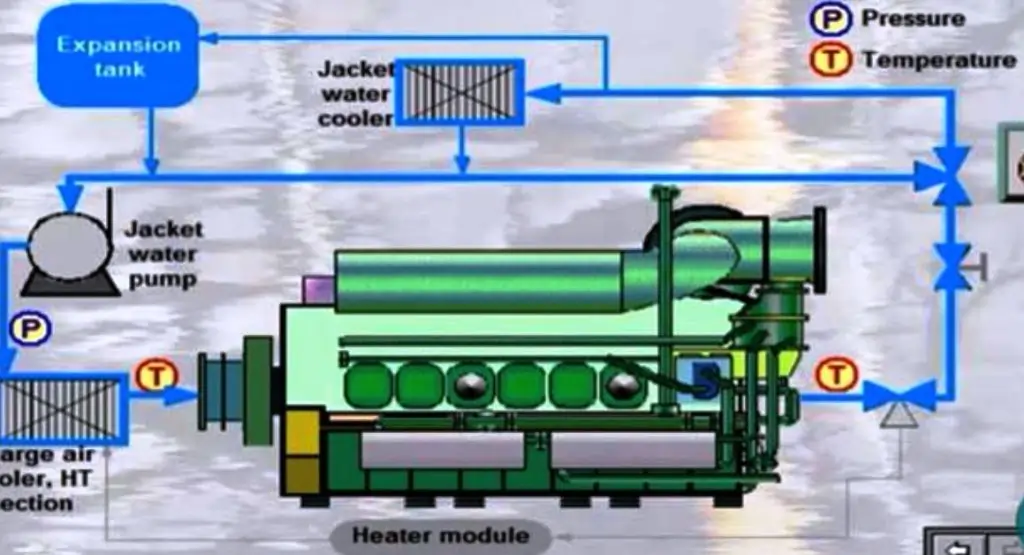
Jacket Cooling Water Test
The jacket cooling water system plays a critical role in maintaining optimal engine temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring smooth operations. This system circulates coolant around the engine block, absorbing excess heat and keeping components at a safe operating temperature. The quality of jacket cooling water directly impacts engine performance, as contaminated or unbalanced coolant can lead to corrosion, scaling, or reduced heat transfer efficiency.
Regular testing of the cooling water is essential to monitor pH levels, chloride content, and other critical factors. Consistent testing not only helps in preventing costly damage to engine components but also extends the lifespan of the engine, ensuring peak performance and reliability over time. In 2024, keeping your jacket cooling water in check is more important than ever for the longevity and efficiency of modern engines.
Purpose of Jacket Cooling Water Testing
Testing jacket cooling water is crucial for maintaining engine health and ensuring efficient performance. The primary purpose of these tests is to monitor the chemical balance of the cooling water, which directly impacts the system’s ability to regulate engine temperature.
Why Testing Jacket Cooling Water is Important
Regular testing is essential for detecting any imbalances in pH levels, chloride content, and other factors that may lead to issues such as corrosion, scaling, or overheating. If left unchecked, these problems can cause severe damage to engine components, leading to costly repairs and downtime.
How Testing Prevents Corrosion, Scaling, and Overheating
- Corrosion: Testing helps identify excessive acidity or alkalinity in the water, which can lead to corrosion of engine parts.
- Scaling: By monitoring water hardness, tests can prevent the buildup of mineral deposits that reduce cooling efficiency.
- Overheating: Ensuring the water is chemically balanced helps the cooling system perform optimally, preventing engine overheating.
Impact on Engine Efficiency and Maintenance
Regular jacket cooling water tests ensure that the engine operates at peak efficiency, reducing the likelihood of component failure. This leads to lower maintenance costs and prolonged engine life, making it a key aspect of any maintenance routine.
Types of Jacket Cooling Water Tests
To ensure the optimal performance of jacket cooling systems, several tests are conducted regularly. Each test is designed to monitor specific parameters that affect engine health.
1. pH Test
The pH level measures the acidity or alkalinity of the cooling water. Maintaining a balanced pH is essential to prevent corrosion and other chemical reactions. The ideal pH range for jacket cooling water is typically between 7.5 and 9.0. Water that is too acidic or too alkaline can corrode engine components, leading to costly repairs.
2. Chloride Content Test
Chlorides are a major contributor to corrosion in engine parts, especially in systems with steel and copper alloys. The chloride content test identifies the level of chlorides present. High levels can accelerate corrosion, while maintaining low chloride levels helps in protecting engine parts from damage.
3. Hardness Test
This test measures the concentration of calcium and magnesium in the water. Water hardness can lead to scaling, which reduces the efficiency of the cooling system by creating deposits on heat exchange surfaces. By identifying hardness levels, corrective actions can be taken to prevent scale buildup.
4. Alkalinity Test
The alkalinity test assesses the water’s capacity to neutralize acids, playing a crucial role in balancing the overall chemistry of the cooling water. Proper alkalinity levels help stabilize pH, preventing corrosion and maintaining the effectiveness of corrosion inhibitors.
5. Nitrite Test
Nitrites act as corrosion inhibitors by forming a protective layer on metal surfaces. The nitrite test is essential for preventing both corrosion and cavitation, ensuring that the cooling system remains protected from wear and degradation over time.
By conducting these tests regularly, the jacket cooling water system can remain efficient and free from issues like corrosion, scaling, and overheating, ensuring long-term engine performance.
3. Jacket Cooling Water Test Procedures
- Detailed step-by-step guide on conducting the tests.
- Tools and instruments needed for each test.
- Safety measures and precautions during testing.
Interpreting Test Results
Understanding the results of jacket cooling water tests is essential for maintaining engine health and preventing potential issues. Each test provides critical insights into the condition of the cooling system and helps identify areas that require attention.
How to Understand Test Data and Identify Potential Problems
Test data should be compared to standard benchmarks for each parameter. If the pH, chloride content, hardness, alkalinity, or nitrite levels deviate from the acceptable range, it can indicate underlying issues such as corrosion, scaling, or chemical imbalance. For instance, an acidic pH may signal corrosion risk, while high hardness could point to scaling concerns.
Normal Ranges and What Deviations Mean for Engine Health
- pH: The ideal range is between 7.5 and 9.0. A lower pH suggests acidic water, leading to corrosion, while a higher pH indicates alkaline conditions, which can also damage engine parts.
- Chloride Content: Should remain below recommended levels (often under 100 ppm) to prevent accelerated corrosion of metal components.
- Hardness: High levels of calcium and magnesium (> 200 ppm) suggest scaling, which reduces cooling efficiency.
- Alkalinity: Should be balanced to maintain pH stability and prevent corrosion or scaling.
- Nitrite Levels: Should be within the recommended range to ensure adequate corrosion protection. Low nitrite levels could mean inadequate corrosion inhibitors, while excessive nitrite may cause pitting.
When to Take Corrective Actions Based on Test Results
Corrective actions should be taken whenever the test results show significant deviations from normal ranges:
- Low pH or High Chloride Levels: Apply corrosion inhibitors to prevent further damage.
- High Hardness: Treat the water with softeners or conditioners to reduce scaling risk.
- Low Alkalinity or Nitrite Levels: Adjust chemical additives to maintain proper water chemistry and enhance protection against corrosion.
Regular interpretation of these test results allows for timely corrective measures, ensuring engine longevity and reducing the risk of major failures.
Common Issues Identified During Jacket Cooling Water Testing
Routine jacket cooling water testing helps identify several common issues that can affect engine performance and longevity. These issues, if not addressed promptly, can lead to significant operational inefficiencies and costly repairs.
1. Corrosion Problems and Their Effects
Corrosion is one of the most frequent problems detected during cooling water tests. It occurs when the water’s pH is imbalanced or when chloride levels are too high. Corrosion can damage metal components, such as cylinder liners, engine blocks, and cooling jackets, leading to:
- Material degradation over time.
- Leaks in the cooling system.
- Reduced engine lifespan due to wear on key components.
2. Scaling Issues and Impact on Cooling Efficiency
Scaling happens when the hardness of the water, particularly calcium and magnesium levels, is too high. These minerals form deposits on the inner surfaces of the cooling system, reducing its ability to transfer heat effectively. The effects of scaling include:
- Decreased heat exchange efficiency, causing the engine to overheat.
- Restricted coolant flow, leading to uneven cooling and localized hotspots.
- Increased fuel consumption due to inefficient cooling and heat dissipation.
3. Cavitation and Overheating Risks
Cavitation occurs when vapor bubbles form in the cooling water, often due to improper nitrite levels or air pockets. These bubbles can collapse with force, causing localized damage to metal surfaces. This can lead to:
- Erosion of key components like cylinder liners.
- Increased wear on pump impellers and other critical parts.
- Overheating, as the cooling system struggles to maintain temperature balance.
By identifying these issues through regular jacket cooling water testing, operators can prevent serious damage, maintain engine efficiency, and reduce the likelihood of system failures.
Maintenance Tips After Jacket Cooling Water Test
After conducting jacket cooling water tests, it’s essential to follow a proactive maintenance routine to ensure the cooling system remains efficient and free of issues like corrosion, scaling, or overheating. Here are some key maintenance tips to keep your engine running smoothly:
1. Regular Monitoring and Testing Schedules
Establishing a regular testing schedule is critical for early detection of issues in the cooling system. It is recommended to perform jacket cooling water tests:
- Monthly for routine checks on pH, chloride, and hardness levels.
- Quarterly for a more in-depth analysis of water chemistry, including nitrite and alkalinity.
- After any major maintenance or repairs to ensure the cooling water remains within the ideal range of parameters.
Frequent testing helps prevent long-term damage and ensures timely corrective measures.
2. Recommended Treatments for Jacket Cooling Water
To maintain the chemical balance of the cooling water and prevent corrosion and scaling, it is advisable to use the following treatments:
- Corrosion Inhibitors: These are essential for protecting metal components from chemical damage, particularly in environments with high chloride levels.
- Scaling Preventers: Water softeners or chemical treatments that reduce calcium and magnesium levels can prevent scale buildup, ensuring efficient heat exchange.
- pH Adjusters: If pH levels fall outside the ideal range, adding appropriate alkaline or acidic agents can restore balance and protect engine parts.
Always follow manufacturer recommendations when selecting and applying water treatments.
3. Importance of Flushing and Cleaning the System Regularly
Flushing the cooling system at regular intervals is vital for removing accumulated debris, scale, and contaminants that can impair performance. The benefits of flushing include:
- Preventing blockages in coolant pathways.
- Removing corrosive particles that may accelerate engine wear.
- Ensuring efficient heat transfer by keeping surfaces clean and free of deposits.
Regular cleaning and flushing, combined with proper water treatment, extend the life of your cooling system and reduce the risk of engine damage.
Best Practices for Ensuring Long-Term Efficiency
Maintaining long-term efficiency in the jacket cooling water system requires a strategic approach that includes regular monitoring, proper water treatment, and teamwork. Following best practices ensures optimal engine performance and prevents costly damage.
1. Regular Testing Intervals and Record-Keeping
Conducting jacket cooling water tests at consistent intervals is essential for early detection of problems such as corrosion, scaling, and chemical imbalances. Establish a monthly or quarterly testing schedule to monitor critical parameters like pH, chloride content, hardness, and nitrite levels.
- Record-keeping is equally important: maintain detailed logs of test results, corrective actions, and treatment schedules. These records allow for trend analysis and timely adjustments to water treatment practices, ensuring sustained system efficiency.
2. Using High-Quality Water Treatment Chemicals
The quality of water treatment chemicals directly impacts the effectiveness of the cooling system. Always use high-quality corrosion inhibitors, scaling preventers, and pH adjusters recommended by the engine manufacturer. Properly dosed chemicals help:
- Prevent the formation of scale, which can block coolant flow.
- Inhibit corrosion, extending the life of engine components.
- Maintain water chemistry within the desired range, improving cooling efficiency.
3. Collaborative Effort Between Engineers and Maintenance Teams
Long-term efficiency is best achieved through a collaborative effort between engineers and maintenance teams. By working together:
- Engineers can interpret test results and recommend appropriate treatments.
- Maintenance teams can implement corrective actions and maintain the system, ensuring that the engine operates efficiently.
- Effective communication between teams ensures that any issues are addressed promptly, avoiding downtime and costly repairs.
FAQ on Jacket Cooling Water Test
Q: How do cooling jackets work?
A: Cooling jackets circulate water around engine components to absorb and dissipate excess heat.
Q: What is the purpose of the cooling water test?
A: It ensures proper water chemistry to prevent corrosion, scaling, and overheating in the engine.
Q: What is the function of a cooling jacket?
A: The cooling jacket regulates engine temperature by transferring heat away from critical areas.
Q: What is a cooling test?
A: A cooling test checks the water’s chemical balance and quality to ensure optimal engine performance.
Conclusion
Regular jacket cooling water testing is essential for maintaining engine health, preventing issues like corrosion and scaling, and ensuring efficient performance. By adhering to proper testing schedules, using high-quality treatment chemicals, and following maintenance best practices, you can extend the lifespan of your engine and avoid costly repairs. Consistent monitoring and a collaborative approach between engineers and maintenance teams ensure that your cooling system operates at peak efficiency, safeguarding your equipment for long-term success.