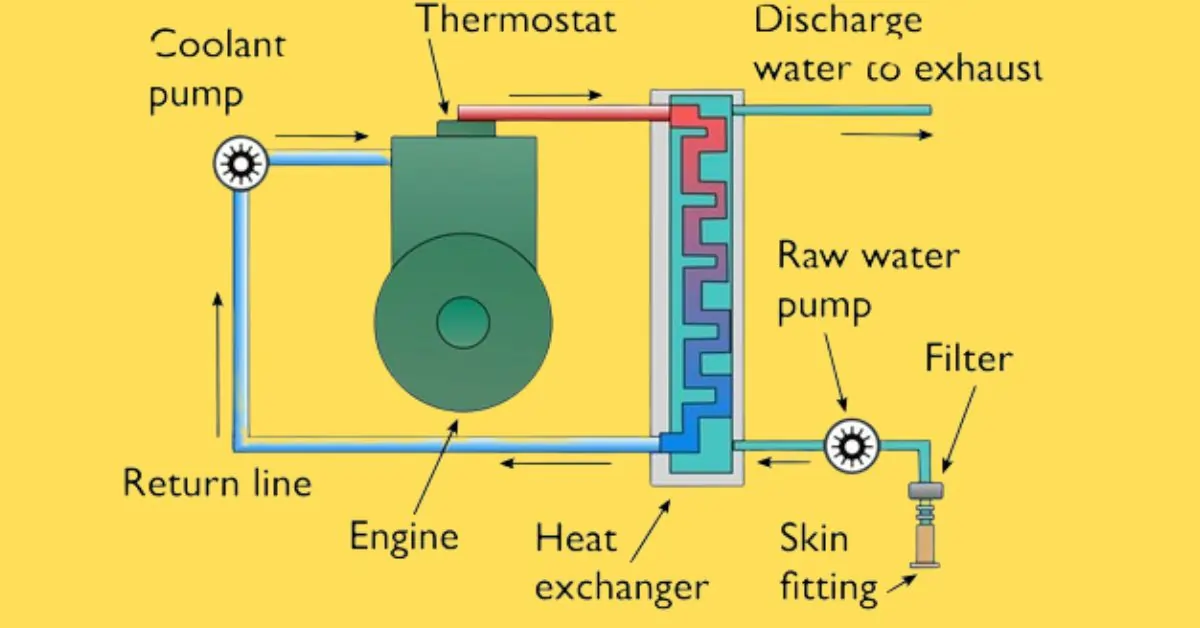
Marine Diesel Engine Cooling System
In the complex world of marine diesel engines, the cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and preventing costly breakdowns. This advanced guide delves into the intricate workings of marine diesel engine cooling systems, exploring essential components, their functions, and the significance of regular maintenance. We’ll discuss the various types of cooling systems, common issues, and practical maintenance tips to ensure your engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Understanding and maintaining the cooling system is vital for extending the lifespan of your engine, improving fuel efficiency, and safeguarding against unexpected failures. Join us as we navigate the depths of marine diesel engine cooling systems and equip you with the knowledge to keep your vessel in top shape
Components of a Marine Diesel Engine Cooling System
A well-functioning cooling system is vital for the optimal performance of marine diesel engines. Each component within the system plays a specific role in regulating engine temperature and preventing overheating. Here, we provide a detailed description of the primary components:
1. Heat Exchangers
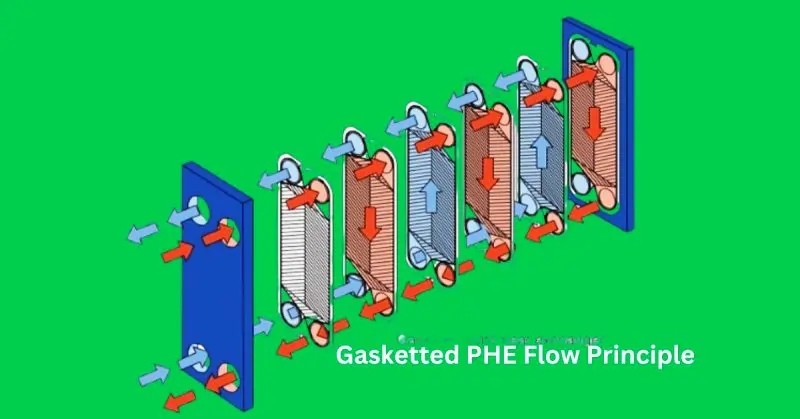
Heat exchangers are critical for transferring heat from the engine coolant to the seawater. They consist of a series of tubes that allow the hot coolant to pass through, where it transfers its heat to the cooler seawater surrounding the tubes. This process efficiently reduces the temperature of the coolant before it cycles back to the engine.
2. Sea Water Pumps

Sea water pumps are responsible for drawing seawater from the ocean and pushing it through the heat exchanger. These pumps must be robust and reliable to ensure a continuous supply of cool seawater, which is essential for maintaining the cooling process.
3. Thermostats
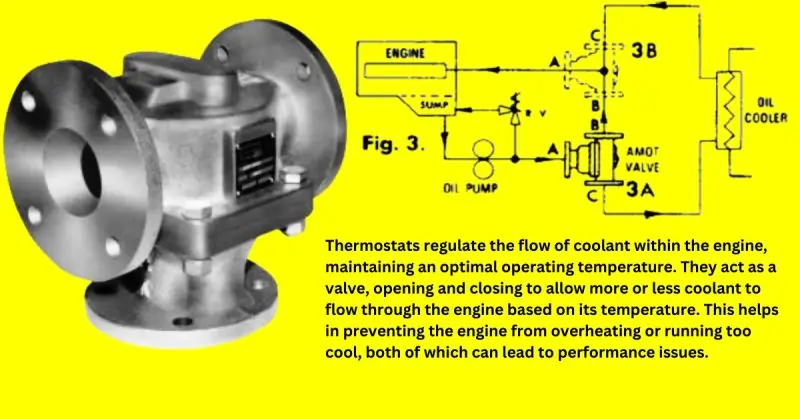
Thermostats regulate the flow of coolant within the engine, maintaining an optimal operating temperature. They act as a valve, opening and closing to allow more or less coolant to flow through the engine based on its temperature. This helps in preventing the engine from overheating or running too cool, both of which can lead to performance issues.
4. Coolant Pumps

Coolant pumps circulate the coolant throughout the engine and the cooling system. These pumps ensure that the coolant moves through the heat exchanger, engine block, and back again, maintaining a constant and efficient cooling cycle.
5. Expansion Tanks

Expansion tanks accommodate the expansion of coolant as it heats up and contracts when it cools down. This component helps in maintaining the correct pressure within the cooling system and prevents coolant loss due to overflow.
6. Piping and Hoses

Piping and hoses connect all components of the cooling system, allowing for the flow of coolant and seawater. These connections must be secure and free of leaks to ensure the system operates efficiently.
7. Strainers and Filters

Strainers and filters are used to remove debris and impurities from the seawater before it enters the heat exchanger. This prevents blockages and maintains the efficiency of the cooling system.
Each of these components works together to ensure the engine remains at an optimal temperature, preventing overheating and maintaining peak performance. Regular maintenance and inspection of these parts are crucial for the longevity and reliability of your marine diesel engine.
Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Importance of Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance of your marine diesel engine cooling system is essential for preventing unexpected breakdowns and ensuring optimal performance. Regular checks and upkeep can identify potential issues early, saving time and money on costly repairs and avoiding inconvenient downtime.
Checklist for Regular Inspections
- Inspect Heat Exchangers
- Check for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Ensure no blockages in the tubes.
- Verify proper coolant flow.
- Check Sea Water Pumps
- Inspect pump impellers for wear and tear.
- Ensure there are no leaks in the pump housing.
- Test for proper operation.
- Evaluate Thermostats
- Test thermostats for correct opening and closing temperatures.
- Replace any faulty thermostats.
- Check for proper coolant flow regulation.
- Examine Coolant Pumps
- Look for leaks or damage.
- Ensure the pump is circulating coolant effectively.
- Check for unusual noises indicating potential issues.
- Assess Expansion Tanks
- Verify the tank is maintaining correct pressure.
- Check for any coolant leaks.
- Ensure the coolant level is within the recommended range.
- Inspect Piping and Hoses
- Look for signs of wear, cracks, or leaks.
- Ensure all connections are secure.
- Replace any damaged hoses or pipes.
- Clean Strainers and Filters
- Regularly remove debris from strainers and filters.
- Ensure the filters are not clogged.
- Replace filters as necessary.
Tips for Cleaning and Maintaining Key Components
- Heat Exchangers: Periodically clean the plates using a brush or chemical cleaning solution to remove scale and debris.
- Sea Water Pumps: Flush with fresh water after each use to prevent salt buildup. Lubricate moving parts regularly.
- Thermostats: Test thermostats periodically in hot water to ensure they open and close correctly.
- Coolant Pumps: Replace coolant as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain efficiency. Ensure proper pump lubrication.
- Expansion Tanks: Check and top off coolant levels regularly. Replace the coolant cap if it shows signs of wear.
- Piping and Hoses: Clean hoses with fresh water after use in saltwater environments. Inspect regularly for any signs of wear.
Signs That Indicate Potential Problems
- Overheating: Consistent engine overheating can indicate issues with the coolant flow or a failing thermostat.
- Coolant Leaks: Puddles of coolant under the engine or low coolant levels can signal leaks in the system.
- Unusual Noises: Strange noises from pumps or other components can indicate mechanical failure.
- Reduced Performance: A noticeable drop in engine performance or efficiency may be a sign of a cooling system problem.
Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial for the longevity and reliability of your marine diesel engine cooling system. By following this checklist and being attentive to signs of potential problems, you can ensure your engine remains in top condition, providing safe and efficient operation.
Effective Troubleshooting Techniques
Common Issues with Marine Diesel Engine Cooling Systems
Marine diesel engine cooling systems can encounter a variety of issues, including:
- Overheating due to blocked heat exchangers or faulty thermostats
- Coolant leaks from damaged hoses or expansion tanks
- Inefficient coolant circulation caused by malfunctioning pumps
- Salt buildup in seawater pumps affecting performance
- Corrosion in system components leading to leaks and failures
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
- Identify Symptoms
- Overheating: Check temperature gauges and engine performance.
- Coolant Leaks: Look for visible coolant puddles and low coolant levels.
- Unusual Noises: Listen for abnormal sounds from pumps or moving parts.
- Reduced Performance: Notice any drop in engine efficiency or power.
- Inspect Heat Exchangers
- Remove and clean the plates to ensure there are no blockages.
- Check for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Examine Sea Water Pumps
- Inspect the impeller and housing for wear and tear.
- Ensure there are no blockages or leaks in the pump.
- Test Thermostats
- Place the thermostat in hot water and verify it opens and closes at the correct temperatures.
- Replace any faulty thermostats.
- Check Coolant Pumps
- Look for leaks or damage around the pump.
- Ensure the pump is properly circulating coolant and listen for unusual noises.
- Assess Expansion Tanks
- Verify the tank is maintaining proper pressure.
- Check for any signs of coolant leaks or damage.
- Inspect Piping and Hoses
- Look for cracks, wear, or leaks in the hoses and pipes.
- Ensure all connections are secure and replace any damaged components.
- Clean Strainers and Filters
- Remove debris and ensure filters are not clogged.
- Replace filters as necessary.
Tools and Equipment Needed
- Basic Hand Tools: Wrenches, screwdrivers, pliers
- Multimeter: For electrical testing of pumps and sensors
- Thermometer: For checking thermostat operation
- Pressure Tester: To test the expansion tank and coolant system pressure
- Cleaning Brushes/Chemicals: For heat exchanger maintenance
- Inspection Mirror: To check hard-to-reach areas
- Replacement Parts: Spare hoses, thermostats, gaskets, and filters
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
- Case Study 1: Overheating Issue
- Problem: A vessel experienced frequent engine overheating.
- Diagnosis: Inspection revealed clogged plates in the heat exchanger.
- Solution: The heat exchanger was removed and cleaned thoroughly. After reassembly, the engine temperature stabilized, resolving the overheating issue.
- Case Study 2: Coolant Leak
- Problem: Low coolant levels were detected, and puddles of coolant were found under the engine.
- Diagnosis: A damaged hose was identified as the source of the leak.
- Solution: The damaged hose was replaced, and the system was pressure-tested to ensure no further leaks. The coolant was refilled, and the issue was resolved.
- Case Study 3: Inefficient Coolant Circulation
- Problem: The engine showed signs of reduced performance.
- Diagnosis: The coolant pump was found to be malfunctioning, with worn impeller blades.
- Solution: The coolant pump was replaced, restoring proper coolant circulation and engine performance.
Selecting the Right Products and Suppliers
Criteria for Choosing High-Quality Cooling System Components
- Material Quality
- Ensure components are made from durable, corrosion-resistant materials suitable for marine environments, such as stainless steel or marine-grade bronze.
- Compatibility
- Verify that the components are compatible with your specific marine diesel engine model and its cooling system specifications.
- Performance Ratings
- Check the performance ratings and specifications to ensure the components meet or exceed the requirements for your engine’s cooling needs.
- Reliability and Durability
- Look for components with a proven track record of reliability and durability. Seek out products that come with comprehensive warranties.
- Certifications and Standards
- Choose components that comply with international marine standards and certifications, such as ISO, ABS, or DNV-GL.
- Customer Reviews and Ratings
- Read customer reviews and ratings to gauge the real-world performance and reliability of the components.
Comparison of Top Suppliers and Manufacturers
- Cummins Marine
- Strengths: Known for high-quality engine parts and extensive service network.
- Popular Products: Marine heat exchangers, seawater pumps, thermostats.
- Rating: 4.8/5
- Volvo Penta
- Strengths: Offers a wide range of marine cooling components with a reputation for durability and performance.
- Popular Products: Cooling pumps, thermostats, complete cooling system kits.
- Rating: 4.7/5
- Yanmar Marine
- Strengths: Renowned for innovation and high standards in marine engine parts.
- Popular Products: Heat exchangers, cooling system sensors, expansion tanks.
- Rating: 4.6/5
- Kohler Marine
- Strengths: Provides robust cooling system components specifically designed for marine applications.
- Popular Products: Coolant pumps, piping systems, strainers.
- Rating: 4.5/5
Reviews of Popular Products on the Market
- Cummins Marine Heat Exchanger
- Review: Highly efficient and durable, easy to install with minimal maintenance required.
- Pros: Long-lasting, effective cooling.
- Cons: Higher initial cost.
- Customer Rating: 4.9/5
- Volvo Penta Seawater Pump
- Review: Reliable and powerful pump with excellent flow rates.
- Pros: Robust construction, reliable performance.
- Cons: Can be noisy.
- Customer Rating: 4.8/5
- Yanmar Marine Thermostat
- Review: Precisely regulates engine temperature, highly reliable.
- Pros: Accurate temperature control, easy replacement.
- Cons: Limited availability in some regions.
- Customer Rating: 4.7/5
Tips for Sourcing Parts in Different Regions
- Local Dealers and Distributors
- Establish relationships with local dealers and distributors who specialize in marine engine parts. They can provide quick access to parts and support.
- Online Marketplaces
- Utilize reputable online marketplaces such as Marine Parts Express, eBay, and Amazon for a wide selection of parts, often with user reviews.
- Manufacturer Direct
- Purchasing directly from manufacturers’ websites can ensure authenticity and access to the latest products and updates.
- Marine Trade Shows and Expos
- Attend marine trade shows and expos to meet suppliers, compare products, and often secure better deals.
- Regional Specialties
- Different regions may have specialties or better availability of certain brands. For instance, European suppliers might have more options for Volvo Penta, while Asian suppliers might excel in Yanmar parts.
Installation and Replacement Guidelines
Detailed Instructions for Installing New Cooling System Components
- Preparation
- Gather Tools and Materials: Ensure you have all necessary tools, including wrenches, screwdrivers, gaskets, and the new components.
- Review Manufacturer Instructions: Always read the manufacturer’s installation manual for specific guidelines.
- Draining the System
- Shut Down the Engine: Allow the engine to cool completely.
- Drain Coolant: Open the drain valve and collect the old coolant in a container for proper disposal.
- Removing Old Components
- Disconnect Piping and Hoses: Use wrenches to loosen and remove hoses and pipes connected to the component being replaced.
- Unbolt Components: Carefully unbolt the old component, taking care not to damage surrounding parts.
- Installing New Components
- Position the New Component: Place the new component in position, aligning it with mounting holes.
- Secure the Component: Bolt the new component in place, ensuring it is securely fastened.
- Reconnect Piping and Hoses: Attach all hoses and pipes, ensuring tight and leak-free connections.
- Refilling the System
- Add Coolant: Fill the system with the appropriate coolant mixture, as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Bleed the System: Remove any air pockets by opening bleeder valves or running the engine briefly and topping off coolant levels.
- Testing
- Check for Leaks: Inspect all connections for any signs of leaks.
- Run the Engine: Start the engine and allow it to reach operating temperature, checking for proper operation of the new component.
Safety Precautions to Follow During Installation
- Wear Protective Gear: Use gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing to prevent injuries.
- Engine Cool Down: Ensure the engine is completely cool before starting any work to avoid burns.
- Proper Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes from coolant or other chemicals.
- Use Proper Tools: Only use the recommended tools to avoid damaging components or causing injury.
- Dispose of Coolant Safely: Collect and dispose of old coolant according to local environmental regulations.
How to Replace Old or Faulty Parts Without Compromising the System
- Assess the Condition: Thoroughly inspect the old component to understand why it failed and check if any surrounding parts were affected.
- Use OEM Parts: Always use Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts for replacements to ensure compatibility and reliability.
- Check Seals and Gaskets: Replace any seals and gaskets to prevent leaks and ensure a tight fit.
- Follow Torque Specifications: Tighten bolts and screws to the manufacturer’s specified torque settings to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening.
- Perform System Checks: After replacement, run a comprehensive check to ensure the new part integrates smoothly with the existing system.
Upgrades and Modifications
Latest Advancements in Cooling System Technology
- Plate Heat Exchangers
- Advancement: Modern plate heat exchangers offer higher efficiency and compact design compared to traditional tube exchangers.
- Benefit: Improved heat transfer and reduced space requirements.
- Smart Thermostats
- Advancement: Smart thermostats with digital controls allow for precise temperature regulation and real-time monitoring.
- Benefit: Enhanced engine performance and prevention of overheating.
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials
- Advancement: New materials like titanium and advanced composites offer superior resistance to corrosion.
- Benefit: Increased longevity and reduced maintenance costs.
- Advanced Coolant Formulations
- Advancement: Enhanced coolant formulations provide better heat transfer and protection against corrosion.
- Benefit: Improved engine efficiency and longer component life.
- Automated Monitoring Systems
- Advancement: Systems that monitor and report on coolant levels, flow rates, and temperature in real-time.
- Benefit: Early detection of issues and automated alerts to prevent failures.
Benefits of Upgrading or Modifying Your Cooling System
- Enhanced Efficiency: Upgraded components can improve the heat exchange process, leading to better engine performance and fuel efficiency.
- Increased Reliability: Modern components reduce the risk of breakdowns and extend the lifespan of your engine.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Advanced materials and technologies require less frequent maintenance and have longer service intervals.
- Improved Safety: Real-time monitoring and smarter controls help prevent overheating and other potential hazards.
- Environmental Benefits: More efficient cooling systems can reduce emissions and environmental impact.
Examples of Successful Upgrades and Their Impact on Performance
- Case Study 1: Plate Heat Exchanger Upgrade
- Situation: A commercial fishing vessel experienced frequent overheating issues with its tube heat exchanger.
- Upgrade: Switched to a modern plate heat exchanger.
- Impact: Improved cooling efficiency by 20%, reduced engine downtime, and lowered fuel consumption by 5%.
- Case Study 2: Smart Thermostat Installation
- Situation: A yacht owner wanted better control over engine temperature.
- Upgrade: Installed a smart thermostat with digital controls and real-time monitoring.
- Impact: Enhanced temperature regulation, reduced overheating incidents, and improved overall engine performance.
- Case Study 3: Corrosion-Resistant Materials
- Situation: A ferry operating in saltwater faced frequent corrosion issues.
- Upgrade: Replaced standard components with titanium and advanced composite materials.
- Impact: Significantly reduced corrosion, extended component life by 50%, and lowered maintenance costs.
How to Determine if an Upgrade is Necessary for Your Engine
- Assess Current Performance
- Signs: Frequent overheating, inefficient cooling, increased fuel consumption, and frequent maintenance issues.
- Action: Conduct a thorough inspection and performance analysis of your current cooling system.
- Review Maintenance Records
- Signs: High frequency of repairs, component replacements, and increased downtime.
- Action: Analyze maintenance records to identify patterns and recurring issues.
- Evaluate Technological Advancements
- Signs: Availability of new technologies that offer better performance and efficiency.
- Action: Compare the latest advancements with your current system to identify potential benefits.
- Consult with Experts
- Signs: Uncertainty about the best course of action or potential benefits of an upgrade.
- Action: Seek advice from marine engine experts or consultants to evaluate the feasibility and benefits of an upgrade.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Signs: High operational and maintenance costs.
- Action: Perform a cost-benefit analysis to determine the long-term savings and performance improvements from an upgrade.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
Best Practices for Extending the Life of Your Cooling System
- Regular Inspection and Cleaning
- Practice: Conduct regular inspections and clean key components such as heat exchangers, seawater pumps, and strainers.
- Benefit: Prevents buildup of debris and corrosion, ensuring efficient operation.
- Use Quality Coolant
- Practice: Always use the manufacturer-recommended coolant and maintain the correct mixture ratio.
- Benefit: Ensures optimal heat transfer and protection against corrosion.
- Monitor Coolant Levels
- Practice: Check coolant levels before each voyage and top off as necessary.
- Benefit: Prevents overheating and maintains proper engine temperature.
- Replace Worn Components Promptly
- Practice: Replace worn or damaged parts immediately, such as hoses, gaskets, and impellers.
- Benefit: Avoids breakdowns and extends the lifespan of the cooling system.
- Lubricate Moving Parts
- Practice: Regularly lubricate pumps and other moving parts as per manufacturer guidelines.
- Benefit: Reduces wear and tear, ensuring smooth operation.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Common Problems
- Flush the System Regularly
- Measure: Perform a complete system flush at least once a year or as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Benefit: Removes contaminants and prevents scale buildup.
- Inspect Seals and Connections
- Measure: Check all seals, connections, and fittings for signs of wear or leakage.
- Benefit: Prevents leaks and ensures system integrity.
- Monitor Temperature Gauges
- Measure: Regularly monitor engine temperature gauges during operation.
- Benefit: Early detection of overheating or cooling inefficiencies.
- Use Corrosion Inhibitors
- Measure: Add corrosion inhibitors to the cooling system as recommended.
- Benefit: Protects metal components from rust and corrosion.
- Check for Airlocks
- Measure: Ensure there are no airlocks in the cooling system, which can cause overheating.
- Benefit: Maintains efficient coolant circulation.
Tips for Operating the Engine to Reduce Stress on the Cooling System
- Avoid Prolonged Idling
- Tip: Minimize extended periods of idling.
- Benefit: Reduces engine wear and overheating risks.
- Maintain Optimal Engine Load
- Tip: Operate the engine within the recommended load range.
- Benefit: Ensures efficient cooling and prevents overloading.
- Gradual Warm-Up and Cool-Down
- Tip: Gradually warm up the engine before full operation and allow it to cool down gradually after use.
- Benefit: Prevents thermal shock and extends component life.
- Monitor Engine Performance
- Tip: Pay attention to any changes in engine performance or unusual noises.
- Benefit: Early identification of potential issues with the cooling system.
- Use Engine at Optimal RPM
- Tip: Operate the engine at the recommended RPM range for optimal performance.
- Benefit: Ensures efficient cooling and reduces engine strain.
Seasonal Maintenance Tips for Different Marine Environments
- Cold Weather Preparation
- Tip: Use antifreeze to protect the cooling system from freezing.
- Benefit: Prevents damage due to ice formation in the system.
- Action: Drain and replace coolant with antifreeze mixture before winter.
- Warm Weather Preparation
- Tip: Ensure proper ventilation and cooling in the engine room.
- Benefit: Prevents overheating in high temperatures.
- Action: Check and clean seawater intake regularly to prevent blockages.
- Saltwater Environment
- Tip: Flush the cooling system with fresh water after each use.
- Benefit: Removes salt deposits and prevents corrosion.
- Action: Use corrosion inhibitors and inspect for rust regularly.
- Freshwater Environment
- Tip: Regularly inspect for algae and organic buildup.
- Benefit: Prevents blockages and maintains cooling efficiency.
- Action: Clean strainers and filters frequently.
FAQ on “Marine Diesel Engine Cooling System”
Q: Why is the cooling system important for marine diesel engines?
A: The cooling system prevents overheating, ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity.
Q: How often should I inspect my cooling system?
A: Inspect your cooling system at least once a year or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Q: What are common signs of cooling system issues?
A: Common signs include overheating, coolant leaks, and unusual noises from the engine.
Q: Can I use any coolant in my marine diesel engine?
A: Always use the manufacturer-recommended coolant for optimal performance and protection.
Conclusion
Maintaining the cooling system of your marine diesel engine is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation. By following best practices, preventive measures, and staying updated with the latest advancements, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your engine and avoid costly breakdowns. Regular inspections, proper maintenance, and timely upgrades are key to keeping your cooling system in top condition. With careful attention to these details, you can enjoy smooth sailing and optimal engine performance in all marine environments.