Oil Mist Detector
Safety is crucial for large marine diesel engines and industrial machines. An important tool for this safety is the oil mist detector. This device finds oil mist inside the crankcase, stopping potential explosions caused by too much oil mist. Oil mist can form from overheating, friction, or mechanical issues, which can harm the engine and safety.
An oil mist detector constantly checks the air inside the crankcase. If it finds too much oil mist, it sounds alarms and can shut down the engine to prevent accidents. This keeps the engine and the whole operation safe from serious damage. Using oil mist detectors helps keep marine and industrial engines running safely and efficiently.
What is an Oil Mist Detector?
An oil mist detector is a crucial safety device used primarily in large marine diesel engines and various industrial applications. Its main function is to detect the presence of oil mist within the crankcase, ensuring safe and efficient engine operation.
Definition and Primary Function
An oil mist detector is a specialized instrument designed to continuously monitor the density of oil mist within the crankcase atmosphere. The primary function of this device is to identify excessive concentrations of oil mist, which can form due to factors like overheating, friction, or mechanical failures. By detecting these concentrations, the oil mist detector helps prevent dangerous conditions that could lead to crankcase explosions.
Overview of Its Role in Preventing Crankcase Explosions

Oil mist within an engine’s crankcase can pose a significant hazard if it reaches a critical concentration. When combined with the right conditions, such as high temperatures or sparks, this mist can ignite and cause a crankcase explosion. Such explosions are highly destructive and can result in severe engine damage, operational downtime, and safety risks to personnel.
The oil mist detector plays a vital role in preventing these incidents by:
- Continuous Monitoring: It constantly checks the levels of oil mist within the crankcase, providing real-time data on mist concentration.
- Early Detection: By identifying rising oil mist levels early, it allows for timely intervention before conditions become hazardous.
- Alarm Systems: When oil mist concentrations exceed safe thresholds, the detector triggers alarms, alerting operators to take immediate action.
- Automatic Safety Measures: In some systems, the detector can initiate automatic responses, such as engine shutdowns, to prevent further escalation of the danger.
Through these functions, oil mist detectors are essential for maintaining engine safety, preventing catastrophic failures, and ensuring the overall efficiency and reliability of marine and industrial engines.
How Oil Mist Detectors Work
Video Credit : https://www.youtube.com/@Marinersgalaxy
Detection Mechanism
Oil mist detectors are vital devices designed to ensure the safe operation of large marine diesel engines and various industrial machinery by detecting oil mist within the crankcase. These detectors employ advanced detection mechanisms to monitor and measure the concentration of oil mist particles in the air. Here’s a detailed explanation of how they work:
Explanation of How Sensors Measure Oil Mist Density
The detection mechanism of an oil mist detector revolves around continuous air sampling and light interaction. The process can be broken down into the following steps:
- Air Sampling: A fan within the detector draws in air samples from the crankcase. This ensures that a constant stream of crankcase atmosphere is analyzed for the presence of oil mist.
- Light Source: The detector contains a lamp that emits a consistent beam of light. This light is directed into a measuring tube where the air sample flows.
- Interaction with Oil Mist Particles: As the light passes through the measuring tube, it interacts with any oil mist particles present in the air sample. Oil mist particles scatter the light, causing changes in the light intensity and direction.
- Sensor Detection: Photo-electric cells, positioned to detect the scattered light, measure the intensity of this scattered light. The amount of scattered light correlates directly with the density of oil mist particles in the air. Higher oil mist concentrations result in more significant light scattering and reduced light intensity reaching the sensors.
- Data Processing: The sensor data is sent to a control unit that processes the information. It compares the measured light intensity against predefined thresholds to determine if the oil mist concentration is within safe limits.
- Alarm and Safety Measures: If the oil mist concentration exceeds the safe threshold, the control unit triggers alarms to alert operators. In some systems, automatic safety measures such as engine shutdowns are initiated to prevent hazardous conditions.
Types of Sensors Used
The primary type of sensor used in oil mist detectors is the optical sensor. These sensors are highly effective in detecting oil mist due to their sensitivity to light scattering. The two main components of optical sensors in this context are:
- Photo-Electric Cells: These are sensitive to changes in light intensity. In an oil mist detector, they detect the amount of light scattered by oil mist particles. The intensity of scattered light provides a precise measurement of oil mist density.
- Optical Sensors: These sensors include mirrors and lenses to direct and focus the light beam through the measuring tube. They ensure that the light interacts effectively with any oil mist particles, maximizing detection accuracy.
Optical sensors are preferred for oil mist detection because of their high sensitivity, reliability, and ability to provide real-time monitoring. They can detect even minute changes in oil mist concentration, ensuring that any increase in oil mist density is promptly identified and addressed.
Alert System
How the Detector Triggers Alarms
Oil mist detectors are designed with sophisticated alert systems to ensure immediate action when unsafe conditions are detected. The alert system operates through a series of steps to identify and respond to excessive oil mist concentrations:
- Continuous Monitoring: The detector continuously samples the crankcase atmosphere, measuring the density of oil mist particles using optical sensors. These sensors relay real-time data to the control unit.
- Data Analysis: The control unit processes the incoming data, comparing the measured oil mist concentration against predefined safety thresholds. These thresholds are set based on safe operating levels determined by engine manufacturers and industry standards.
- Threshold Exceedance: When the oil mist concentration exceeds the predetermined safe threshold, the control unit recognizes this as a potential hazard. The system is programmed to respond immediately to such conditions.
- Alarm Activation: Upon detecting unsafe oil mist levels, the control unit activates the alarm system. This typically involves both visual and audible alarms:
- Visual Alarms: Flashing lights or indicator panels are used to provide a clear visual warning to operators.
- Audible Alarms: Sirens or buzzers sound to draw immediate attention to the issue, ensuring that personnel are alerted even if they are not in the immediate vicinity.
Safety Measures When Thresholds Are Exceeded
When the oil mist detector triggers an alarm due to high oil mist concentrations, several safety measures can be automatically initiated to prevent engine damage and ensure the safety of personnel:
- Engine Shutdown: One of the most critical safety measures is the automatic shutdown of the engine. By stopping the engine, the system prevents further operation under hazardous conditions, reducing the risk of crankcase explosions and severe damage.
- Ventilation Activation: In some systems, the detector can activate additional ventilation to reduce the concentration of oil mist in the crankcase. This helps dissipate the mist and lowers the risk of ignition.
- Cooling Systems Engagement: The system can trigger cooling mechanisms to lower the temperature within the crankcase, preventing further vaporization of oil and reducing oil mist formation.
- Emergency Notifications: Beyond local alarms, the system can send emergency notifications to remote monitoring stations or responsible personnel. This ensures that appropriate actions are taken swiftly, even if on-site operators are unable to respond immediately.
- System Lockout: The control unit can initiate a lockout, preventing the engine from being restarted until the issue has been thoroughly investigated and resolved. This ensures that the engine is not operated under unsafe conditions.
- Diagnostic Logging: The system logs diagnostic data when an alarm is triggered. This includes the exact oil mist concentration, the time of the alarm, and other relevant parameters. This information is crucial for troubleshooting and understanding the root cause of the high oil mist levels.
Explanation of an Oil Mist Detector
An oil mist detector is a sophisticated device designed to enhance the safety and operational efficiency of large marine diesel engines and industrial machinery by detecting the presence of oil mist within the crankcase. Here’s an explanation of how it works, incorporating key components:
Components and Their Functions
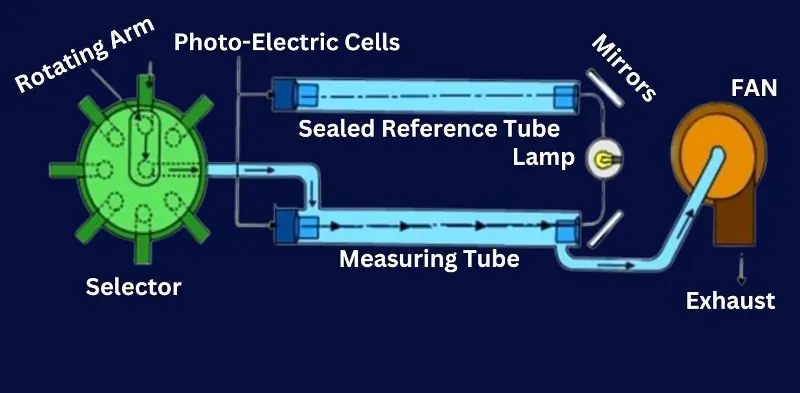
- Fan: The fan draws in samples of the crankcase atmosphere into the detector. This ensures a continuous flow of air and oil mist through the detection system for accurate real-time monitoring.
- Exhaust: The exhaust component expels the analyzed air back into the environment or crankcase after it has passed through the detection system. This helps maintain proper airflow and pressure within the system.
- Mirrors: Mirrors within the detector are used to direct and focus light beams from the lamp onto the measuring tube. This ensures that the light is accurately aligned for optimal detection of oil mist particles.
- Sealed Reference Tube: The sealed reference tube contains a known, fixed concentration of clean air or a specific oil mist concentration. It serves as a baseline for calibrating the detector, ensuring the accuracy of measurements and comparisons.
- Photo-Electric Cells: Photo-electric cells are sensors that detect light intensity. In an oil mist detector, they measure the amount of light scattered by oil mist particles in the measuring tube. A decrease in light intensity indicates the presence and concentration of oil mist.
- Rotating Arm: The rotating arm moves the measuring tube or mirrors to ensure that the light beam and air sample are properly aligned. This allows the detector to take accurate readings from various parts of the crankcase atmosphere.
- Lamp: The lamp provides a consistent light source that shines through the measuring tube. The intensity and clarity of this light are crucial for detecting oil mist particles, as they scatter the light, causing measurable changes in intensity detected by the photo-electric cells.
- Measuring Tube: The measuring tube is where the actual detection of oil mist takes place. Air samples drawn in by the fan pass through this tube, and the light from the lamp interacts with the mist particles here. The photo-electric cells measure the scattered light to determine mist concentration.
- Selector: The selector controls the flow of air samples to the measuring tube. It can switch between different sampling points or sources, ensuring that the detector provides a comprehensive analysis of the crankcase atmosphere.
How It Works
The fan draws a sample of the crankcase atmosphere into the oil mist detector. This air passes through the measuring tube, where it is exposed to light from the lamp. Mirrors direct this light precisely, ensuring it interacts with any oil mist particles present.
As the light passes through the measuring tube, oil mist particles scatter the light. Photo-electric cells detect this scattered light, and the intensity of the scattered light correlates with the concentration of oil mist in the air sample.
The sealed reference tube provides a calibration point, ensuring the detector’s readings are accurate. The rotating arm and selector allow the system to sample air from different locations and align the components for precise measurement.
Finally, the exhaust expels the analyzed air, maintaining proper airflow and pressure within the system. If the detector identifies a concentration of oil mist that exceeds safe levels, it triggers alarms and can initiate automatic safety measures, such as shutting down the engine, to prevent potential crankcase explosions.
Key Formulas for Understanding Oil Mist Detectors
1. Light Scattering and Oil Mist Concentration
The principle of light scattering can be represented by Rayleigh scattering or Mie scattering theories, depending on the size of the oil mist particles relative to the wavelength of the light. For small particles (Rayleigh scattering):

2. Beer-Lambert Law
For understanding the attenuation of light as it passes through a medium containing oil mist:

3. Concentration Calculation
To calculate the concentration of oil mist particles from the measured light intensity:

4. Threshold Exceedance
To set a threshold for safety measures, you can define a maximum allowable concentration Cmax and compare it to the measured concentration c:
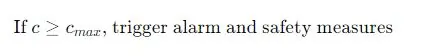
The Purpose of an Oil Mist Detector
Detailed Explanation of Its Primary Function
An oil mist detector is a critical safety device installed in large marine diesel engines and various industrial machinery. Its primary function is to continuously monitor the atmosphere within the crankcase for the presence of oil mist. The detector employs advanced sensing technologies to detect and measure the concentration of oil mist particles in the air. When these particles reach or exceed a predetermined safe threshold, the detector triggers alarms and can initiate automatic safety measures such as engine shutdowns. This proactive monitoring and response system is essential for preventing hazardous conditions and ensuring the safe operation of engines.
Importance of Detecting Excessive Oil Mist
Detecting excessive oil mist is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Crankcase Explosions: High concentrations of oil mist can create a flammable environment within the crankcase. When exposed to high temperatures or sparks, this mist can ignite, leading to catastrophic crankcase explosions. Early detection and intervention are vital to preventing such dangerous incidents.
- Maintaining Engine Integrity: Excessive oil mist can indicate underlying issues within the engine, such as overheating, friction, or mechanical failures. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly helps maintain the engine’s structural integrity and operational reliability.
- Ensuring Operational Safety: Regular monitoring and detection of oil mist enhance overall safety. By preventing explosions and identifying potential engine problems early, the oil mist detector protects personnel and equipment from harm.
- Reducing Maintenance Costs: Early detection of oil mist-related issues allows for timely maintenance and repairs, reducing the risk of severe engine damage and costly downtime.
Causes of Oil Mist Formation
Oil mist formation within the crankcase can result from various factors, including:
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause lubricating oil to vaporize, creating oil mist. Overheating may occur due to inadequate cooling, high engine loads, or poor lubrication.
- Friction: Increased friction between moving engine parts can generate heat and cause oil to vaporize, leading to the formation of oil mist. Friction may arise from improper lubrication, worn-out components, or misalignment of parts.
- Mechanical Failures: Mechanical issues such as broken piston rings, damaged bearings, or cracks in the crankcase can lead to oil mist formation. These failures can cause oil to leak and vaporize, creating a hazardous environment within the crankcase.
- Hot Spots Due to Bearings: Bearings can develop hot spots from excessive friction, misalignment, or inadequate lubrication. These hot spots significantly raise the temperature of surrounding areas, causing oil to vaporize into mist. Monitoring for these conditions helps prevent bearing failures and subsequent engine damage.
- Exhaust Blow-by: Exhaust blow-by occurs when combustion gases escape past the piston rings into the crankcase. These gases can carry oil particles, creating oil mist. This condition not only contributes to oil mist formation but also indicates potential issues with piston rings or cylinder wear that need to be addressed.
Essential Tips for Using Oil Mist Detectors
Regular Maintenance: Importance of Routine Checks and Servicing
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of oil mist detectors. Routine checks and servicing help in:
- Detecting Wear and Tear: Regular inspections can identify signs of wear and tear in the components, allowing for timely repairs or replacements.
- Ensuring Functionality: Routine maintenance ensures that all parts of the detector are functioning correctly, reducing the risk of malfunction.
- Preventing False Alarms: Regular servicing helps in maintaining the accuracy of the detector, preventing false alarms that can disrupt operations.
- Extending Lifespan: Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of the detector, ensuring reliable performance over time.
Proper Installation: Ensuring Correct Setup for Accurate Detection
Proper installation of oil mist detectors is essential for accurate and reliable operation. Key considerations include:
- Location: Install the detector in strategic locations where oil mist is most likely to form, such as near bearings, pistons, and other high-friction areas.
- Orientation: Ensure that the detector is oriented correctly to capture air samples effectively.
- Sealing: Properly seal connections to prevent air leaks that could affect the accuracy of measurements.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines to ensure the detector functions as intended.
Calibration: Regular Calibration for Accurate Sensor Readings
Regular calibration is essential for maintaining the accuracy of oil mist detectors. Calibration involves:
- Baseline Settings: Establishing and maintaining baseline settings for the detector to ensure consistency in measurements.
- Frequency: Performing calibration at regular intervals as recommended by the manufacturer or based on operational conditions.
- Reference Standards: Using known reference standards to calibrate the detector, ensuring that sensor readings are accurate.
- Record Keeping: Keeping detailed records of calibration activities to track performance and identify trends.
Training: Educating Staff on the Importance and Operation of the Detector
Proper training is crucial for ensuring that staff can effectively operate and respond to oil mist detectors. Training should cover:
- Functionality: Educating staff on how the detector works and its role in preventing crankcase explosions.
- Operation: Teaching staff how to operate the detector, including starting, stopping, and testing the system.
- Alarm Response: Training staff on how to respond to alarms, including immediate actions and follow-up procedures.
- Maintenance Procedures: Providing instructions on routine maintenance and calibration tasks.
Integration with Safety Systems: Ensuring the Detector is Part of a Comprehensive Safety System
Integrating oil mist detectors with comprehensive safety systems enhances overall operational safety. Key aspects include:
- Alarm Systems: Connecting the detector to centralized alarm systems to ensure immediate notification of high oil mist levels.
- Shutdown Mechanisms: Integrating the detector with automatic engine shutdown systems to prevent operation under hazardous conditions.
- Data Logging: Implementing data logging features to record and analyze detector readings over time, aiding in preventive maintenance and troubleshooting.
- System Coordination: Ensuring that the detector works in coordination with other safety systems, such as fire suppression and ventilation systems.
Immediate Response: Protocols for Responding to Alarms
Having clear protocols for responding to alarms ensures swift and effective action. Response protocols should include:
- Immediate Actions: Detailed steps for immediate actions to be taken by operators upon hearing an alarm, such as shutting down the engine or increasing ventilation.
- Emergency Procedures: Established emergency procedures for evacuating personnel if necessary.
- Notification: Protocols for notifying relevant personnel, including maintenance teams and safety officers.
- Investigation and Reporting: Procedures for investigating the cause of the alarm and documenting findings for future reference.
FAQ on Oil Mist Detector
Q: What is the primary function of an oil mist detector?
A: To detect and measure oil mist in the crankcase, preventing explosions.
Q: How does an oil mist detector alert operators to high oil mist levels?
A: By triggering visual and audible alarms and initiating safety measures.
Q: Why is regular calibration of an oil mist detector important?
A: To ensure accurate and reliable detection of oil mist.
Q: What are common causes of oil mist formation in engines?
A: Overheating, friction, mechanical failures, hot spots, and exhaust blow-by.
Conclusion
Oil mist detectors are essential for maintaining the safety and efficiency of large marine diesel engines and industrial machinery. By continuously monitoring oil mist levels, these devices prevent dangerous crankcase explosions, ensure operational integrity, and protect both equipment and personnel. Regular maintenance, proper installation, calibration, and staff training are critical to their effective use. Implementing oil mist detectors as part of a comprehensive safety system is a proactive step towards safeguarding your operations and ensuring long-term reliability. Stay vigilant, and ensure your oil mist detectors are always in top working condition.
