Overhauling Of Centrifugal Pump
Centrifugal pumps are essential components in marine and industrial applications, providing reliable fluid transfer for various systems, from cooling water to fuel handling. Their efficient operation ensures smooth processes, making them critical in environments where downtime can lead to costly disruptions. Over time, however, wear and tear can affect pump performance, leading to inefficiency, leaks, and potential system failures.
Regular overhauling of centrifugal pumps is crucial to prevent these issues, ensuring that the pump operates at peak efficiency and prolonging its lifespan. A thorough overhaul not only restores performance but also helps detect potential problems before they become serious.
In this post, we will cover the complete procedure for overhauling a centrifugal pump, from disassembly to testing, along with best practices and common mistakes to avoid. This guide will help you maintain your pumps for optimal performance and longevity, minimizing unexpected breakdowns.
Pump Overhaul Warning Signs
| Sign | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Reduced Efficiency | Lower flow or pressure, slower system response |
| Unusual Vibrations | Misalignment, worn bearings or unbalanced impeller |
| Fluid Leaks | Deteriorated seals/gaskets, pressure loss risk |
| Abnormal Noises | Grinding/knocking—possible bearing or impeller issue |
| Increased Energy Use | Wear causing higher power for same output |
| Overheating | Lubrication failure or blocked flow |
| Frequent Shutdowns | Underlying mechanical or electrical fault |
Overhaul Steps—At a Glance
| Step | Action | Key Reminder |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Isolate & Drain Pump | Power off, wear PPE |
| 2 | Disassemble & Inspect Parts | Use correct tools, record damage |
| 3 | Clean Components | Remove all debris, inspect further |
| 4 | Repair/Replace Worn Items | Use OEM parts for reliability |
| 5 | Reassemble & Align | Follow torque specs, check seals |
| 6 | Lubricate & Test Run | Listen for noise, check leaks |
| 7 | Monitor Performance | Log data, schedule next inspection |
What is a Centrifugal Pump?
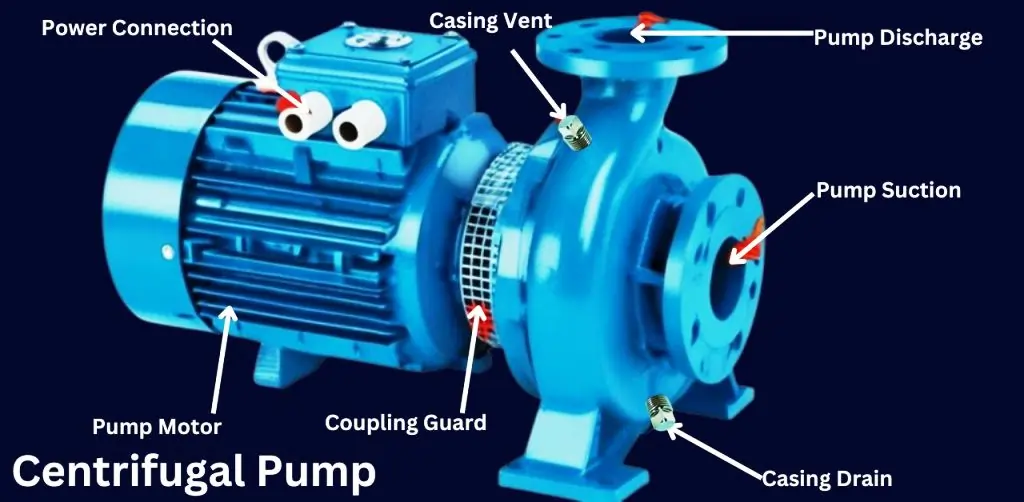
A centrifugal pump is a mechanical device used to move fluids by converting rotational energy from a motor into hydrodynamic energy. It is widely used in marine and industrial applications to transfer liquids such as water, chemicals, and fuel efficiently. The pump operates by using an impeller, which rotates at high speed, creating a centrifugal force that moves the fluid through the system.
Centrifugal Pump Working Principles
The working principle of a centrifugal pump is based on the transfer of rotational energy from an impeller to the fluid. As the impeller rotates, it accelerates the fluid outward from the center (eye) of the impeller to the edges, increasing its velocity. This kinetic energy is then converted into pressure energy as the fluid flows through the volute casing, allowing it to move through the discharge piping.
Key Components of a Centrifugal Pump
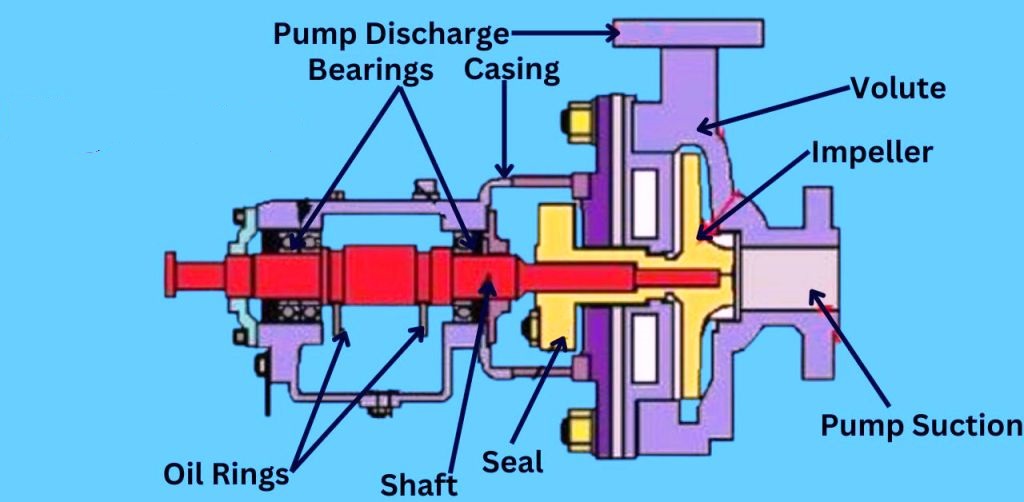
A centrifugal pump operates by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy using centrifugal force. Below are the key components of a centrifugal pump that work together to ensure efficient fluid movement:
1. Pump Discharge
The pump discharge is the outlet where pressurized fluid exits the centrifugal pump. After gaining pressure through centrifugal force generated by the impeller, the fluid is directed through this port to the pipeline or system.
2. Bearing
Bearings support the rotating shaft of the pump, ensuring smooth operation by reducing friction. They are essential for maintaining alignment and minimizing wear on the pump’s rotating parts.
3. Casing
The casing encloses the internal components of the centrifugal pump, providing a protective shell. It guides the fluid from the pump suction to the discharge and helps contain the fluid under pressure.
4. Volute
The volute is a spiral-shaped casing that collects the high-velocity fluid discharged by the impeller and converts its velocity, created by centrifugal forces, into pressure. This ensures smooth fluid flow into the discharge.
5. Impeller
The impeller is the heart of the centrifugal pump, creating the centrifugal force necessary to move the fluid. As the impeller rotates, it accelerates the fluid outward, increasing its velocity and pressure.
6. Pump Suction
The pump suction is the inlet through which the fluid enters the centrifugal pump. It directs fluid into the center (eye) of the impeller, where centrifugal force will move the fluid to the outer edges.
7. Seal
The seal prevents fluid leakage from the pump casing, particularly at the point where the shaft passes through. Proper sealing is critical to maintaining the pressure generated by the centrifugal forces inside the pump.
8. Shaft
The shaft connects the impeller to the motor, transmitting the rotational energy that drives the impeller. This energy is then used to create centrifugal force, which moves the fluid.
9. Oil Rings
Oil rings ensure that the bearings are properly lubricated, reducing friction and wear. This helps maintain the efficient rotation of the shaft and smooth functioning of the pump under centrifugal forces.
Signs That Your Centrifugal Pump Needs Overhauling
Regular maintenance and timely overhauling are essential for ensuring the long-term performance of a centrifugal pump. Below is a table listing common signs that indicate your centrifugal pump may need an overhaul, along with brief descriptions of each issue.
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Efficiency | A noticeable drop in pump performance, such as slower fluid movement or lower pressure, often due to worn-out components or internal obstructions. |
| Unusual Vibrations | Excessive vibrations can be a sign of misalignment, bearing wear, or an imbalanced impeller, all of which require inspection and possible repair. |
| Fluid Leaks | Leaks around seals or gaskets indicate that the sealing components have deteriorated and need replacement to maintain pressure and prevent fluid loss. |
| Abnormal Noises | Grinding, knocking, or whining noises suggest internal damage, such as worn bearings or a faulty impeller, which may require immediate attention. |
| Increased Energy Consumption | A rise in energy usage without corresponding output may be due to internal wear, leading to decreased efficiency and requiring an overhaul. |
| Overheating | Consistent overheating can indicate issues with bearings, lubrication, or flow blockages, signaling the need for internal inspection. |
| Frequent Shutdowns | If the pump shuts down unexpectedly or fails to start, it may be a sign of mechanical or electrical failure, often fixed during overhauling. |
Preparation Before Overhauling a Centrifugal Pump
Proper preparation is essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of the overhauling process of a centrifugal pump. Below are the key steps to take before starting the overhaul:
1. Safety Precautions and Shutdown Procedures
- Lockout/Tagout: Before beginning the overhauling process, ensure the pump is completely disconnected from the power source by following lockout/tagout procedures. This prevents accidental startup during maintenance.
- Depressurization: Ensure the pump and connected piping system are fully depressurized to avoid potential hazards from high-pressure fluids.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE such as gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing to protect against hazardous chemicals or fluids that may still be present in the system.
- Hazard Identification: Conduct a risk assessment to identify any potential hazards specific to the pump or system being overhauled.
2. Tools and Equipment Needed for Overhauling
- Basic Tools: Wrenches, screwdrivers, and torque tools for disassembly and reassembly.
- Lifting Equipment: Hoists or cranes may be required to safely handle and lift heavy components such as the pump casing or impeller.
- Measuring Instruments: Dial indicators, feeler gauges, and micrometers for checking component tolerances and alignment.
- Cleaning Tools: Wire brushes, cleaning solvents, and cloths to clean the pump parts before reassembly.
- Replacement Parts: Seals, bearings, and other consumable components that may need replacement during the overhaul.
- Lubrication Materials: Oils and greases for properly lubricating bearings and other moving parts during reassembly.
3. Draining and Isolating the Pump from the System
- Drain the Pump: Open the drain valves to remove any remaining fluid from the pump and connected piping. Ensure that all fluid is safely disposed of according to environmental regulations.
- Isolate the Pump: Close all inlet and outlet valves to isolate the pump from the system. This prevents the accidental entry of fluid into the pump during the overhaul.
- Vent the System: Open vent valves to release any residual pressure that may remain in the system after draining. This ensures a safe working environment before disassembly.
What is the Procedure for Overhauling of a Centrifugal Pump?
Video credit: https://www.youtube.com/@SailorMan
The overhauling process of a centrifugal pump involves several key steps to ensure that the pump is restored to optimal working condition. Below is the detailed procedure:
Step 1: Disassembly of the Pump
- Disconnecting the Pump from the Piping System: Start by isolating the pump from the system by closing inlet and outlet valves. Ensure the pump is fully drained, and all remaining pressure is released. Disconnect the pump from the piping system and power source.
- Removing the Casing and Inspecting Internal Parts: Carefully remove the pump casing to access the internal components. Inspect the impeller, shaft, bearings, and seals for any visible signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
Step 2: Inspection of Parts
- Detailed Inspection of the Impeller, Seals, Bearings, and Wear Rings: Conduct a thorough inspection of the impeller, seals, bearings, and wear rings. Look for cracks, erosion, or misalignment.
- Checking for Wear, Corrosion, and Alignment Issues: Check for signs of wear on rotating parts, corrosion on metallic surfaces, and ensure the alignment of the shaft and impeller. Any misalignment could cause further damage if not corrected.
Step 3: Cleaning and Repair
- Cleaning All Internal Parts: Use appropriate cleaning agents and brushes to clean all components, ensuring no debris or contamination remains.
- Repairing or Replacing Damaged Parts: If any components, such as the impeller, seals, or bearings, show significant wear or damage, they must be repaired or replaced. Always use parts recommended by the manufacturer for the best fit and longevity.
Step 4: Reassembly of the Pump
- Properly Reassembling the Pump Components Following Manufacturer Guidelines: Reassemble the pump carefully, following the manufacturer’s specifications. Ensure that seals, bearings, and the impeller are correctly positioned.
- Torque Settings and Alignment Checks: During reassembly, use torque wrenches to ensure all bolts and connections are tightened to the manufacturer’s recommended specifications. Check the alignment of the pump shaft to avoid operational issues.
Step 5: Testing After Overhauling
- Running Tests to Ensure Efficient Operation: Once the pump is reassembled, reconnect it to the system and run it under controlled conditions. Check the flow rate, pressure, and overall performance.
- Checking for Leaks, Vibration Levels, and Noise: Monitor the pump closely for any unusual vibrations, noises, or leaks. These could indicate improper assembly or lingering internal issues that need further attention.
Best Practices During Centrifugal Pump Overhauling
Adhering to best practices during the overhauling of a centrifugal pump is essential for ensuring optimal performance, reducing downtime, and extending the pump’s operational life. Below are the key best practices to follow:
1. Importance of Using Original Manufacturer Parts
- Why Use Original Parts: Always use parts supplied or recommended by the original manufacturer during an overhaul. These components are specifically designed for the pump, ensuring perfect fit, proper functionality, and durability.
- Avoiding Non-Genuine Parts: Using non-genuine or aftermarket parts may compromise the pump’s performance, increase wear, and reduce efficiency, potentially leading to early failures.
- Warranty and Compliance: Sticking to original parts also ensures that the pump remains under warranty and in compliance with manufacturer guidelines.
2. Regular Maintenance and Scheduled Inspections
- Prevention Over Cure: Implementing a regular maintenance schedule is essential for catching minor issues before they become significant problems. Early detection of wear or misalignment through scheduled inspections can prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- Inspection Guidelines: During inspections, check key components such as the impeller, shaft, seals, bearings, and wear rings for signs of corrosion, cracks, or misalignment. Use manufacturer-recommended inspection intervals based on the pump’s usage and environment.
- Log Maintenance Data: Maintain detailed records of each inspection and overhaul, including dates, components replaced, and performance data. This helps in tracking the condition of the pump over time and improving future maintenance efforts.
3. Proper Lubrication and Cooling for Extended Pump Life
- Lubrication: Ensure that all bearings and moving parts receive proper lubrication according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, wear, and overheating, ultimately causing premature failure.
- Cooling Systems: Verify that the cooling system, if present, is functioning correctly. Proper cooling is vital in preventing overheating of the pump during extended operation, which can lead to thermal damage and reduced component life.
- Use of Correct Lubricants: Always use the lubricants recommended by the pump’s manufacturer, as using incompatible lubricants can cause damage to seals, bearings, or other internal components.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Overhauling of a Centrifugal Pump
While overhauling a centrifugal pump, certain common mistakes can lead to performance issues, reduced efficiency, or even pump failure. Avoiding these errors is critical to ensuring a successful overhaul. Below are the common mistakes and how to prevent them:
1. Skipping Critical Inspection Points
- Thorough Inspection is Key: One of the most common mistakes during overhauling is not thoroughly inspecting all critical components such as the impeller, seals, bearings, and wear rings. Skipping these inspection points can lead to overlooking potential damage or wear that may affect pump performance.
- Undetected Wear or Corrosion: Failing to check for signs of wear, corrosion, or misalignment in components can result in premature failure after reassembly. Ensure that every internal part is inspected carefully before proceeding with repairs or replacements.
2. Incorrect Reassembly and Alignment Issues
- Following Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Reassembling the pump incorrectly, especially without following the manufacturer’s torque specifications and alignment procedures, can cause serious operational issues. Misaligned shafts or improperly fitted seals can lead to excessive vibration, leaks, or even component failure.
- Checking Alignment: It is crucial to verify the alignment of the pump’s rotating parts, such as the impeller and shaft, during reassembly. Misalignment not only reduces efficiency but also accelerates wear on bearings and seals, shortening the pump’s lifespan.
3. Neglecting to Test the Pump After the Overhaul
- Importance of Post-Overhaul Testing: Once the pump is reassembled, skipping the final testing phase is a critical mistake. Post-overhaul testing helps ensure that the pump operates efficiently and that all components are functioning properly.
- Checking for Leaks, Vibration, and Noise: Conduct a test run under controlled conditions to monitor for leaks, abnormal vibration, or noise. Neglecting this step could result in undetected issues that could damage the pump or system when it is placed back into full operation.
FAQs About Centrifugal Pump Overhauling
Q: What is the centrifugal pump overhaul procedure?
A: The process involves shutting off power, draining the pump, inspecting parts, replacing worn components, and reassembling the pump.
Q: What is a pump overhaul?
A: A pump overhaul restores the pump to like-new condition by replacing damaged or worn parts.
Q: What is the overhauling process?
A: Overhauling involves inspecting the pump, making repairs or replacing parts based on their condition.
Q: Is overhaul the same as repair?
A: Overhaul includes major repairs and changes to restore the pump to full working condition.
Conclusion
Overhauling a centrifugal pump is essential to maintaining its efficiency, extending its lifespan, and preventing costly breakdowns. By following a structured process that includes disassembly, inspection, cleaning, repair, reassembly, and thorough testing, you can ensure that the pump operates at its best. Adhering to best practices such as using original manufacturer parts, conducting regular maintenance, and proper lubrication will further enhance the pump’s reliability. Avoiding common mistakes like skipping critical inspection points, improper reassembly, and neglecting post-overhaul testing is crucial for a successful overhaul. With the right approach, you can keep your centrifugal pumps running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
