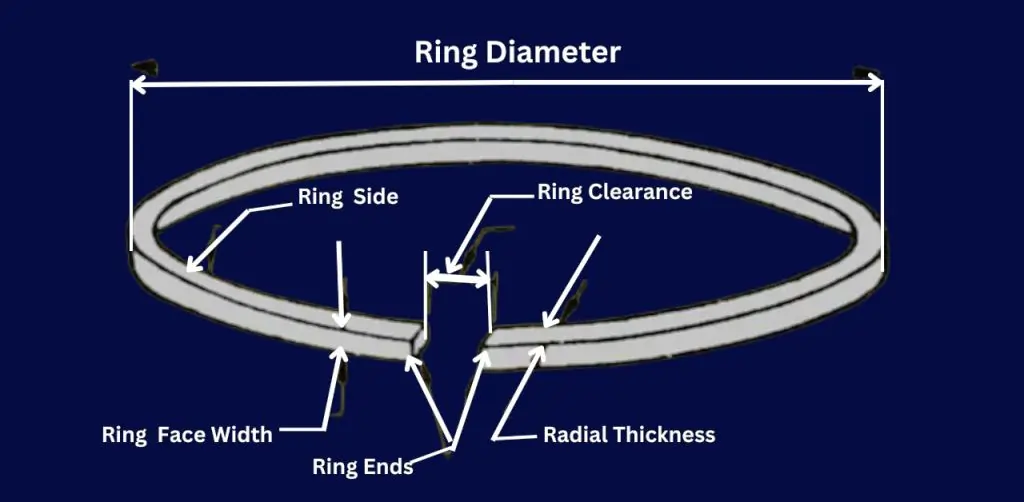
Piston Ring Clearance
Piston rings play a vital role in the smooth operation of marine diesel engines, acting as a seal between the piston and cylinder wall. Their function ensures optimal compression, prevents gas leakage, and controls oil consumption, all of which are crucial for maintaining engine efficiency. However, the effectiveness of piston rings heavily depends on precise clearances—specifically butt, axial, and back (radial) clearance.
These clearances allow the rings to expand and contract with temperature changes, ensuring consistent performance. In large marine diesel engines, where operating conditions are extreme, maintaining proper piston ring clearance is critical to preventing issues like blow-by, excessive wear, and loss of power, all of which could lead to costly repairs and downtime.2. What is Piston Ring Clearance?
What is Piston Ring Clearance?
Piston ring clearance refers to the small gaps between the piston rings and their surrounding components, such as the cylinder wall and piston groove. These clearances allow the piston rings to move freely and perform their function under varying operating conditions, particularly as temperatures fluctuate within a marine diesel engine.
Accurate clearances are essential for maintaining marine engine efficiency. When the clearances are properly set, the piston rings can create an effective seal, preventing gas leakage (blow-by) and controlling oil consumption. This, in turn, ensures optimal compression, improves fuel efficiency, and minimizes wear and tear on engine components. In large marine diesel engines, where performance and durability are critical, even minor deviations in piston ring clearance can lead to significant issues, such as reduced power, increased emissions, and potential engine failure. Regular inspection and maintenance of these clearances are vital to ensure long-term engine reliability.
Butt Clearance in Piston Rings
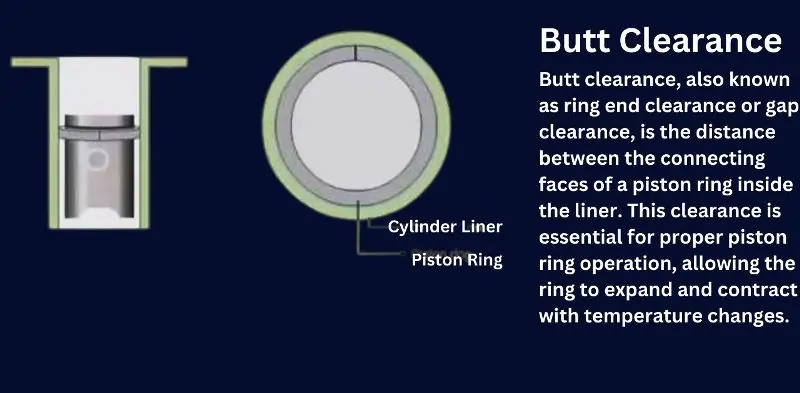
Butt clearance, also known as ring end clearance or gap clearance, is the distance between the connecting faces of a piston ring inside the liner. This clearance is essential for proper piston ring operation, allowing the ring to expand and contract with temperature changes.
- Function of Butt Clearance:
- Allows for thermal expansion of the piston ring during engine operation.
- Prevents excessive wear and maintains an effective seal in the cylinder.
- Impact of Improper Butt Clearance:
- If too small:
- The ends of the ring may touch due to thermal expansion, causing the ring to press against the liner.
- Increased friction can result in ring breakage and piston seizure.
- If too large:
- Combustion gases may blow by the rings, reducing compression pressure.
- Exhaust gases could enter the crankcase, leading to engine inefficiency.
- If too small:
- Measuring and Adjusting Butt Clearance:
- Insert the piston ring at the bottom of the liner, ensuring it aligns with the liner axis.
- Use a feeler gauge to measure the clearance between the ring ends.
- Take measurements at both forward-aft and port-starboard positions.
Keeping butt clearance within manufacturer specifications is critical for maintaining engine performance and preventing damage.
Axial Clearance in Piston Rings
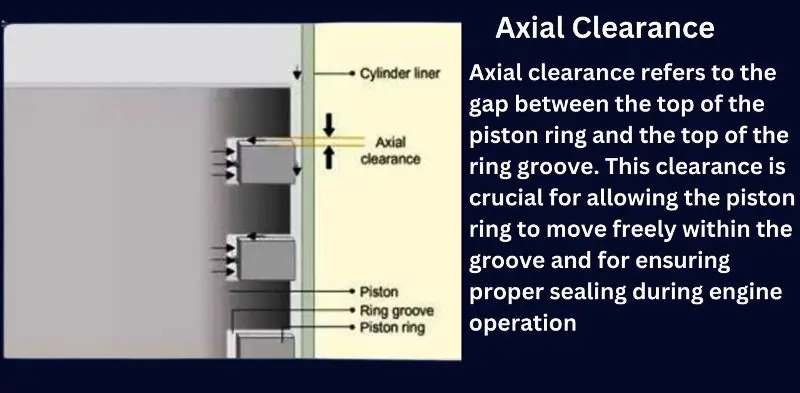
Axial clearance refers to the gap between the top of the piston ring and the top of the ring groove. This clearance is crucial for allowing the piston ring to move freely within the groove and for ensuring proper sealing during engine operation.
- Importance of Axial Clearance:
- It allows combustion gases to exert pressure behind the piston rings, pushing them toward the liner to create a tight seal.
- Proper axial clearance ensures effective gas sealing, preventing blow-by and enhancing engine efficiency.
- Effects of Improper Axial Clearance:
- If too small:
- Combustion gases cannot flow behind the rings, reducing the effectiveness of the seal.
- This may lead to inefficient compression and poor engine performance.
- If too large:
- The ring may not fit tightly, leading to gas leakage and increased wear on the ring and groove.
- If too small:
- Measuring Axial Clearance:
- Fit the piston ring in its respective groove, ensuring it rests on the lower surface of the groove.
- Use a feeler gauge to measure the gap between the top of the ring and the upper surface of the groove.
- Record two sets of readings: forward-aft and port-starboard for accurate assessment.
Maintaining axial clearance within manufacturer-specified limits is essential for optimal piston ring movement, effective sealing, and long-term engine performance in marine engines.
Back Clearance (Radial Clearance) in Piston Rings
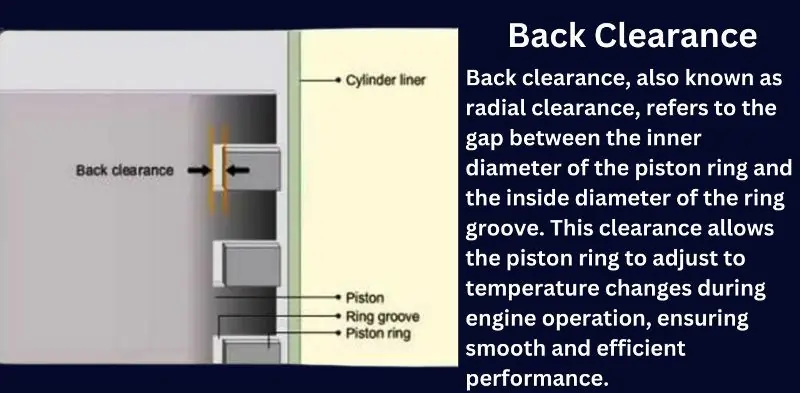
Back clearance, also known as radial clearance, refers to the gap between the inner diameter of the piston ring and the inside diameter of the ring groove. This clearance allows the piston ring to adjust to temperature changes during engine operation, ensuring smooth and efficient performance.
- Role of Back Clearance:
- Ensures that the outer face of the piston ring remains inside the groove and does not make direct contact with the cylinder liner.
- Allows the piston ring to move freely, preventing it from taking side thrust, which could lead to increased friction and potential piston seizure.
- Importance of Proper Back Clearance:
- If there is no back clearance, the piston ring will experience side thrust, leading to excessive friction, wear, and potentially damaging the engine by causing piston seizure.
- Proper clearance prevents mechanical strain on the ring and groove, maintaining engine efficiency.
- How to Check Back Clearance:
- Measure the depth of the piston ring groove using a depth gauge.
- Measure the thickness of the piston ring.
- Take these measurements at least six different positions around the groove circumference for accuracy.
- Calculate the back clearance using the formula:
Back Clearance = Ring Groove Depth – Ring Thickness.
Maintaining correct back clearance during overhauls is critical for allowing piston rings to function effectively in marine engines, ensuring smooth operation and preventing damage.
Important Formulas for Piston Ring Clearance
- Butt Clearance (Ring End Gap)
- Formula: Butt Clearance=Measured Gap Between Ring Ends.
- Ideal Range: Typically 0.05 to 0.10 mm.
- Axial Clearance
- Formula: Axial Clearance=Ring Groove Depth−Piston Ring Thickness
- Ideal Range: Typically 0.025 to 0.076 mm.
- Back Clearance (Radial Clearance)
- Formula: Back Clearance=Ring Groove Depth−Ring Thickness
- Ideal Range: Typically 0.05 to 0.10 mm.
- Side Clearance (Piston to Cylinder Wall)
- Formula: Side Clearance=Cylinder Bore Diameter−Piston Diameter
- Ideal Range: Typically 0.038 to 0.089 mm.
Effects of Incorrect Piston Ring Clearances
Incorrect piston ring clearances, whether insufficient or excessive, can cause significant problems in marine engines. These clearances are crucial for maintaining engine efficiency and preventing premature wear or damage.
- Problems Caused by Insufficient Clearance:
- Excessive Friction: When the clearance is too small, the piston rings cannot expand properly under high temperatures, leading to increased friction between the ring and cylinder wall. This can result in ring breakage, piston seizure, and ultimately, engine failure.
- Reduced Sealing: Insufficient clearance may prevent the piston ring from moving freely within its groove, compromising the seal between the piston and cylinder wall.
- Problems Caused by Excessive Clearance:
- Blow-By: Excessive clearance allows combustion gases to escape past the rings into the crankcase, causing loss of compression, which results in reduced engine power.
- Increased Oil Consumption: When the piston rings do not form a proper seal, engine oil can seep into the combustion chamber, leading to higher oil consumption and exhaust smoke.
Maintaining the proper piston ring clearances is essential to avoid these issues and ensure engine longevity and performance. Regular inspection and precise adjustments during overhauls are critical to preventing these problems.
Tips for Proper Piston Ring Clearance Adjustment
Maintaining optimal piston ring clearance is essential for the smooth operation of marine engines. Follow these practical guidelines to ensure correct adjustments and prevent engine wear or failure.
- Adhere to Manufacturer Specifications:
- Always refer to the engine manufacturer’s clearance limits for butt, axial, and back clearances.
- Deviating from these values can result in reduced performance or engine damage.
- Use Precision Tools:
- Employ precision tools like feeler gauges, depth gauges, and micrometers to measure piston ring clearances accurately.
- Ensure that the piston ring is perfectly aligned within the groove during measurements to get correct readings.
- Measure in Multiple Positions:
- Take measurements at several positions around the piston ring and groove (typically six) to account for irregularities in the ring or groove.
- This ensures that clearances are consistent and even across the entire ring.
- Check Clearances During Engine Overhauls:
- Regularly inspect and adjust piston ring clearances during scheduled overhauls.
- Ensure that the rings, grooves, and liners are clean and free of deposits before measurements.
- Record Measurements for Future Reference:
- Keep detailed records of all clearance measurements taken during maintenance.
- This helps in tracking wear patterns and can aid in future troubleshooting.
By following these tips and using proper measurement techniques, you can maintain the correct piston ring clearances, ensuring long-term engine reliability and efficiency.
FAQ on Piston Ring Clearance
Q: What is proper piston ring clearance?
A: It’s the gap allowing piston rings to expand and seal properly, typically 0.05 to 0.10 mm.
Q: What is the standard piston clearance?
A: Standard piston clearance varies by engine but is usually between 0.038 to 0.089 mm
Q: What is the axial clearance of piston ring?
A: Axial clearance is the gap between the top of the ring and the groove, typically 0.025 to 0.076 mm.
Q: What is the side clearance of a piston?
A: Side or back clearance is typically between 0.05 to 0.10 mm for proper piston movement.
Conclusion
Maintaining proper piston ring clearance is essential for the efficient operation of marine diesel engines. Whether it’s butt clearance, axial clearance, or back (radial) clearance, each plays a critical role in ensuring effective sealing, preventing blow-by, minimizing oil consumption, and maintaining overall engine performance. Incorrect clearances can lead to increased friction, excessive wear, and even catastrophic engine failure. By following manufacturer specifications and using precise measurement techniques, marine engineers can ensure the longevity and reliability of their engines. Regular inspection and adjustment of piston ring clearances during overhauls are key to preventing costly repairs and downtime, making it a vital part of marine engine maintenance.