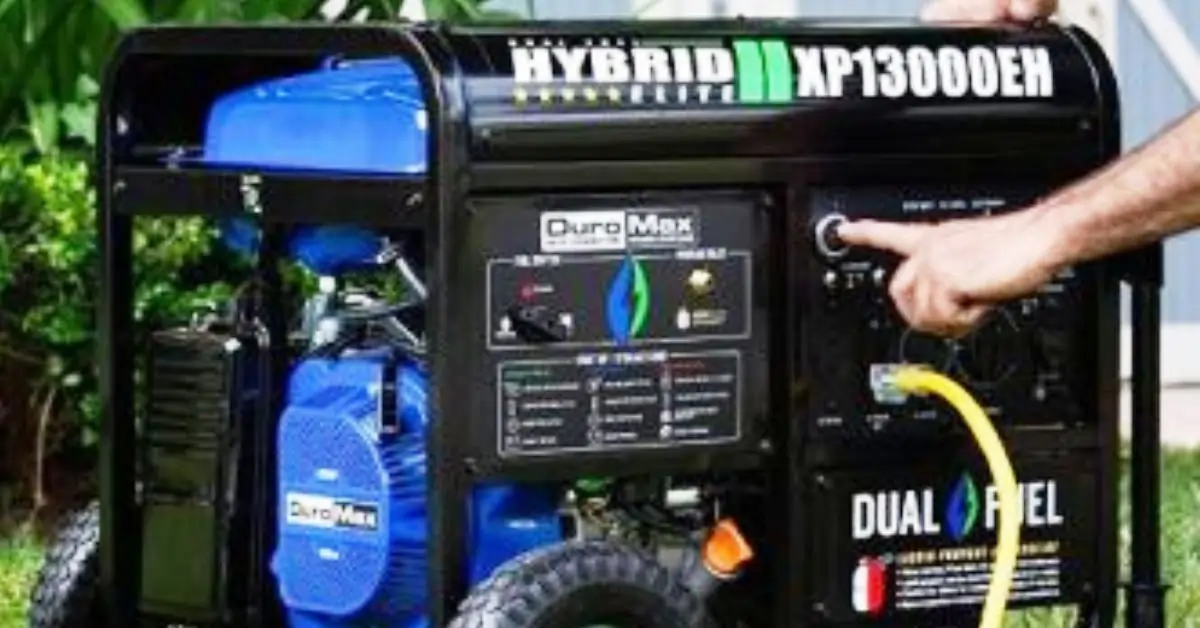
Portable Natural Gas Generator
A portable natural gas generator is a type of power generator that runs on natural gas to produce electricity. It is created to be compact and easy to move, enabling it to be used in various settings like job sites, outdoor events, or emergencies. Unlike gasoline or diesel generators, these generators emit fewer pollutants and have better fuel consumption rates. They are generally quieter and require less upkeep, making them a preferred choice for residential and commercial applications.
Benefits of a Portable Natural Gas Generator

There are several benefits and advantages of using a portable natural gas generator, including:
- Cost-effective fuel source: Natural gas is often less expensive than gasoline or diesel, making it a more affordable option for powering your generator.
- Cleaner emissions: Portable natural gas generators emit lower levels of pollutants, making them a more environmentally friendly choice.
- Reliable power source: Natural gas is a reliable fuel source, with a steady supply available in most areas, making it a dependable option for backup power during emergencies.
- Quieter operation: Portable natural gas generators operate more quietly than traditional generators, making them a better option for use in residential areas or other noise-sensitive environments.
- Lower maintenance: Natural gas generators typically require less maintenance than gasoline or diesel generators, saving you time and money in upkeep.
- Longevity: Natural gas generators tend to have a longer lifespan than traditional generators, providing a more cost-effective and durable solution for your power needs.
Key Formulas for Portable Natural Gas Generator Performance
1. Generator Power Output
This formula calculates the electrical power output of the generator based on its capacity.
P = V×I×PF
Where:
- P = Power output (Watts)
- V = Voltage (Volts)
- I = Current (Amperes)
- PF = Power factor (typically 0.8 to 1)
2. Fuel Consumption Rate
This formula estimates the fuel consumption rate based on the generator’s capacity.
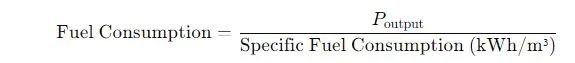
Where:
- Fuel Consumption = Volume of natural gas consumed per hour (m³/h)
- Poutput = Actual power output (kW), which could be a fraction of the generator’s capacity
- Specific Fuel Consumption = Fuel required to produce 1 kWh of energy (m³/kWh)
3. Run Time Calculation
This formula determines the generator’s run time based on its fuel capacity and consumption.
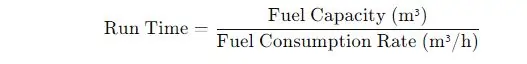
Where:
- Run Time = Operational time before refueling (hours)
- Fuel Capacity = Total fuel storage capacity (m³)
- Fuel Consumption Rate = Rate of fuel consumption based on load (m³/h)
4. Heat Rate
This formula calculates the generator’s efficiency, with capacity factored in.
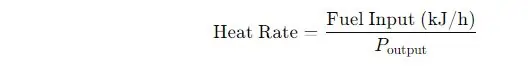
Where:
- Heat Rate = Efficiency measure (kJ/kWh)
- Fuel Input = Energy content of the natural gas used (kJ/h)
- Poutput = Actual power output (kW)
5. Noise Level Calculation
This formula estimates the perceived noise level, taking the generator’s capacity into account.
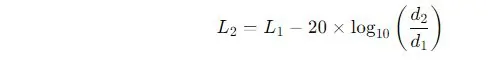
Where:
- L2 = Noise level at distance d2 (dB)
- L1= Noise level at reference distance d1 (dB)
- d1 = Reference distance (e.g., 1 meter)
- d2 = Distance where the noise level is measured
How to Calculate the Right Generator Capacity for Your Needs
1. List All Devices and Appliances
Make a list of all the electrical devices and appliances you intend to power with the generator. Include everything from lights and refrigerators to larger equipment like HVAC systems or industrial machinery.
2. Determine the Power Requirements
For each device, note the power requirement, which is usually listed in watts (W) on the device’s label or in the user manual. If the power is listed in amperes (A), you can convert it to watts using the formula:
Power (W)=Voltage (V)×Current (A)
For example, if an appliance operates at 120V and requires 10A, its power requirement is:
Power (W)= 120V×10A=1200W
3. Consider Starting and Running Watts
Some appliances, especially those with motors, require a higher initial surge of power to start up (starting watts) than they do to run continuously (running watts). Include both values in your calculations:
- Running Watts: Continuous power needed by the appliance to operate.
- Starting Watts: Extra power required for a few seconds to start the appliance.
4. Calculate Total Power Requirement
Add up the running watts of all the devices to get the total running watts. Then, identify the highest starting watts among the appliances (you typically don’t need to add up all starting watts, just consider the highest one).
Total Generator Capacity (W)=Total Running Watts+Highest Starting Watts
5. Apply a Safety Margin
To ensure the generator can handle unexpected surges and to prevent it from running at full capacity all the time (which could reduce its lifespan), it’s advisable to add a safety margin of 1020%:
Required Generator Capacity (W)=Total Generator Capacity (W)×1.2
6. Choose the Generator Capacity
Select a generator with a capacity equal to or greater than the calculated required generator capacity. Generators are typically rated in kilowatts (kW), so convert the final wattage to kilowatts by dividing by 1,000:
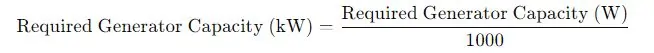
Example Calculation:
Suppose you want to power the following appliances:
- Refrigerator: 800W (running), 1200W (starting)
- Lights: 300W
- TV: 150W
- Air Conditioner: 1500W (running), 3000W (starting)
Total Running Watts:
800W+300W+150W+1500W=2750W
Highest Starting Watts:
3000W(AirConditioner)
Total Generator Capacity:
2750W+3000W=5750W
Adding a 20% Safety Margin:
5750W×1.2=6900W
Generator Size:
6900W/1000=6.9kW
So, you would need a generator with a capacity of at least 7 kW to safely power your devices.
Working of Portable Natural Gas Generators
Parts of a Portable Natural Gas Generator

A portable natural gas generator consists of several key components, including:
- Engine: The engine is the main component of the generator and is responsible for converting natural gas into mechanical energy.
- Alternator: The alternator is connected to the engine and produces electricity through the use of a rotating magnetic field.
- Fuel system: The fuel system delivers natural gas to the engine, which is burned to produce mechanical energy.
- Voltage regulator: The voltage regulator regulates the generator’s output voltage, ensuring that it remains within safe levels.
- Control panel: The control panel allows the user to start and stop the generator, monitor its performance, and adjust its settings.
- Cooling system: The cooling system helps regulate the engine’s temperature, preventing it from overheating during operation.
- Exhaust system: The exhaust system removes the byproducts of combustion from the engine, preventing harmful pollutants from entering the air.
Overall, these components work together to produce a reliable and efficient electricity source for various applications.
Converting Natural Gas to Electricity
- The fuel system delivers natural gas to the engine.
- The natural gas is mixed with air and compressed.
- The compressed mixture is ignited by a spark and combusts, creating mechanical energy.
- The mechanical energy is used to rotate the generator’s alternator.
- The alternator uses a magnetic field to produce an electric current.
- The voltage regulator ensures that the electricity produced remains consistent and safe.
Choosing a Portable Natural Gas Generator: Key Factors

Choosing a portable natural gas generator requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
- Power Output: Determine the amount of power you will need for your intended use, and choose a generator with a suitable power output.
- Fuel Efficiency: Look for a generator that has a high fuel efficiency rating to reduce costs and minimize environmental impact.
- Portability: Consider the weight, size, and ease of transportation of the generator to ensure it can be moved around easily.
- Noise Level: Determine the acceptable noise level for your intended use and choose a generator that meets those requirements.
- Run Time: Consider the length of time you will need the generator to run without refueling and choose one with an appropriate run time.
- Price: Compare the prices of different generators and choose the best value for your budget.
- Safety Features: Look for generators with safety features such as overload protection and automatic shut-off in case of low oil levels.
Considering these factors, you can choose a portable natural gas generator that meets your needs and requirements.
Using and Maintaining a Portable Natural Gas Generator
Setting Up and Operating a Portable Natural Gas Generator
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to set up and operate a portable natural gas generator:
- Choose a well-ventilated area: Find a dry, well-ventilated area away from windows, doors, and vents.
- Connect the fuel source: Connect the natural gas source to the generator using the appropriate fittings and hoses.
- Check the oil level: Check the oil level in the engine and fill it to the recommended level if necessary.
- Turn on the fuel supply: Turn on the natural gas supply and the fuel valve on the generator.
- Start the generator: Pull the starter cord or push the electric start button to start the generator.
- Check the power output: Check the power output of the generator using a multimeter or by plugging in a device to confirm that it is producing electricity.
- Use the generator: Connect your appliances to the generator using the appropriate cords and start using it.
- Monitor the generator: Keep an eye on the generator to ensure it is running smoothly and safely.
- Turn off the generator: Once you are done using the generator, turn off the fuel supply and let it cool down before storing it.
To maintain the generator and maximize its lifespan, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. This may include tasks such as changing the oil, replacing the air filter, and checking the spark plugs. It’s also important to store the generator in a dry, cool area when not in use and to keep it clean and free of debris.
Maximizing the Lifespan of Your Portable Natural Gas Generator
To make sure your portable natural gas generator keeps working well for a long time, here are some simple things you can do:
- Regular Maintenance: Do basic maintenance like changing the oil and replacing the air filter. This keeps the generator running smoothly.
- Proper Storage: Store the generator in a dry and cool place when you’re not using it. This stops rust and damage from happening.
- Good Fuel: Use high-quality natural gas to keep the fuel system clean and ensure the generator works at its best.
- Don’t Overload: Don’t use too much power with the generator. Too much can hurt the engine and make it not last as long.
- Limit Run Time: Use the generator for the time the manufacturer recommends. Using it too much can make it get too hot and cause problems.
- Clean Cooling System: Keep the generator’s cooling system clean from dirt and stuff. This stops it from getting too hot and helps it last longer.
By doing these simple things, you can ensure your portable natural gas generator stays in good shape for many years and gives you power whenever needed.
How long can you run a portable natural gas generator?
Unlike larger standby generators, portable generators are designed to operate for shorter periods, usually ranging from 6 to 18 hours at a stretch.
Portable generators are quite versatile and can be used for different purposes.
However, it’s crucial to note that portable generators are not meant for extended or long-term use, such as during prolonged power outages that last several days or weeks.
For situations requiring longer power backup, standby generators are a better choice. Standby generators are made to keep running nonstop for a long time, which is great for homes, businesses, and places that can’t have the power to go out for a long time.
On the other hand, portable natural gas generators are useful for short-term power needs, like when you’re camping or when the power goes out for a little while. They’re handy and easy to use for these situations. However, they are not recommended for continuous, long-term use, where standby generators are better suited to ensure uninterrupted power during extended outages.
Are natural gas portable generators worth it?
Are natural gas portable generators a good choice? Let’s break it down.
First, compared to generators that use gasoline or diesel, natural gas generators have some benefits. They’re often cost-effective in the long run because natural gas is usually cheaper. Natural gas is a cleaner fuel, so these generators make fewer harmful things that go into the air. That’s good for the planet and for the air we breathe.
But here’s the thing: natural gas generators might not work well for every situation. They’re more flexible than some other generators. You need a natural gas supply to make them run, which means you might need a connection to a natural gas line. This limits where you can use them.
So, are they worth it? A natural gas generator can be a great choice if you have easy access to natural gas and want a cost-effective and eco-friendly way to get power for your home or business. But if you need a more flexible option or don’t have access to natural gas, you should look at other types of generators. It depends on what you need and where you are.
Which is better, an inverter or a portable generator?
It depends on what you need when deciding between an inverter generator and a traditional portable generator.
Inverter generators are like the modern, tech-savvy option. Inverter generators are good because they provide safe power that won’t damage sensitive gadgets like laptops or phones.
On the other hand, traditional portable generators are like the heavy lifters.
However, they’re not as good with sensitive gadgets because their power can be rough around the edges. They can also be noisier compared to inverter generators.
So, in a nutshell, If you want clean, efficient, and quiet power for camping or powering your gadgets, use an inverter generator.
What are the disadvantages of a portable generator?
Portable generators are useful for providing electricity when needed but can also be dangerous. Here are some important things to know:
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Generators produce carbon monoxide, which you can’t see or smell. Breathing in too much of it can make you sick or even kill you. Always use generators outside, away from windows and doors, so this gas doesn’t get inside your home.
Electric Shock: Generators make electricity, and if you don’t use them correctly, you could get an electric shock, like getting a powerful jolt of electricity. To stay safe, follow the instructions carefully when plugging things into the generator, and use special outdoor extension cords.
Fire and Burns: Generators get hot when they run, and if they’re not on a safe surface, they can start fires. It’s essential to put them in a stable, non-flammable spot and keep anything that can catch fire away from them. Also, be careful when adding fuel because spilled fuel can catch fire, too.
Noise: Generators can be very loud, which might bother you and your neighbors. Some generators are quieter than others, so you can choose one that makes less noise if that’s important.
In short, portable generators can be a big help, but they have risks, too. You must use them correctly to avoid problems like carbon monoxide poisoning, electric shocks, fires, and too much noise. Always follow the safety rules to keep yourself and others safe.
Which generator is best for AC?
Choosing the right generator for your air conditioner is important to keep your space cool during power outages or in places without electricity. Here’s a simple guide to help you decide:
Small Air Conditioner (Around 5000 BTU): If you have a small window unit like that in a bedroom or small living space, a generator with a power output of around 1000 watts should do the trick. This will let you comfortably run the AC and a few other small devices.
Medium Air Conditioner (Around 8000-10,000 BTU): For medium-sized window air conditioners, which are often used in larger rooms or spaces, a generator with a capacity of at least 1250 watts is recommended. This ensures your AC runs smoothly without any issues.
Large Air Conditioner (Around 14,000 BTU): If you have a larger window unit with about 14,000 BTUs, you’ll need a more powerful generator. A 2000-watt generator should be sufficient to keep your AC and other appliances running.
Multiple Appliances: If you want to power your AC and other appliances simultaneously during an outage, using a larger generator is a good idea. A 3000-watt generator or more will allow you to run your AC, lights, fans, and even a refrigerator.
In summary, the size of the generator you need for your air conditioner depends on the BTU rating of your AC unit. A 1000-watt generator is suitable for small ACs, a 1250-watt generator for medium-sized units, and a 2000-watt generator for larger ones. If you plan to power multiple appliances, consider a generator with higher wattage to ensure all your needs are met. Choosing the right generator to stay comfortable when the heat is on is essential.
Why do portable generators fail?
Portable generators are like superheroes during power outages, but sometimes, they can let you down when you need them the most. Knowing why they might not work can help you avoid problems and ensure your generator is always ready to save the day.
Battery Troubles: Imagine the battery in your car; generators have something similar. They need a good battery to start up and control their functions. If the battery isn’t working well because of loose connections or something called sulfation (it’s like a battery getting clogged), the generator might not start. Regularly taking care of the battery by cleaning it and making sure it’s connected properly is important to avoid this issue.
Cooling Down Matters: Generators have engines that can get hot when they’re running. To stop them from getting too hot and breaking, they’re designed to turn off automatically if they get too hot. But if there’s not enough coolant (it’s like water for the engine) to keep them cool, they might shut down unexpectedly. Making sure there’s enough coolant is crucial.
Fuel Problems: Just like your car needs good fuel, generators do too. If the fuel is old or dirty, it can clog up the generator’s fuel system, making it stall or not start. Checking the fuel and using additives to keep it clean can prevent this problem.
Maintenance Matters: Generators need love and care, just like machines. Things like dirty air filters, clogged fuel filters, or old spark plugs can mess up how they work and cause them to fail. Regularly looking after your generator, as the manufacturer recommends, is the way to keep it working well.
Don’t Overload: Generators have limits. If you plug in too many things at once, it’s like asking someone to carry too much, and they might give out. Knowing how much your generator can handle and not exceed that limit is important.
Getting Old: Everything gets older, even generators. Over time, parts can wear out, and the generator might not work as well as it used to. Regular maintenance can help it last longer, but eventually, it might need to retire.
So, while generators are awesome, they can have issues. Taking care of them and understanding these common problems can help you have a reliable backup power source for when you need it.
Blog post conclusion
Portable Gas Generators are the best source to meet your emergency power requirements.
Please take into account these critical factors when selecting a generator. Also, it’s a good idea to follow a basic guide for putting it together and running it and to do some easy maintenance.
With the appropriate portable natural gas generator and regular care, you can stay connected to electricity wherever you are.
In addition to the power source, you also get peace of mind when choosing a portable Natural gas generator. So, whether for your home, outdoor activities, or off-grid adventures, a portable natural gas generator can keep you powered up, no matter the circumstances.
FAQ and answers on portable natural gas generators
Q: What is a portable natural gas generator?
A: A portable natural gas generator is a device that converts natural gas into electricity for various applications.
Q: How does it work?
A: It works by burning natural gas to turn an internal combustion engine, which, in turn, generates electrical power.
Q: What are the advantages of a portable natural gas generator?
A: Portable natural gas generators are efficient, produce cleaner emissions, and are often more cost-effective than other fuel options.
Q: Can I use a portable natural gas generator indoors?
A: No, it’s important to use them in well-ventilated outdoor or well-ventilated spaces due to exhaust and safety considerations.
