Proximity Switch Sensor
Proximity Switch Sensors are essential in modern automation, detecting objects without direct contact. They operate on principles like inductive, capacitive, and magnetic, each suited for different environments. These sensors are crucial for improving efficiency, reducing mechanical wear, and enhancing safety in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and packaging. For instance, they keep assembly lines running smoothly in manufacturing and aid in parking assistance in the automotive sector.
In this post, we will explore the top four types of Proximity Switch Sensors, their unique benefits, and common applications. Understanding these aspects will help you select the best sensor for your needs, leading to optimized performance and increased productivity.
Inductive Proximity Sensors
Operating Principle
Inductive Proximity Sensors operate based on the principle of electromagnetic fields. These sensors generate an oscillating electromagnetic field through a coil. When a metallic object enters this field, it induces eddy currents in the metal, causing a change in the electromagnetic field. This change is detected by the sensor, which then triggers an output signal indicating the presence of the metallic object.
Key Applications
- Manufacturing Processes: Inductive Proximity Sensors are extensively used in manufacturing to detect the presence and position of metal components. They ensure precise and efficient operations by continuously monitoring parts in automated systems.
- Assembly Lines: On assembly lines, these sensors are crucial for controlling and monitoring the movement of metallic parts. They help maintain the accuracy and timing of each step in the assembly process, enhancing productivity and reducing errors.
- Metal Detection: Inductive sensors are ideal for metal detection applications, ensuring that metallic objects are accurately identified and tracked. This is vital in quality control, safety systems, and material handling processes.
- Marine Applications: In the marine industry, Inductive Proximity Sensors monitor the positions and movements of metal components in various equipment and machinery. They are essential for navigation systems, detecting metal obstructions, and ensuring the proper functioning of metal parts in harsh marine environments.
Benefits
- High Reliability in Industrial Environments: Inductive Proximity Sensors are highly reliable, providing consistent performance in challenging industrial settings. They are unaffected by dust, dirt, or oil, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- Durable and Robust Design: These sensors are designed to be durable and robust, withstanding mechanical stress, vibrations, and temperature fluctuations. Their sturdy construction ensures a long lifespan and reduced maintenance needs.
Proximity Switch Sensor Circuit Description
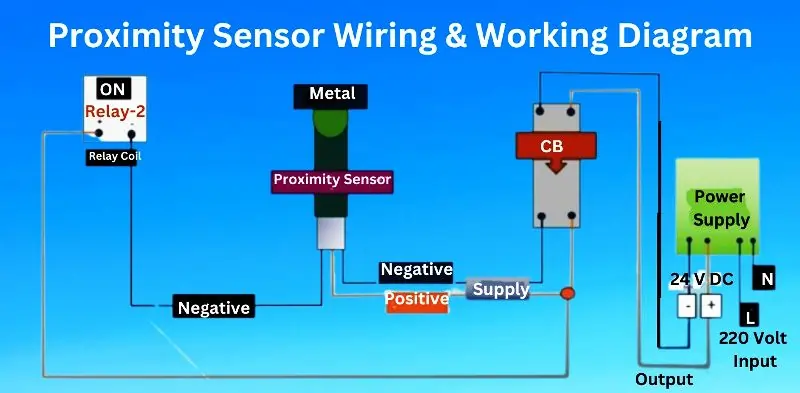
Components
- Power Supply:
- 24 V DC: This is the primary power supply for the proximity sensor and the relay circuits. It provides a stable voltage required for the operation of the sensor and control components.
- N (Neutral) and L (Live): These refer to the AC power lines supplying 220V AC to the power supply unit that converts it to 24V DC.
- 220 Volt Input:
- This is the main AC power source supplying 220V AC to the power supply unit.
- Output:
- The output from the proximity sensor is typically a switching signal (either digital or analog) that activates other components in the circuit, such as relays.
- CB (Circuit Breaker):
- A circuit breaker is used to protect the electrical circuit from overload or short circuit conditions. It ensures safety by disconnecting the power supply in case of a fault.
- Metal:
- The target object that the proximity sensor detects. When the metal object comes close to the sensor, it triggers the sensor’s output.
- Proximity Sensor:
- The primary sensing component that detects the presence of the metal object. It operates based on the principle of inductance or capacitance changes. When the metal object is within the sensing range, the sensor output changes state (ON/OFF).
- Supply:
- Negative (–): The negative terminal of the 24V DC power supply.
- Positive (+): The positive terminal of the 24V DC power supply.
- Relay Coil:
- A relay coil is an electromagnet that, when energized, activates the relay switch. This allows the circuit to control high-power devices with low-power signals from the proximity sensor.
- ON:
- This indicates the state of the relay or other output device. When the proximity sensor detects the metal object, it changes its state to “ON,” energizing the relay coil.
- Relay-2:
- This is an additional relay in the circuit, used to control another part of the system or to provide additional isolation and control.
Circuit Operation
- Power Supply and Conversion:
- The circuit receives 220V AC from the main power lines (L and N). The power supply unit converts this 220V AC to 24V DC, which is used to power the proximity sensor and relay coils.
- Sensor Detection:
- The proximity sensor is connected to the 24V DC supply. It continuously monitors the presence of the metal object. When the metal object comes close to the sensor, it detects the object and changes its output state.
- Signal Transmission:
- The output signal from the proximity sensor is sent to the relay coil. The sensor’s output can be either normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC), depending on the configuration.
- Relay Activation:
- When the sensor detects the metal object and its output state changes to “ON,” the relay coil is energized by the 24V DC supply. The energized relay coil closes the relay contacts, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
- Relay-2 Operation:
- If there is a second relay (Relay-2) in the circuit, it can be configured to perform additional functions, such as controlling another part of the system. Relay-2 is activated by the same or a different signal from the proximity sensor, providing more complex control options.
- Circuit Protection:
- The circuit breaker (CB) ensures that in case of an overload or short circuit, the power supply is cut off to prevent damage to the circuit components.
Faraday’s Law of Induction in Inductive Proximity Sensors

Explanation
Electromagnetic Field Generation: The sensor’s coil generates an oscillating electromagnetic field. This field is produced by an alternating current passing through the coil.
Detection of Metallic Objects: When a metallic object enters the electromagnetic field, it induces eddy currents within the metal. These eddy currents create their own magnetic fields that oppose the original field (Lenz’s Law). This interaction causes a change in the total magnetic flux Φ through the coil.
Induced EMF: According to Faraday’s Law, the change in magnetic flux Φ induces an electromotive force ε in the coil. The sensor circuitry detects this change in EMF, which is then processed to determine the presence of the metallic object.
Capacitive Proximity Sensors
Operating Principle
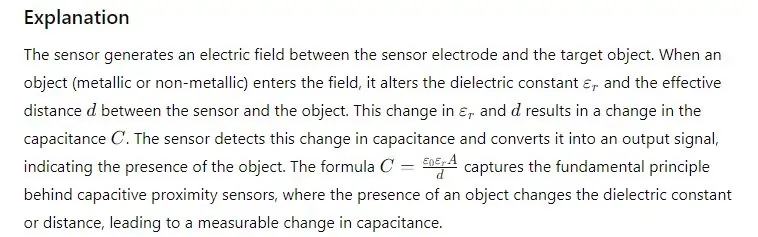
Capacitive Proximity Sensors operate based on the principle of capacitance changes. These sensors consist of two conductive plates, one of which acts as the sensor electrode and the other as the target. When an object (either metallic or non-metallic) approaches the sensor, it changes the dielectric constant between the plates, resulting in a change in capacitance. The sensor detects this capacitance change and generates an output signal indicating the presence of the object.
Key Applications
- Plastic and Liquid Detection: Capacitive Proximity Sensors are highly effective in detecting plastic and liquid materials. They are used in applications such as level detection in tanks and containers, ensuring accurate monitoring and control of material levels.
- Packaging Industries: In packaging industries, these sensors are employed to detect and count items such as plastic bottles, cartons, and containers. They help automate the packaging process, ensuring efficiency and accuracy.
- Material Handling: Capacitive sensors play a crucial role in material handling applications by detecting the presence and position of various materials. They are used in conveyor systems, robotic arms, and automated storage systems to ensure smooth and precise operations.
- Marine Applications: In marine environments, capacitive proximity sensors are used for detecting the levels of liquids in tanks and monitoring the presence of materials in various containers. They are essential for navigation systems, ballast tank monitoring, and ensuring the proper functioning of equipment in harsh marine conditions.
Benefits
- Versatility in Material Detection: Capacitive Proximity Sensors are versatile and can detect a wide range of materials, including plastics, liquids, and non-metallic substances. This makes them suitable for diverse applications across different industries.
- Suitable for Diverse Industrial Uses: These sensors are designed to withstand challenging industrial environments. Their ability to detect both metallic and non-metallic objects makes them ideal for various industrial uses, from manufacturing to packaging and material handling.
Capacitive Proximity Sensors are essential components in modern automation systems, offering reliable and versatile detection capabilities. Their ability to detect a wide range of materials and suitability for diverse industrial and marine applications make them valuable assets in enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Formula for Capacitive Proximity Sensors
The capacitance CCC of a capacitive proximity sensor, modeled as a parallel plate capacitor, can be calculated using the formula:

Photoelectric Proximity Sensors
Operating Principle
Photoelectric Proximity Sensors operate based on the principle of light beam interruption. These sensors emit a beam of light, usually infrared, from a transmitter. When an object interrupts this light beam, the sensor detects the change and generates an output signal.
The basic working involves three key components:
- Transmitter (Light Source): Emits a continuous beam of light.
- Receiver (Photodetector): Detects the light beam.
- Control Unit: Processes the signal from the receiver and generates an output.
When the emitted light beam is interrupted by an object, the receiver no longer detects the light, prompting the control unit to switch the sensor’s output state, indicating the presence of the object.
Key Applications
- Packaging Systems: Photoelectric sensors are widely used in packaging systems to detect the presence or absence of items. They ensure that packages are correctly positioned and help in triggering actions such as sorting, filling, and sealing.
- Conveyor Belt Monitoring: These sensors are crucial in monitoring objects on conveyor belts. They detect objects passing by and can be used to count items, detect jams, or trigger other automated responses to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
- Object Counting and Sorting: In various industries, photoelectric sensors are employed for counting and sorting objects. They provide accurate and high-speed detection, essential for automated processes in manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution.
Benefits
- High Accuracy and Speed: Photoelectric sensors offer precise detection and quick response times, making them suitable for high-speed applications.
- Non-contact Detection: As these sensors detect objects without physical contact, they are ideal for applications where the target objects should not be touched or contaminated.
- Versatile and Flexible: They can detect a wide range of materials, including transparent, opaque, and reflective objects, providing versatility in various industrial applications.
Formula
While there isn’t a specific formula directly used in the basic functioning of photoelectric proximity sensors, understanding the intensity of light and the distance for optimal performance can involve the Inverse Square Law of light, which states:

Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
Operating Principle
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors operate by emitting ultrasonic pulses and measuring the time it takes for the echoes to return after hitting an object. This time-of-flight measurement is used to calculate the distance to the object based on the speed of sound in the medium.
- Ultrasonic Pulses: The sensor emits high-frequency sound waves (typically above 20 kHz, which is beyond the range of human hearing) from a transducer.
- Echo Return Time: When these sound waves hit an object, they reflect back to the sensor. The sensor’s receiver then detects the echoed sound waves.
- Distance Calculation: The sensor calculates the distance to the object using the formula:

Key Applications of Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
| Key Applications | Description |
|---|---|
| Level Measurement | Ultrasonic sensors are used to measure the level of liquids or solids in tanks and silos. They provide accurate level readings, which are crucial for inventory management and process control. |
| Distance Measurement | These sensors are used to measure distances in various applications, such as in automated storage and retrieval systems, ensuring precise placement and retrieval of items. |
| Obstacle Detection in Robotics | In robotics, ultrasonic sensors help detect obstacles, enabling robots to navigate safely. They are essential for collision avoidance and path planning in autonomous systems. |
Benefits of Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Suitable for Harsh Environments | Ultrasonic sensors can operate reliably in harsh environments, including those with dust, smoke, or steam, where optical sensors might fail. |
| Accurate Measurement of Distances | These sensors provide highly accurate distance measurements, making them suitable for applications requiring precise detection and control. |
| Non-contact Measurement | Ultrasonic sensors measure distances without physical contact with the target object, making them ideal for applications where the target should not be touched or contaminated. |
Key Features and Advantages of Proximity Switch Sensors
| Key Features | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Non-contact Detection | Minimizes wear and tear<br>Enhances sensor lifespan |
| Versatility | Detection of various materials<br>Application flexibility |
| Reliability | Consistent performance<br>Durable in different environmental conditions |
| Safety | Avoids physical contact<br>Reduces risk of damage to objects or machinery |
Common Applications of Proximity Switch Sensors
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation and Manufacturing | Part detection and machinery control |
| Security Systems | Intruder detection<br>Access control systems |
| Automotive Industry | Parking sensors<br>Collision avoidance systems |
| Robotics | Navigation and obstacle avoidance |
Detailed Descriptions
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation and Manufacturing | Proximity switch sensors are crucial for part detection and machinery control in automated systems. They ensure precise and reliable operation, improving production efficiency and reducing downtime. |
| Security Systems | In security systems, these sensors are used for intruder detection and access control. They provide a non-contact method to monitor and secure areas, enhancing safety and security. |
| Automotive Industry | Proximity switch sensors are essential in automotive applications such as parking sensors and collision avoidance systems. They help in detecting obstacles and ensuring safe navigation of vehicles. |
| Robotics | In robotics, proximity switch sensors are used for navigation and obstacle avoidance. They enable robots to detect and maneuver around objects, ensuring efficient and safe operation in various environments. |
FAQ on Proximity Switch Sensor
Q: What are the benefits of using proximity switch sensors?
A: They offer non-contact detection, versatility, reliability, and enhanced safety in various applications.
Q: What are common applications of proximity switch sensors?
A: They are used in automation and manufacturing, security systems, automotive industry, and robotics.
Q: How does a proximity switch sensor work?
A: It operates by emitting an electromagnetic field or a beam of light and detecting changes when an object enters its range.
Q: What is a proximity switch sensor?
A: A proximity switch sensor detects the presence or absence of objects without direct physical contact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, proximity switch sensors are indispensable components in modern automation and control systems. We have explored their operating principles, key applications, and benefits across various industries. These sensors, with their non-contact detection capability, enhance operational efficiency and safety in manufacturing, security systems, automotive, and robotics.
Selecting the right proximity switch sensor is crucial for optimizing performance in specific applications. Understanding the different types of sensors and their unique benefits ensures you choose the most suitable one for your needs, leading to improved accuracy, reliability, and longevity of your systems.
The versatility of proximity switch sensors allows them to detect various materials and perform consistently in diverse environmental conditions. Their ability to provide non-contact detection minimizes wear and tear, enhancing the lifespan of both the sensor and the machinery. By integrating proximity switch sensors into your applications, you can achieve precise control, reduce downtime, and enhance overall productivity.
Investing in the right proximity switch sensor not only improves efficiency but also ensures the safety and reliability of your operations, making them a valuable asset in any industrial or automation setup.
