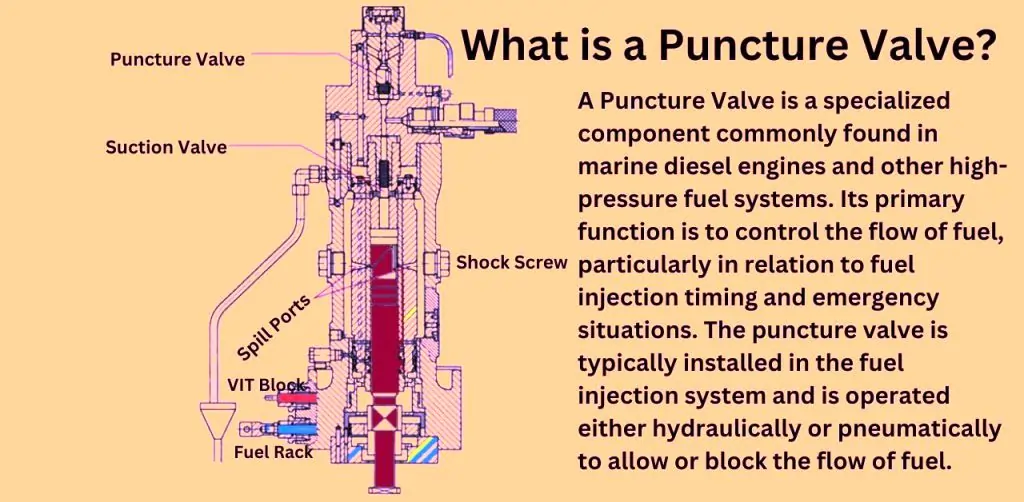
What is Puncture Valves
A puncture valve is a critical component in marine diesel engines, designed to regulate fuel injection and ensure the safety of the engine. Found within the high-pressure fuel system, the puncture valve controls the flow of fuel to the injectors, playing a key role in the smooth operation of marine engines. In emergency situations or during engine malfunctions, the puncture valve can instantly cut off the fuel supply, helping to prevent potential damage or catastrophic engine failure.
This function not only enhances operational safety but also protects the engine from issues like fuel overloading or runaway conditions. By precisely controlling when and how fuel is delivered, puncture valves ensure optimal engine performance and prevent costly damage, making them an essential safeguard in marine engineering. Proper understanding and maintenance of these valves are vital for reliable, long-term engine operation.
What is a Puncture Valve?
A puncture valve is a vital safety device used in marine diesel engines to regulate the flow of fuel. Its primary function is to control or completely stop the injection of fuel into the combustion chamber under certain conditions, such as during engine shutdowns or in emergency situations. This ensures that the engine does not receive fuel when it’s not needed, preventing uncontrolled combustion and potential damage to the engine.
Definition and Basic Explanation of a Puncture Valve
The puncture valve is designed to interrupt fuel delivery by closing off the fuel passage to the injectors. It can be operated hydraulically, pneumatically, or mechanically depending on the engine design. When activated, the puncture valve effectively halts fuel injection, either to stop the engine or protect it from operating under unsafe conditions like overheating or overloading.
Where Puncture Valves Are Typically Used in Marine Diesel Engines
Puncture valves are commonly found in high-pressure fuel injection systems of large marine diesel engines, particularly in those used on ships and marine vessels. These engines require precise control over fuel injection to operate efficiently and safely, making the puncture valve an essential component for both routine operations and emergency shutdowns.
Function of a Puncture Valve
The puncture valve plays a crucial role in controlling fuel injection in marine diesel engines. Its primary function is to regulate and, when necessary, halt the flow of fuel to the injectors, ensuring that the fuel injection process occurs precisely when required. This ability to control fuel delivery is vital for maintaining efficient engine performance and preventing engine damage in abnormal conditions.
Role of Puncture Valves in Fuel Injection Control
The puncture valve is integrated into the engine’s high-pressure fuel system, where it governs the injection of fuel into the combustion chamber. During normal operation, the valve allows the proper amount of fuel to be injected at the right time to ensure optimal combustion. In the event of an emergency or when the engine needs to shut down, the puncture valve is activated to stop fuel from being injected into the cylinders.
How the Puncture Valve Prevents Fuel from Entering the Combustion Chamber
When the puncture valve is triggered, it closes off the fuel passage to the injectors, effectively blocking any fuel from entering the combustion chamber. This prevents unwanted combustion, which can occur during engine overloads, malfunctions, or during shutdowns. By halting the fuel injection process, the puncture valve ensures that the engine remains safe and avoids potential damage caused by uncontrolled fuel entry.
Key Safety Mechanisms of the Puncture Valve
The puncture valve is a vital safety mechanism in marine diesel engines, designed to protect the engine from damage during emergency situations and operational malfunctions. Its ability to immediately control and stop fuel injection makes it an essential component for ensuring the engine operates safely, even under adverse conditions.
How Puncture Valves Protect the Engine in Emergency Situations
During emergencies such as engine overheating, overloading, or fuel system failure, the puncture valve activates to cut off the fuel supply to the injectors. By preventing further fuel injection, the valve ensures that combustion stops, reducing the risk of severe engine damage or hazardous operating conditions. This rapid response is crucial for minimizing potential harm to both the engine and the surrounding machinery, protecting the vessel’s overall safety.
Role in Preventing Engine Runaway and Stopping Fuel Injection During Malfunctions
Engine runaway occurs when an engine continues to operate uncontrollably, even after the throttle is closed. The puncture valve acts as a safeguard in such scenarios by shutting down the fuel supply, effectively stopping fuel from entering the combustion chamber. By halting fuel injection, the puncture valve prevents engine runaway, which could otherwise lead to catastrophic engine failure. This function is also critical in other malfunctions where fuel delivery needs to be immediately interrupted to avoid further engine damage.
In essence, the puncture valve serves as a fail-safe mechanism, ensuring that the engine remains under control in both routine operations and emergencies.
Types of Puncture Valves
Puncture valves come in various designs, each suited to different applications based on the engine type and operational requirements. The most common types include hydraulic, pneumatic, and mechanical puncture valves. Each of these designs offers unique functionalities and is applied in different marine engine systems to effectively control fuel injection and safeguard engine performance.
Hydraulic Puncture Valves
Hydraulic puncture valves use pressurized hydraulic fluid to control the opening and closing of the fuel passage. These valves are highly reliable, as they provide precise control over fuel injection and can be easily integrated into complex engine systems.
- Applications: Hydraulic puncture valves are commonly found in large marine engines that require high levels of accuracy and control, such as in propulsion systems or heavy-duty industrial marine engines. They are often used in systems where rapid response and high-pressure control are necessary.
Pneumatic Puncture Valves
Pneumatic puncture valves operate using compressed air to activate the valve mechanism. These valves are known for their simplicity and ease of maintenance, as they do not rely on intricate hydraulic systems.
- Applications: Pneumatic puncture valves are typically used in medium-sized marine engines and auxiliary systems. They are favored in applications where lower maintenance complexity and ease of operation are important, such as in shipboard auxiliary engines and generators.
Mechanical Puncture Valves
Mechanical puncture valves are operated manually or through mechanical linkages. These valves are more straightforward in design and do not rely on external power sources like hydraulic fluid or compressed air. However, they require manual or mechanical input to function.
- Applications: Mechanical puncture valves are usually found in smaller marine engines or backup systems where automatic control may not be necessary. They are often used in older engine designs or simpler systems that do not demand sophisticated control mechanisms.
Advantages of Using a Puncture Valve
The puncture valve offers significant advantages in marine engine operations, particularly in terms of safety and operational efficiency. As a critical component in the fuel injection system, it ensures that the engine runs smoothly under normal conditions and protects it during emergencies by halting fuel supply when necessary.
Safety Benefits for Marine Engine Operations
One of the primary advantages of a puncture valve is its ability to enhance safety within marine engine operations. By controlling the flow of fuel to the engine, the puncture valve prevents dangerous situations like engine overloads, excessive heat, or runaway engines, which could result in severe damage or failure. It acts as a safeguard by immediately cutting off fuel supply when abnormal conditions are detected, helping to avoid accidents or catastrophic engine damage. This automatic response ensures that the engine operates within safe parameters at all times.
Efficient Engine Shutdown and Emergency Response
The puncture valve is also highly efficient in facilitating engine shutdown, especially in emergency situations. When an emergency arises, such as an overheating engine or a malfunctioning fuel system, the puncture valve swiftly cuts off the fuel injection, effectively stopping the engine and preventing further harm. This fast response minimizes the risk of damage and reduces downtime, as it allows the crew to address the issue quickly and resume operations with minimal delays. Additionally, it ensures a controlled shutdown that avoids sudden power loss, protecting other engine components from strain.
Common Issues and Maintenance of Puncture Valves
| Common Issues and Maintenance of Puncture Valves | Details |
|---|---|
| Potential Malfunctions | How to Detect Them |
| Sticking or Seized Valves | Valves may become stuck due to carbon buildup, debris, or contaminants, causing uncontrolled fuel flow or failure to shut off fuel supply. |
| Leakages | Worn-out seals or damaged components may cause the valve to leak, leading to improper fuel control and loss of fuel pressure. |
| Valve Actuator Failure | Hydraulic or pneumatic actuators can lose efficiency due to mechanical wear, fluid contamination, or loss of pressure, leading to delayed or failed valve operation. |
| Regular Maintenance Practices | To Ensure Valve Performance |
| Routine Cleaning | Clean the puncture valve and fuel system to prevent carbon buildup and debris. Regular flushing helps avoid contamination. |
| Seal and Component Inspection | Regularly inspect seals, gaskets, and components for wear or damage. Replace them as part of preventive maintenance to prevent leaks. |
| Actuator Maintenance | Check for fluid contamination and ensure proper pressure levels. Inspect and calibrate actuators for optimal performance. |
| Regular Testing | Conduct routine valve testing to ensure proper shutoff function and respond to control signals, identifying potential issues early. |
FAQs on Puncture Valve
Q- What is a puncture valve?
A- A puncture valve controls and stops fuel injection in marine engines to prevent uncontrolled combustion.
Q- How does a puncture valve enhance engine safety?
A- It cuts off the fuel supply in emergencies, preventing engine damage and runaway situations.
Q- What are the types of puncture valves?
A- Puncture valves come in hydraulic, pneumatic, and mechanical designs, suited to different engine types.
Q- What causes puncture valve malfunctions?
A- Common causes include carbon buildup, fluid contamination, worn seals, or actuator failure.
Conclusion
The puncture valve is an essential safety component in marine diesel engines, playing a crucial role in controlling fuel injection and preventing uncontrolled combustion. By ensuring that fuel injection can be stopped immediately in emergency situations, the puncture valve helps protect the engine from potential damage and dangerous conditions like engine runaway. With different designs, including hydraulic, pneumatic, and mechanical, puncture valves are suited to a variety of marine engine systems. Regular maintenance and proper inspection are key to avoiding common issues like carbon buildup, fluid contamination, and actuator failure, ensuring the reliable performance of the valve and the safety of the engine.