Retrofit Emission Control Device
The electricity demand is larger than ever in today’s quickly changing world, and many sectors rely on diesel generators (DG) to deliver a steady power supply in remote areas or during grid outages. However, the environment and public health may suffer as a result of the emissions generated by these DG sets. Retrofitting DG sets with emission control technology has become a vital solution to address this problem. This blog post will go over the principles of retrofitted emission control technology for distributed generation systems, its significance, and how it may help your business and the environment.
What Is Retrofitted Emission Control Equipment For DG Set
Devices or systems added to current diesel generators to lessen the hazardous pollutants they emit into the environment are referred to as retrofitted emission control equipment for DG sets. Before pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM) are released into the atmosphere, this apparatus is designed to either catch or convert them into less hazardous forms. This procedure serves to improve public health and air quality in addition to helping to comply with environmental requirements and standards. Businesses may ensure that their diesel generators run more cleanly and minimize their environmental impact while ensuring a steady supply of electricity by adding emission control technology.
Why Emission Upgrades Matter for DG Sets
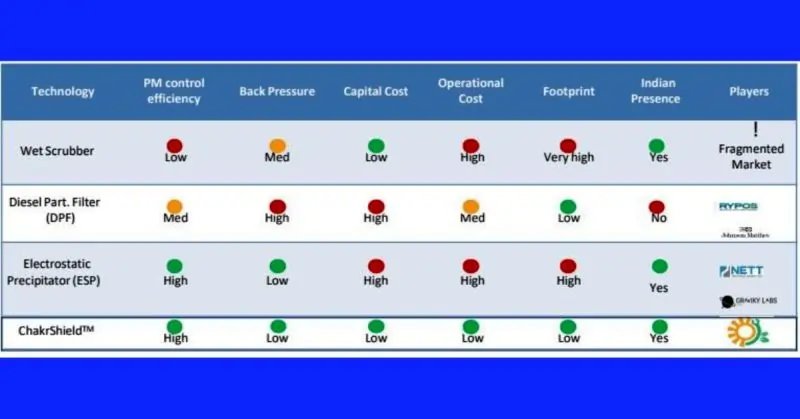
Retrofitting emission control equipment onto diesel generators (DG sets) is a crucial environmental and health safeguard in our increasingly industrialized world. This measure addresses the significant challenge of mitigating air pollution from one of the most common sources of backup and remote power supply. Here are the key reasons that underline the importance of installing such systems:
- Environmental Protection: DG sets release a variety of harmful emissions, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM), which contribute to air pollution and climate change. Retrofitting emission control equipment significantly reduces these pollutants, protecting the environment from their detrimental effects.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many regions have strict regulations governing the emissions from diesel generators. Retrofitting emission control equipment ensures compliance with these laws, helping businesses avoid fines and legal issues while contributing to national and global efforts to reduce pollution.
- Health Benefits: The pollutants emitted by DG sets can have severe health impacts, including respiratory problems, heart disease, and cancer. By reducing these emissions, retrofitting emission control equipment directly contributes to improving public health and reducing healthcare costs associated with pollution-related illnesses.
- Operational Efficiency: Modern emission control systems can improve the operational efficiency of DG sets by optimizing combustion and reducing fuel consumption. This can lead to cost savings over time, offsetting the initial investment in retrofitting the equipment.
- Enhanced Corporate Image: Businesses that take proactive steps to reduce their environmental impact often enjoy a positive reputation among consumers, clients, and the community. Retrofitting emission control equipment on DG sets demonstrates a commitment to sustainability, enhancing a company’s image and competitive edge.
- Future-proofing Operations: As environmental regulations become stricter and public awareness of air quality issues grows, investing in emission control equipment now can future-proof a business’s operations. It prepares companies for upcoming standards and ensures their DG sets can continue to operate without disruption.
Emission Control Devices for DG Sets
One of the most important steps in reducing the environmental impact of diesel generator sets (DG sets) is retrofitting emission control equipment. Diverse apparatuses have been designed to concentrate on distinct contaminants found in diesel exhaust, utilizing distinct techniques to minimize emissions. An outline of the primary categories of modified emission control devices is provided below:
Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC)
Diesel oxidation catalysts function by changing toxic gasses chemically into less toxic byproducts. Installed in the exhaust system, DOCs selectively target hydrocarbons (HC), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO), oxidizing them to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Since DOCs effectively lessen diesel exhaust’s odor and apparent smoke, they are a preferred option for first emission reduction initiatives.
Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF)
Diesel Particulate Filters are made to collect particulate matter and soot from diesel engine exhaust. Through a process known as regeneration, the DPF physically holds the particles and periodically burns them off, either passively using the heat from the exhaust or vigorously using additional heating components. DPFs considerably improve air quality by effectively lowering particulate matter emissions.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
To lower nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, diesel exhaust fluid, also known as DEF, or urea solution, is injected into the exhaust stream before it passes past a catalyst in a selective catalytic reduction system. By converting NOx into nitrogen (N2) and water vapor (H2O), the chemical reaction considerably lowers one of the most dangerous pollutants that diesel combustion produces. Because of SCR systems’ excellent NOx reduction efficacy, they are crucial for adhering to strict emission regulations.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
The process of recirculating some of the engine’s exhaust gas back into the intake air is known as exhaust gas recirculation, and it helps lower nitrogen oxide emissions. By lowering the temperature of combustion, this technique also lowers the amount of NOx that is produced during combustion. EGR is especially useful in engines that frequently run at high combustion temperatures since it offers a comparatively easy method of achieving appreciably lower NOx emissions.
Every one of these modified emission control systems aims to lower specific kinds of pollutants while providing unique advantages. These technologies when combined can make diesel generators significantly cleaner, improving public health and air quality while guaranteeing regulatory compliance.
Key Features of RECD
Retrofit Emission Control Devices (RECDs) for diesel generators (DG sets) incorporate a host of innovative features designed to enhance performance, environmental compliance, and operational efficiency. These systems represent a significant advancement in emission control technology, offering a sustainable solution for reducing the environmental impact of diesel power generation. Below are the key features of RECDs that make them a critical component in modern power systems:
Energy Efficiency
One of the standout features of RECDs is their ability to operate efficiently without the need for active regeneration. This means they can maintain energy efficiency across various exhaust temperatures, ensuring that the system’s performance isn’t compromised by fluctuating operating conditions. This energy-efficient operation helps in reducing fuel consumption and, by extension, operational costs.
Versatility
RECDs are engineered to accommodate a wide array of DG set conditions, making them versatile solutions for different power requirements and installations. Their design supports remote installation, allowing for flexibility in placement and integration into existing power systems. This versatility ensures that emission control doesn’t come at the cost of convenience or functionality.
Flow Efficiency
Unlike conventional filter-based technologies, RECDs offer minimal flow restriction. This feature is crucial for maintaining the engine’s performance by ensuring that exhaust gases can flow freely without causing back pressure. The result is a system that enhances emission control without sacrificing engine efficiency or power output.
DG Operational Efficiency
The incorporation of RECDs into diesel generators does not impact the operational efficiency of the units. This seamless integration ensures that power generation remains consistent and reliable, even with the added benefits of emission reduction. Operators can thus enjoy cleaner operations without any compromise on the generator’s performance.
Advanced Monitoring
RECDs come equipped with state-of-the-art onboard diagnostics and Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities. This advanced technology enables cloud-based monitoring and notifications, providing real-time insights into the system’s performance and any maintenance needs. Such proactive monitoring can help in preempting potential issues, ensuring uninterrupted power supply and system longevity.
Waste to Wealth
An innovative aspect of RECDs is their ability to convert waste into wealth. The particulate matter collected by these devices can be repurposed as a valuable raw material for industries like paint and plastics. This not only reduces waste and secondary pollution but also offers an additional revenue stream from the by-products of emission control.
Durability and Maintenance
Designed to withstand all weather conditions, RECDs boast a durable and low-maintenance construction. Their robust design ensures a long operational life, reducing the need for frequent replacements or extensive upkeep. This durability is essential for ensuring continuous and cost-effective emission control across various applications.
How RECD Works
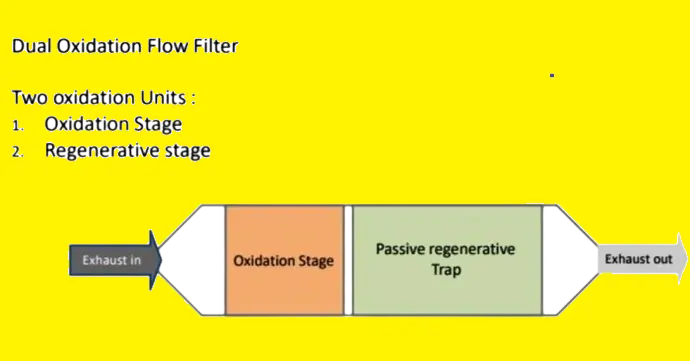
The Retrofit Emission Control Device (RECD) operates on the cutting-edge principle of electrostatic precipitation, a groundbreaking approach to emission control that eschews traditional filters in favor of a more efficient and innovative method. This advanced technology is specifically designed to target and capture particulate matter (PM) and carbon emissions from diesel generators (DG sets), boasting an impressive efficiency rate of over 70%. Here’s a deeper dive into how RECDs work to achieve cleaner air and enhanced combustion efficiency:
Electrostatic Precipitation: The Heart of RECD
At the core of the RECD is electrostatic precipitation, a process that utilizes electrical charges to remove particles from the exhaust gas. As the exhaust passes through the device, particulate matter and carbon are charged electrically. These charged particles are then attracted to and captured by electrodes with an opposite charge within the device, effectively removing them from the exhaust stream before it is released into the atmosphere.
Computerized Control for Optimal Performance
The operation of the RECD is finely tuned by advanced computerized controls. These controls meticulously manage the electrostatic precipitation process, ensuring that the charging, attraction, and capture of particulate matter are conducted with utmost efficiency. By continuously monitoring and adjusting the system, these controls optimize the combustion process within the DG set. This not only maximizes the removal of harmful emissions but also enhances the overall combustion efficiency of the generator.
The Result: Cleaner Air and Improved Efficiency
The implementation of RECD technology leads to a substantial reduction in the emission of particulate matter and carbon, pollutants that are particularly harmful to both human health and the environment. By capturing these emissions with more than 70% efficiency, RECDs significantly contribute to cleaner air quality. Moreover, the optimization of the combustion process facilitated by the device’s computerized controls can lead to improvements in fuel efficiency. This not only reduces the environmental impact of diesel generators but also enhances their operational performance, making RECDs a win-win solution for both the planet and generator operators.
In essence, the Retrofit Emission Control Device harnesses the power of electrostatic precipitation and intelligent system management to provide a highly effective means of reducing emissions from diesel generators. This innovative approach not only meets the growing demands for environmental compliance but also supports the pursuit of more sustainable and efficient power generation practices.
Retrofit Emission Control Technology
How it happens
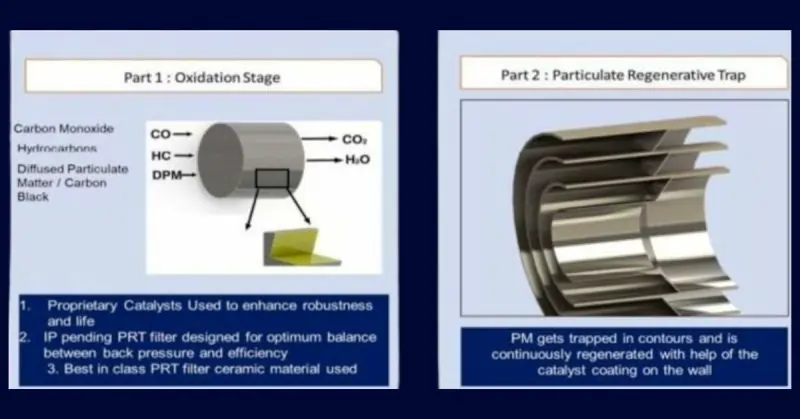
Retrofit Emission Control Technology (RECD) embodies a practical and efficient solution to the pressing challenge of reducing emissions from diesel generators (DG sets). This technology is encapsulated in a robust stainless steel enclosure, seamlessly integrating with the generator’s exhaust system to filter out harmful pollutants before they can be released into the environment. Here’s an in-depth look at how RECD technology is revolutionizing pollution control for diesel generators:
Design and Integration
The core of RECD technology is its design—a durable stainless steel box that houses the sophisticated emission control system. This design is not just about durability; it’s about compatibility and ease of installation. Whether the diesel generator is a new model fresh off the production line or an older unit that has been in service for years, the RECD can be easily integrated without significant modifications. This ease of installation ensures that the benefits of emission control can be realized quickly and without disrupting existing operations.
Pollution Control Mechanism
Once integrated into the exhaust system of a diesel generator, the RECD goes to work capturing and neutralizing a broad spectrum of pollutants. This includes particulate matter (PM), which consists of tiny particles that can penetrate deep into human lungs; carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly; nitrogen oxide (NOx), which contributes to smog and acid rain; and other harmful emissions. By targeting these pollutants, RECD technology significantly reduces the environmental and health risks associated with diesel generator emissions.
Meeting Regulatory Standards and Enhancing Sustainability
As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, the ability of diesel generators to meet these standards becomes crucial for continued operation. RECD technology ensures compliance with these regulations, safeguarding businesses from potential fines and legal issues. Beyond compliance, retrofit emission control devices underscore a commitment to sustainability. By reducing the emission of pollutants, RECDs contribute to cleaner air quality and a healthier urban environment. This commitment to environmental stewardship is becoming increasingly important to customers, stakeholders, and the community at large.
The Impact of Retrofit Emission Control Technology
The adoption of RECD technology marks a significant step forward in the effort to mitigate the environmental impact of diesel power generation. By providing a scalable solution that can be applied to a wide range of diesel generators, RECDs offer a pathway to cleaner energy use across industries. This technology not only aligns with global environmental goals but also enhances the operational sustainability of businesses relying on diesel generators for power.
Are emission problems expensive?
Yes, fixing emission issues with diesel generators (DG sets) can indeed come with a cost. If your DG set fails an emission test and requires repairs, the starting cost can vary significantly depending on the problem’s nature and the generator’s size. Typically, minor repairs might start from a few hundred dollars, but more complex issues can easily escalate to thousands. For replacing the exhaust system of a DG set, the cost can also vary widely, starting from around $500 to $2,000 or more, depending on the DG set’s specifications and the system’s complexity.
The lifespan of a DG set’s exhaust system depends on various factors, including maintenance practices and operational conditions, but with diligent care, it is designed to last for the substantial operational life of the generator.
FAQ on What Is Retrofitted Emission Control Equipment”
Q- What is retrofitted emission control equipment?
A: It’s a device added to diesel generators to reduce harmful emissions and improve air quality.
Q: How does retrofitted emission control equipment work?
A: It captures or converts pollutants like NOx and particulate matter into less harmful substances before they’re released into the air.
Q: Can retrofitted emission control equipment be installed on any DG set?
A: Yes, it’s designed for easy integration with both new and existing diesel generators.
Q: What are the benefits of installing retrofitted emission control equipment?
A: It significantly reduces environmental pollution, ensures regulatory compliance, and may enhance the operational efficiency of DG sets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, retrofitting emission control equipment on diesel generators is not just a regulatory necessity but a crucial step towards sustainable operations. By understanding and implementing this advanced technology, businesses can significantly reduce their environmental footprint, ensuring cleaner air and a healthier planet. The benefits of such equipment extend beyond compliance, offering enhanced operational efficiency, public health protection, and a positive contribution to global environmental goals.
Embracing retrofitted emission control equipment for DG sets represents a forward-thinking approach to energy use, highlighting a commitment to innovation, responsibility, and the well-being of our communities. It’s clear that in the journey towards a more sustainable future, retrofitting emission control equipment on diesel generators plays a pivotal role, making it an indispensable choice for any organization looking to make a difference, one generator at a time.
