Semiconductors in 2024
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, semiconductors stand at the heart of innovation, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. These tiny but mighty components are essential in modern electronics, enabling advancements that shape our daily lives and drive industrial growth. As we are in 2024, staying updated with the latest trends in semiconductor technology becomes crucial for professionals and enthusiasts alike. Understanding these emerging trends can provide valuable insights into future developments, helping businesses and individuals make informed decisions.
This blog post aims to explore the most significant trends and impacts in the semiconductor industry for 2024. By delving into the advancements and challenges, we seek to offer a comprehensive overview that not only highlights the current state of the industry but also forecasts the innovations that will define the next generation of semiconductor applications. Join us as we navigate the fascinating world of semiconductors and uncover the future of technology.
Overview of the Semiconductor Industry in 2024
Current State of the Semiconductor Industry
As we navigate through 2024, the semiconductor industry continues to be a cornerstone of technological progress. Semiconductors are integral to a myriad of applications, from consumer electronics to automotive and industrial automation. The industry has seen remarkable resilience and growth, despite facing numerous challenges, including supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions. Innovations in materials, design, and manufacturing processes have propelled the sector forward, ensuring it remains at the forefront of global technological advancements.
Key Statistics and Market Growth
The semiconductor industry is projected to experience robust growth in 2024. According to recent market reports, the global semiconductor market size is expected to surpass $600 billion, driven by the increasing demand for advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, 5G connectivity, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8% over the next five years. Notably, the automotive semiconductor market is expected to witness the highest growth, fueled by the rise in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies.
Major Players in the Industry
Several key players dominate the semiconductor landscape, each contributing significantly to the industry’s growth and innovation. Companies such as Intel, Samsung, and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) lead the market with their cutting-edge technologies and extensive research and development efforts. Intel remains a powerhouse in processor technology, while Samsung excels in memory and integrated circuit design. TSMC is the world’s largest dedicated independent semiconductor foundry, known for its advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Other notable companies include NVIDIA, renowned for its graphics processing units (GPUs) and AI solutions, and Qualcomm, a leader in wireless technology and semiconductor solutions. These industry giants, along with emerging players, continue to drive competition and innovation, ensuring that the semiconductor sector remains dynamic and forward-looking.
Key Formulas and Concepts in Semiconductor Technology
1. Charge Carrier Density
The charge carrier density in intrinsic semiconductors determines the number of free electrons and holes present in the material at thermal equilibrium.

2. Drift Current Density
The drift current density represents the flow of charge carriers due to an applied electric field.

3. Conductivity
The electrical conductivity of a semiconductor is influenced by the concentration and mobility of both electrons and holes.

4. Mobility
Mobility quantifies how quickly charge carriers can move through a semiconductor material when subjected to an electric field.

5. Energy Band Gap
The energy band gap is a fundamental property that determines the electrical conductivity of the semiconductor material. For silicon, it can be estimated using an empirical formula that accounts for temperature variations.
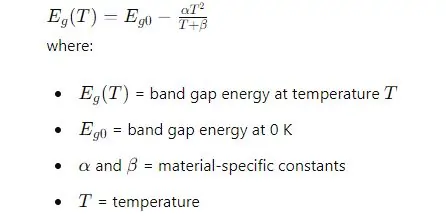
Emerging Trends in Semiconductor Technology
A. Advanced Materials
Use of New Materials like GaN and SiC
In 2024, the semiconductor industry is witnessing significant advancements in the use of new materials such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC). These materials offer superior performance compared to traditional silicon-based semiconductors. GaN and SiC are known for their high electron mobility, thermal conductivity, and ability to operate at higher voltages and temperatures.
What is SiC and GaN?
Silicon is a single chemical element, widely used in semiconductor technology for its excellent properties. In contrast, Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a compound of silicon and carbon, and Gallium Nitride (GaN) is a compound of gallium and nitrogen. Due to their composite nature, SiC and GaN are known as “Compound Semiconductors.” These compounds offer superior performance in high-temperature and high-frequency applications compared to silicon, making them increasingly important in advanced electronics.
Benefits and Applications
The benefits of GaN and SiC include higher efficiency, reduced energy losses, and improved power density. These materials are increasingly used in applications such as power electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. For instance, GaN transistors are revolutionizing power adapters and wireless chargers, while SiC devices are enhancing the performance of electric vehicle inverters and solar inverters.
B. Miniaturization and Nanotechnology
Progress in Reducing Chip Sizes
The trend towards miniaturization continues to drive the semiconductor industry, with ongoing efforts to reduce chip sizes using advanced nanotechnology. This progress is essential for meeting the growing demand for more compact and efficient electronic devices.
Impact on Performance and Power Consumption
Smaller chip sizes lead to increased transistor density, which enhances the performance and functionality of semiconductors. Additionally, miniaturization helps in reducing power consumption, enabling the development of energy-efficient devices. This is particularly important for applications in mobile devices, where battery life is a critical factor.
C. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
AI-Driven Semiconductor Design
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are playing a pivotal role in semiconductor design. AI algorithms are being used to optimize the design process, improving efficiency and reducing time-to-market for new semiconductor products.
Applications in Smart Devices and Automation
The integration of AI and ML in semiconductors is driving advancements in smart devices and automation. AI-enabled semiconductors power applications such as voice recognition, image processing, and predictive maintenance in industrial automation. These smart semiconductors are integral to the development of intelligent systems that can learn and adapt over time.
D. Quantum Computing
Development of Quantum Semiconductors
Quantum computing represents a frontier in semiconductor technology. The development of quantum semiconductors involves leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to create powerful computing systems that can solve complex problems beyond the reach of classical computers.
Potential Breakthroughs and Challenges
Quantum semiconductors hold the potential for breakthroughs in fields such as cryptography, material science, and drug discovery. However, significant challenges remain, including maintaining quantum coherence and scaling up quantum systems. Researchers are actively working on overcoming these hurdles to unlock the full potential of quantum computing.
E. 5G and Beyond
Role of Semiconductors in 5G Technology
Semiconductors are crucial to the deployment and expansion of 5G technology. They enable the high-speed data processing and low-latency communication required for 5G networks. The advancements in semiconductor technology are essential for the performance and reliability of 5G infrastructure.
Future Trends in Wireless Communication
Looking beyond 5G, semiconductors will continue to play a key role in the evolution of wireless communication technologies. This includes the development of 6G, which promises even faster speeds and more reliable connections. Emerging trends in this space involve the use of advanced semiconductor materials and designs to support the increasing demands of global connectivity.
Impact on Various Industries
A. Consumer Electronics
Innovations in Smartphones, Wearables, and Home Devices
The semiconductor industry continues to drive innovation in consumer electronics, with significant advancements in smartphones, wearables, and home devices. In 2024, we see smartphones with enhanced processing power, energy efficiency, and advanced features such as AI-driven cameras and augmented reality capabilities. Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers benefit from improved sensor technology and longer battery life, thanks to cutting-edge semiconductors. Home devices, including smart speakers and home automation systems, are becoming more intelligent and integrated, providing seamless user experiences.
B. Automotive Industry
Semiconductors in Electric Vehicles and Autonomous Driving
The automotive industry is undergoing a transformative shift, heavily influenced by advancements in semiconductor technology. Semiconductors are crucial in the development and operation of electric vehicles (EVs), contributing to efficient power management and enhanced battery performance. In autonomous driving, semiconductors enable advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), real-time data processing, and AI-driven decision-making. These innovations are accelerating the adoption of EVs and self-driving cars, promising safer and more sustainable transportation solutions.
C. Healthcare
Advances in Medical Devices and Diagnostics
The healthcare sector is experiencing a revolution, with semiconductors playing a pivotal role in the advancement of medical devices and diagnostics. Modern medical devices, such as portable monitors, imaging systems, and wearable health trackers, rely on high-performance semiconductors for accurate and real-time data processing. Innovations in semiconductor technology are also enhancing diagnostic tools, enabling early detection and personalized treatment plans. These advancements are improving patient outcomes and transforming healthcare delivery.
D. Industrial Automation
Role in Robotics and Manufacturing Processes
In industrial automation, semiconductors are integral to the development of advanced robotics and efficient manufacturing processes. Semiconductors enable the creation of intelligent robots capable of performing complex tasks with precision and speed. They also facilitate the implementation of smart manufacturing systems, where interconnected machines communicate and collaborate to optimize production. These technologies enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and enable the creation of more flexible and adaptive manufacturing environments.
E. Renewable Energy
Enhancements in Solar Panels and Energy Storage
The renewable energy sector is benefiting significantly from advancements in semiconductor technology. In solar energy, semiconductors are improving the efficiency and affordability of photovoltaic panels, making solar power more accessible and viable. Innovations in semiconductors are also crucial for the development of advanced energy storage solutions, such as high-capacity batteries and supercapacitors. These enhancements support the integration of renewable energy into the grid, enabling more reliable and sustainable energy systems.
Challenges Facing the Semiconductor Industry
Supply Chain Issues
The semiconductor industry is grappling with significant supply chain issues, which have been exacerbated by global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions. These disruptions have led to shortages in critical components, delaying production and increasing costs for manufacturers. The complexity of the semiconductor supply chain, which involves multiple stages of production spread across different countries, adds to the challenge. Companies are now focusing on enhancing supply chain resilience by diversifying suppliers, increasing inventory levels, and investing in local manufacturing capabilities to mitigate the risks associated with global disruptions.
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
As the demand for semiconductors continues to rise, so do the environmental and sustainability concerns associated with their production. The manufacturing process for semiconductors is resource-intensive, requiring substantial amounts of water, energy, and raw materials. Additionally, the production generates significant amounts of waste and greenhouse gas emissions. To address these issues, the industry is increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency in manufacturing processes, and recycling materials. Companies are also investing in research and development to create more environmentally friendly semiconductor technologies.
Talent and Skills Shortage
The rapid advancement of semiconductor technology has led to a growing demand for skilled professionals in the field. However, there is a significant talent and skills shortage that poses a challenge for the industry. The complexity of semiconductor design and manufacturing requires expertise in various disciplines, including materials science, electrical engineering, and computer science. To bridge this gap, companies and educational institutions are collaborating to develop specialized training programs and curricula aimed at cultivating the next generation of semiconductor experts. Additionally, initiatives to attract and retain talent through competitive compensation, career development opportunities, and a focus on diversity and inclusion are being prioritized.
Geopolitical Factors and Trade Tensions
Geopolitical factors and trade tensions are increasingly impacting the semiconductor industry. The global nature of semiconductor supply chains makes them vulnerable to political instability, trade restrictions, and tariffs. For example, trade disputes between major economies such as the United States and China have led to restrictions on the export and import of critical semiconductor components and technologies. These tensions can disrupt the supply chain, increase costs, and create uncertainty for companies operating in the industry. In response, businesses are seeking to navigate these challenges by diversifying their markets, establishing strategic partnerships, and advocating for policies that promote free and fair trade.
Future Prospects and Predictions
Expert Opinions and Forecasts
The future of the semiconductor industry looks promising, with experts predicting continued growth and innovation. Analysts forecast that the global semiconductor market will surpass $1 trillion by 2030, driven by advancements in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), quantum computing, and 5G connectivity. Industry leaders emphasize the importance of investing in research and development to maintain this growth trajectory. Additionally, the ongoing digital transformation across various sectors is expected to fuel demand for semiconductor solutions, ensuring the industry’s vitality in the years to come.
Potential Game-Changers in the Next Decade
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is poised to be a significant game-changer for the semiconductor industry. Quantum semiconductors could revolutionize computing power and solve complex problems that are currently beyond the reach of classical computers. This breakthrough could have far-reaching implications across industries, from cryptography and finance to healthcare and artificial intelligence.
Advanced AI Integration
The integration of AI into semiconductor design and manufacturing processes will lead to unprecedented efficiencies and capabilities. AI-driven chip design will enable the creation of more sophisticated and energy-efficient semiconductors, fostering innovations in smart devices, autonomous systems, and data centers.
6G and Beyond
While 5G is still being rolled out globally, the groundwork for 6G technology is already being laid. 6G is expected to offer even higher speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connectivity. Semiconductors will play a crucial role in the development and deployment of 6G networks, supporting the next generation of wireless communication.
Sustainable Technologies
Environmental sustainability will continue to drive innovation in semiconductor technology. The development of eco-friendly manufacturing processes and materials will be essential in reducing the industry’s carbon footprint. Sustainable semiconductors will be critical in supporting the global push towards greener technologies and renewable energy sources.
Strategies for Businesses to Adapt and Thrive
Invest in Research and Development
To stay ahead in the competitive semiconductor landscape, businesses must prioritize investment in research and development. This will enable the discovery of new materials, processes, and applications that can drive innovation and maintain technological leadership.
Enhance Supply Chain Resilience
Building a resilient supply chain is crucial for mitigating risks associated with global disruptions. Diversifying suppliers, increasing inventory levels, and investing in local manufacturing capabilities can help businesses navigate supply chain challenges and ensure continuity in production.
Foster Talent Development
Addressing the talent and skills shortage requires a proactive approach to talent development. Businesses should collaborate with educational institutions to create specialized training programs and curricula. Offering competitive compensation, career development opportunities, and fostering an inclusive work environment will attract and retain top talent.
Embrace Sustainability
Adopting sustainable practices is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic advantage. Businesses should focus on reducing their environmental impact by utilizing renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and recycling materials. Sustainable practices will not only enhance corporate reputation but also align with the growing demand for eco-friendly technologies.
Navigate Geopolitical Challenges
To mitigate the impact of geopolitical factors and trade tensions, businesses should diversify their markets and establish strategic partnerships. Engaging in advocacy for policies that promote free and fair trade will also be essential in maintaining stability and growth in the semiconductor industry.
FAQs on Semiconductors
Q1: What are semiconductors used for?
A1: They control electrical currents in devices like computers and smartphones.
Q2: How do semiconductors impact the automotive industry?
A2: They enhance electric vehicles and autonomous driving.
Q3: What materials are commonly used in semiconductors?
A3: Silicon, Gallium Nitride (GaN), and Silicon Carbide (SiC).
Q4: Why is there a shortage of semiconductors?
A4: Due to supply chain issues and high demand.
Conclusion
The semiconductor industry is at the heart of technological innovation, driving advancements across various sectors from consumer electronics to renewable energy. In 2024, the industry faces both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. Emerging trends like advanced materials, AI integration, and quantum computing promise to reshape the future, while supply chain issues, environmental concerns, and talent shortages present obstacles to overcome. By staying informed about these developments and adopting strategic approaches, businesses can navigate this dynamic landscape successfully. As we look ahead, the continued evolution of semiconductor technology will be crucial in shaping a smarter, more connected, and sustainable world.