What Is Solenoid Valve
Solenoid valves are essential electromechanical devices that control the flow of liquids and gases by converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. In the marine industry, these valves are critical for ensuring efficient and safe operation of various systems, from fuel management and steering gear to HVAC and ballast control. The precise control and automation provided by solenoid valves enhance the reliability and performance of marine vessels, making them indispensable in modern maritime technology.
In this blog post, we will explore the seven powerful ways solenoid valves work and their diverse marine applications. We’ll delve into the functionality of different types of solenoid valves, including pneumatic, electric, hydraulic, and gas solenoid valves, and examine their specific uses in marine environments. Additionally, we will discuss how solenoid valves contribute to temperature and flow control on ships, highlighting their role in optimizing performance and safety. Whether you’re a marine engineer or industry professional, this guide will offer valuable insights into the critical role of solenoid valves in maritime operations.
Understanding Solenoid Valves
Definition and Basic Working Principle
Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices used to control the flow of liquids or gases in various systems. These valves operate by using an electric current to create a magnetic field, which in turn actuates a plunger or piston to open or close the valve, thereby regulating the flow. The simplicity and efficiency of solenoid valves make them a vital component in many industrial and marine applications.
Key Components of a Solenoid Valve
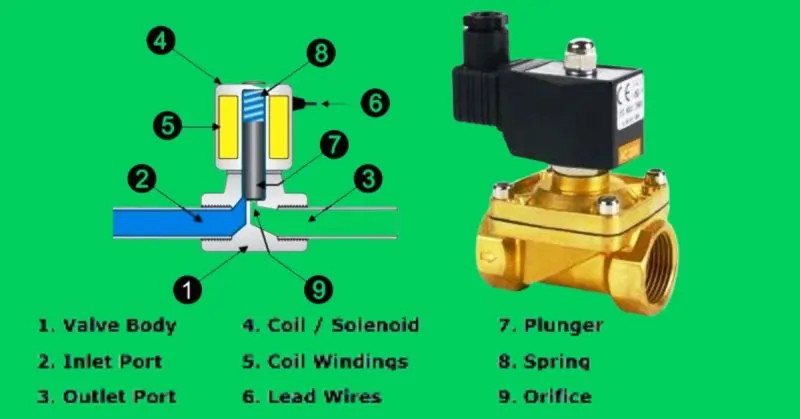

Image Source: https://engineerscommunity.com/
- Solenoid Coil: This is the electromagnet of the valve, consisting of a wire coil that generates a magnetic field when electric current passes through it.
- Plunger or Armature: A movable iron or steel component that is pulled into the coil’s magnetic field, which moves to open or close the valve.
- Valve Body: The main structure housing the valve components, typically made of brass, stainless steel, or plastic, designed to handle the specific type of fluid.
- Spring: A mechanical spring that helps return the plunger to its original position when the solenoid is de-energized.
- Orifice: The opening through which the fluid passes, controlled by the movement of the plunger.
- Seal: A gasket or ring that ensures a tight closure when the valve is in the closed position, preventing leaks.
These components work together to allow precise control of fluid flow in various systems, making solenoid valves essential for efficient and reliable operation.
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve: Functionality and Marine Uses
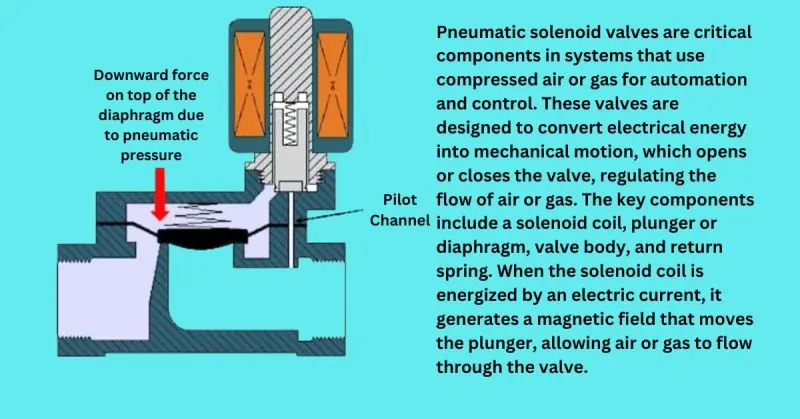
Specifics of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Pneumatic solenoid valves are critical components in systems that use compressed air or gas for automation and control. These valves are designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, which opens or closes the valve, regulating the flow of air or gas. The key components include a solenoid coil, plunger or diaphragm, valve body, and return spring. When the solenoid coil is energized by an electric current, it generates a magnetic field that moves the plunger, allowing air or gas to flow through the valve.
How They Differ from Standard Pneumatic Valves
Pneumatic solenoid valves differ from standard pneumatic valves primarily in their mode of operation:
- Electrical Actuation: Pneumatic solenoid valves are actuated by an electric signal, which allows for remote and automated control, unlike manual or pilot-operated standard pneumatic valves.
- Precision and Speed: Solenoid valves offer precise and rapid switching capabilities, essential for applications requiring quick response times.
- Integration with Control Systems: These valves can be easily integrated into automated control systems, enhancing efficiency and functionality in complex operations.
- Compact Design: Solenoid valves often have a more compact and lightweight design compared to traditional pneumatic valves, making them suitable for applications with space constraints.
Common Marine Applications and Benefits
Pneumatic solenoid valves are extensively used in marine applications due to their reliability, precision, and ability to withstand harsh marine environments. Key marine applications include:
- Ballast Systems: Solenoid valves control the flow of air and water in ballast tanks, enabling ships to adjust buoyancy and stability. This precise control is essential for maintaining the balance and safety of the vessel during loading, unloading, and navigation.
- Deck Machinery: These valves are used to control pneumatic winches, cranes, and other deck machinery. Their rapid response and automation capabilities improve the efficiency and safety of lifting and handling operations on deck.
- Engine Room Equipment: In engine rooms, solenoid valves manage the flow of air to compressors, fuel injectors, and ventilation systems. This ensures optimal performance and efficiency of critical machinery and equipment.
- Steering Systems: Pneumatic solenoid valves control the flow of compressed air to steering actuators and cylinders, enabling precise maneuvering and course adjustments. Reliable steering control is vital for the safe navigation of marine vessels.
Benefits of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves in Marine Applications
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automated and precise control of air flow reduces the need for manual intervention, streamlining operations and increasing overall efficiency.
- Improved Safety: Remote operation and quick response times minimize the risk of accidents and enhance the safety of onboard systems.
- Durability and Reliability: Designed to withstand harsh marine environments, pneumatic solenoid valves offer long-lasting performance and reduced maintenance requirements.
- Flexibility: The ability to integrate with automated control systems allows for flexible and adaptive operation, essential for complex marine applications.
Electric Solenoid Valve: Mechanism and Marine Uses
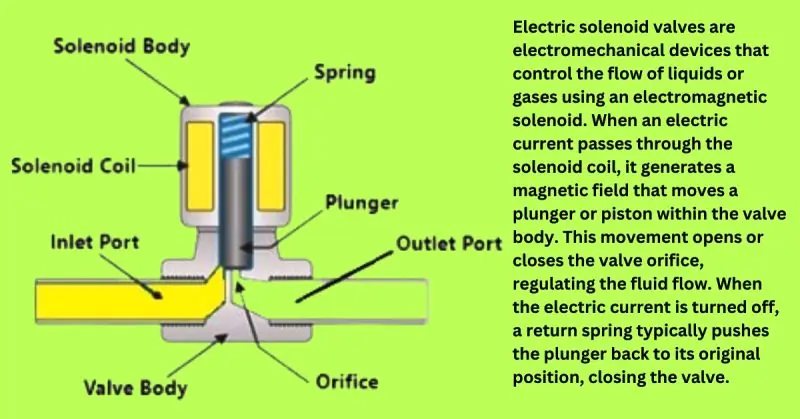
Working Principle of Electric Solenoid Valves
Electric solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that control the flow of liquids or gases using an electromagnetic solenoid. When an electric current passes through the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field that moves a plunger or piston within the valve body. This movement opens or closes the valve orifice, regulating the fluid flow. When the electric current is turned off, a return spring typically pushes the plunger back to its original position, closing the valve.
Key components include:
- Solenoid Coil: Generates the magnetic field when energized.
- Plunger or Piston: Moves to open or close the valve orifice.
- Valve Body: Encases the internal components and provides the passage for fluid flow.
- Spring: Returns the plunger to its default position when the solenoid is de-energized.
- Valve Seat: Ensures a tight seal when the valve is closed to prevent leaks.
Examples of Marine Applications
Electric solenoid valves are widely used in marine environments due to their precise control and reliability. Here are some key applications:
- Fuel Injection Systems: Electric solenoid valves regulate the flow of fuel into the engine cylinders, ensuring efficient combustion and optimal engine performance. Precise control over fuel delivery helps maintain engine efficiency and reduces emissions.
- Bilge Pump Control: In bilge systems, solenoid valves control the flow of water to and from the bilge pumps. Automated control ensures timely removal of water from the bilge, preventing flooding and maintaining vessel stability.
- Cooling Systems: Solenoid valves manage the flow of coolant through the engine and other heat-generating equipment. Proper temperature regulation is crucial for preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity of marine machinery.
- Fire Suppression Systems: Electric solenoid valves are used in fire suppression systems to control the release of fire-extinguishing agents, such as CO2 or foam. Quick and reliable valve operation is vital for effective fire response.
- Ballast Water Management: Solenoid valves regulate the flow of water into and out of ballast tanks, enabling ships to maintain proper buoyancy and stability. Automated ballast systems improve the efficiency and safety of vessel operations.
Advantages of Using Electric Solenoid Valves in Marine Environments
- Precision and Accuracy: Electric solenoid valves offer precise control over fluid flow, essential for maintaining optimal operating conditions in marine systems.
- Rapid Response: The electromagnetic actuation provides fast switching times, which is critical for applications requiring quick response, such as fuel injection and fire suppression systems.
- Automation and Remote Control: Solenoid valves can be easily integrated with automated control systems, enabling remote operation and monitoring. This enhances operational efficiency and safety.
- Durability and Reliability: Designed to withstand harsh marine conditions, electric solenoid valves are built with materials resistant to corrosion and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric solenoid valves consume relatively low power, making them energy-efficient solutions for controlling fluid flow in various marine applications.
Read more…….https://marinediesel.co.in/electric-solenoid-valve/
Hydraulic Solenoid Valve: Operation and Marine Uses
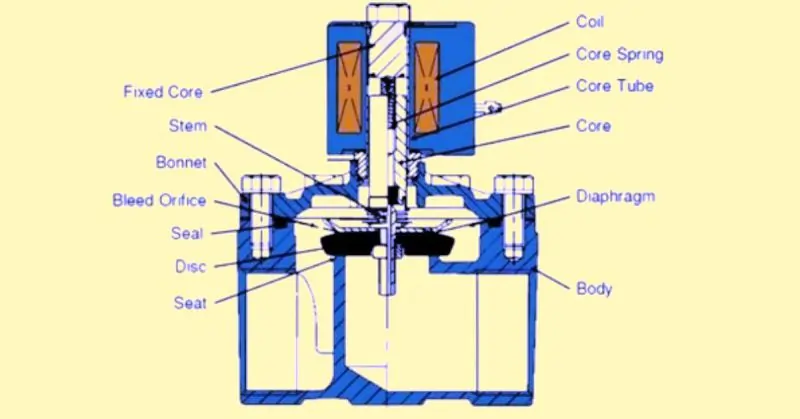
Detailed Explanation of Hydraulic Solenoid Valves
Hydraulic solenoid valves are specialized devices designed to control the flow and direction of hydraulic fluid in various systems. These valves use an electromagnetic solenoid to actuate a spool or poppet within the valve body. When the solenoid is energized, it creates a magnetic field that moves the spool or poppet, changing the flow path of the hydraulic fluid. This operation can either open, close, or redirect the flow, providing precise control over hydraulic systems.
Key components include:
- Solenoid Coil: Generates the magnetic field when energized.
- Spool or Poppet: Moves within the valve body to control fluid flow.
- Valve Body: Houses the internal components and provides the flow passages.
- Spring: Returns the spool or poppet to its default position when the solenoid is de-energized.
- Valve Ports: Inlet and outlet ports for hydraulic fluid to flow through the valve.
How They Operate Under Hydraulic Pressure
Hydraulic solenoid valves operate by controlling the position of the spool or poppet within the valve body. The process can be described in several steps:
- Energizing the Solenoid: An electric current passes through the solenoid coil, generating a magnetic field.
- Actuating the Spool or Poppet: The magnetic field moves the spool or poppet, altering the flow path of the hydraulic fluid.
- Controlling Flow: The movement of the spool or poppet either opens or closes the valve ports, or redirects the fluid to different pathways.
- De-energizing the Solenoid: When the electric current is switched off, the spring mechanism returns the spool or poppet to its original position, resetting the flow path.
Hydraulic solenoid valves are designed to handle high-pressure hydraulic fluids, ensuring reliable performance even in demanding conditions. Their ability to provide precise control under varying pressures makes them essential in hydraulic systems.
Marine Uses
Hydraulic solenoid valves are integral to numerous marine applications, where precise and reliable control of hydraulic fluid is critical for the operation of various systems. Key marine uses include:
- Steering Gear Systems: Hydraulic solenoid valves control the flow of hydraulic fluid to the steering actuators, enabling precise and responsive maneuvering of the vessel. Reliable steering control is essential for safe navigation.
- Hatch Covers: These valves manage the hydraulic cylinders that open and close hatch covers on cargo ships. Automated control ensures efficient cargo handling and secure sealing of hatch covers to protect against water ingress.
- Winch Controls: In winch systems, hydraulic solenoid valves regulate the hydraulic motors that drive the winches. Precise control is crucial for lifting and handling heavy loads, ensuring safety and efficiency in deck operations.
- Stabilizers: Hydraulic solenoid valves are used in stabilizer systems to control the movement of stabilizing fins or tanks, reducing roll and improving vessel stability in rough seas.
- Anchor Handling: These valves control the hydraulic windlasses used for raising and lowering anchors, providing smooth and controlled operation.
Advantages of Using Hydraulic Solenoid Valves in Marine Environments
- Precision and Accuracy: Hydraulic solenoid valves offer precise control over fluid flow, essential for maintaining optimal performance in critical marine systems.
- High Pressure Handling: Designed to operate under high hydraulic pressures, these valves ensure reliable performance in demanding marine applications.
- Durability and Reliability: Built to withstand harsh marine conditions, including saltwater exposure and extreme temperatures, hydraulic solenoid valves offer long-term durability.
- Automation and Remote Control: Easily integrated with automated control systems, these valves enable remote operation and monitoring, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
- Energy Efficiency: Hydraulic systems controlled by solenoid valves are typically more energy-efficient, reducing power consumption and operational costs.
Gas Solenoid Valve: How They Work and Marine Uses
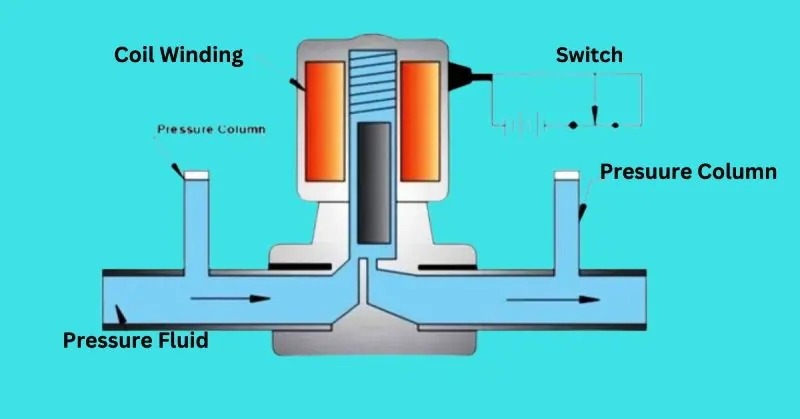
Working Mechanism of Gas Solenoid Valves
Gas solenoid valves are designed to control the flow of gaseous substances, such as natural gas, propane, and compressed air, through an electromechanical process. The operation involves an electric solenoid that actuates a plunger or diaphragm to open or close the valve orifice, thereby regulating gas flow. When an electric current is applied to the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field that moves the plunger away from the valve seat, allowing gas to flow through. When the current is turned off, a spring mechanism returns the plunger to its original position, closing the valve and stopping the flow.
Key components include:
- Solenoid Coil: Creates the magnetic field when energized.
- Plunger or Diaphragm: Moves to open or close the gas passage.
- Valve Body: Houses the internal components and provides the flow passage for the gas.
- Spring: Returns the plunger or diaphragm to its default position when de-energized.
- Valve Seat: Ensures a tight seal to prevent gas leakage when the valve is closed.
Safety Features and Critical Marine Applications
Gas solenoid valves are equipped with several safety features to ensure reliable operation and prevent hazardous situations in marine environments:
- Fail-Safe Design: In the event of power loss, the valve automatically closes to prevent gas leaks, enhancing safety.
- Explosion-Proof Housing: Some valves are designed with explosion-proof enclosures to contain any potential ignition within the valve body.
- Pressure Relief Mechanisms: Features that relieve excess pressure to prevent system failures and ensure safe operation.
- Leak Detection: Advanced valves may include sensors to detect gas leaks and automatically shut down the valve.
Critical marine applications include:
- Gas Detection Systems: Gas solenoid valves are integral to systems that monitor and control gas levels, ensuring immediate shutoff in case of leaks, thereby preventing potential hazards.
- LNG Handling: In liquefied natural gas (LNG) systems, these valves control the flow of gas during loading, unloading, and storage operations, ensuring safe handling and distribution.
- Fuel Supply Systems: Used in marine engines to control the flow of gaseous fuels, ensuring efficient and safe combustion processes.
- Heating Systems: Control the flow of gas in marine boilers and heaters, maintaining safe and efficient operation.
Use Cases in Marine Gas Control and Distribution
Gas solenoid valves are essential in various marine gas control and distribution systems due to their precise control and reliability:
- Fuel Supply Lines: Control the flow of fuel gases to marine engines, ensuring consistent and safe fuel delivery for optimal engine performance.
- Gas-Powered Equipment: Manage the supply of gas to equipment such as stoves, heaters, and other appliances onboard, ensuring safe and controlled operation.
- Safety Shutoff Systems: Integrated into emergency shutoff systems to quickly stop the flow of gas in case of a leak or other hazardous conditions, enhancing onboard safety.
- Gas Detection and Monitoring: Used in conjunction with gas detection systems to automatically shut off gas flow if dangerous levels are detected, preventing accidents and ensuring safety.
Advantages of Using Gas Solenoid Valves in Marine Environments
- Precision Control: Gas solenoid valves offer precise regulation of gas flow, essential for maintaining safe and efficient operations in marine systems.
- Rapid Response: The electromagnetic actuation provides fast switching times, critical for applications requiring quick response, such as emergency shutoff systems.
- Automation and Remote Control: Easily integrated with automated control systems, enabling remote operation and monitoring, which enhances operational efficiency and safety.
- Durability and Reliability: Designed to withstand harsh marine conditions, including exposure to saltwater and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
- Energy Efficiency: Gas solenoid valves consume relatively low power, making them an energy-efficient solution for controlling gas flow in various marine applications.
Temperature Control in Solenoid Valves for Marine Applications
How Solenoid Valves Regulate Temperature in Marine Systems
Solenoid valves are crucial in regulating temperature within marine systems by controlling the flow of heating or cooling fluids. These valves function by using an electric solenoid to actuate a plunger or diaphragm, which opens or closes the valve orifice, thereby controlling the flow of fluids such as water, refrigerants, or glycol. When integrated with temperature sensors and control units, solenoid valves adjust the flow rate based on real-time temperature readings, ensuring precise and efficient thermal management.
Key mechanisms include:
- On/Off Control: Solenoid valves provide simple binary control, fully opening to allow maximum fluid flow or closing to stop it completely.
- Proportional Control: Advanced solenoid valves offer proportional control, modulating the flow rate in response to varying signals from temperature controllers, allowing for fine-tuned temperature regulation.
- Integration with Automated Systems: These valves can be seamlessly integrated with marine automation systems, enabling remote monitoring and control of temperature regulation processes.
Applications in Marine Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems
Solenoid valves are essential components in marine HVAC systems, playing a critical role in maintaining comfortable and safe environmental conditions on board ships. Specific applications include:
- Chilled Water Systems: Solenoid valves regulate the flow of chilled water in air conditioning systems, controlling the cooling output to maintain desired cabin temperatures. By adjusting the flow based on temperature sensor feedback, these valves ensure efficient cooling performance.
- Heating Systems: In marine heating applications, solenoid valves manage the flow of hot water or steam to radiators and heat exchangers. They help maintain consistent and optimal heating levels, ensuring crew comfort and preventing freezing conditions in colder climates.
- Ventilation Systems: Solenoid valves control the flow of conditioned air in ventilation systems, ensuring proper air distribution and temperature regulation throughout the vessel. This includes managing the supply and exhaust airflows to maintain indoor air quality and thermal comfort.
- Refrigeration Systems: In marine refrigeration systems, solenoid valves regulate the flow of refrigerants to and from evaporators and condensers. Precise control of refrigerant flow is crucial for maintaining the correct temperatures in storage areas, such as cold rooms and freezers, ensuring the preservation of perishable goods.
- Engine Room Cooling: Solenoid valves are used in engine room cooling systems to control the flow of coolant to engine components, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal engine performance. Effective temperature regulation is essential for maintaining engine reliability and efficiency.
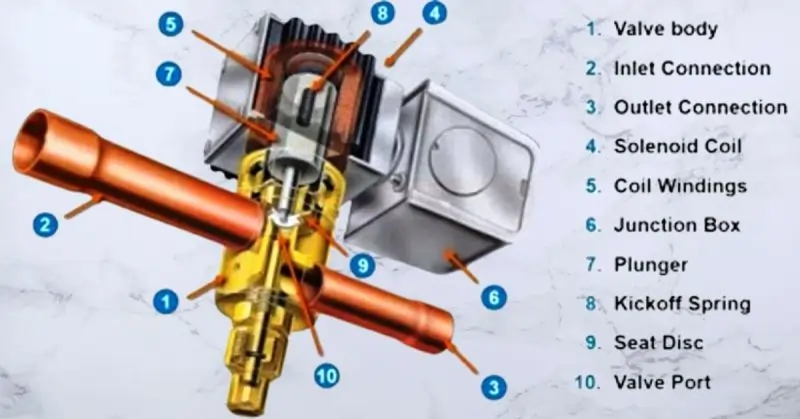
Main Components of Solenoid Valves
- Valve Body: The main structure that houses the internal components and provides the flow passages for the fluid.
- Inlet Connection: The port where the fluid enters the valve.
- Outlet Connection: The port where the fluid exits the valve.
- Solenoid Coil: An electromagnetic coil that generates a magnetic field when energized, actuating the plunger or diaphragm.
- Coil Windings: The wire windings within the solenoid coil that create the magnetic field when electric current flows through them.
- Junction Box: The enclosure that houses the electrical connections for the solenoid coil, protecting them from the marine environment.
- Plunger: The movable component within the valve that opens or closes the valve orifice in response to the magnetic field generated by the solenoid coil.
- Kickoff Spring: The spring that returns the plunger to its original position when the solenoid coil is de-energized.
- Seal Disc: The sealing element that ensures a tight closure when the valve is in the closed position, preventing fluid leakage.
- Valve Port: The openings in the valve body through which the fluid flows.
Benefits of Using Solenoid Valves for Temperature Control in Marine Applications
- Precision and Accuracy: Solenoid valves offer precise control over fluid flow, essential for accurate temperature regulation and maintaining optimal thermal conditions.
- Automation and Integration: Easily integrated with automated control systems, solenoid valves enable remote monitoring and adjustment, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing manual intervention.
- Energy Efficiency: By optimizing the flow of heating and cooling fluids, solenoid valves contribute to energy savings, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- Reliability and Durability: Designed to withstand harsh marine environments, solenoid valves are built with robust materials that resist corrosion and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Safety: Proper temperature control using solenoid valves helps prevent overheating and freezing conditions, protecting equipment and ensuring the safety and comfort of the crew.
FAQ on “Solenoid Valve”
Q: What is a solenoid valve used for?
A: It controls the flow of liquids or gases.
Q: How does a solenoid valve work?
A: It uses an electric current to move a plunger.
Q: Where are solenoid valves used in marine applications?
A: In HVAC, fuel systems, bilge pumps, and ballast systems.
Q: What are the advantages of solenoid valves in marine environments?
A: They offer precise control, quick response, and durability.
Conclusion
Solenoid valves are indispensable for effective temperature regulation in marine HVAC systems, offering precision, automation, and reliability. Their ability to control the flow of heating and cooling fluids ensures optimal thermal conditions, enhancing both safety and comfort on board. By integrating these advanced valves into marine applications, vessels can achieve greater operational efficiency, energy savings, and long-term durability. Solenoid valves are a key component in maintaining the well-being of crew members and the reliable performance of essential marine systems.
