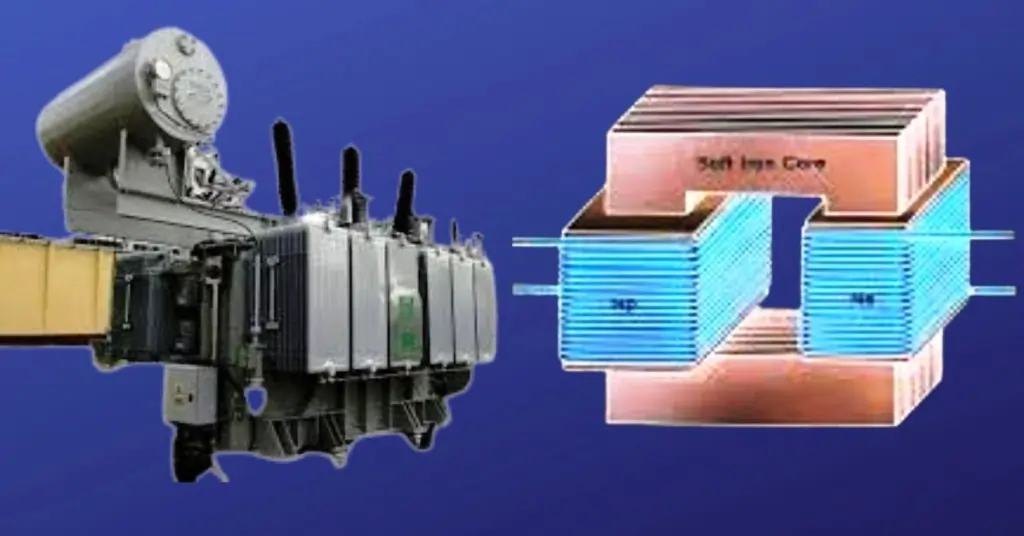
Step Down Transformer
Step down transformers are essential components in electrical systems, designed to reduce high voltage to a lower, safer level for various applications. These transformers play a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of electrical devices by adapting the voltage to suitable levels, thus preventing equipment damage and enhancing safety. They are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, making them indispensable in modern electrical infrastructure.
This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive guide on step down transformers, covering the basics of how they work, the different types available, and their various uses. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to understand how these transformers can benefit your appliances, or a professional seeking detailed specifications and installation tips, this guide will equip you with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions. Join us as we explore seven powerful facts, types, and practical uses of step down transformers.
How a Step Down Transformer Works with Components
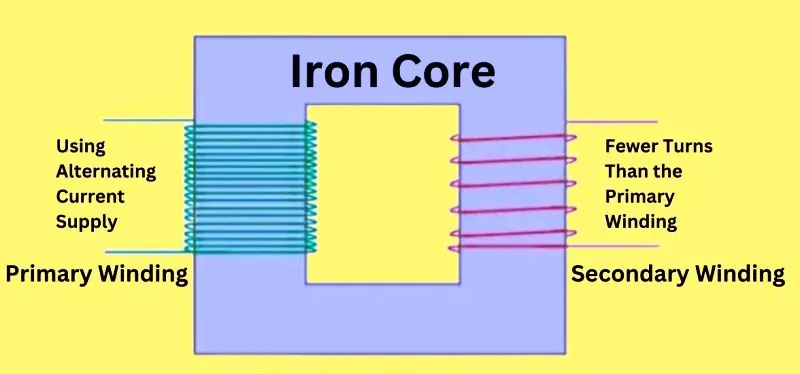
A step down transformer operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction to convert high voltage to a lower voltage suitable for various applications. Here’s a detailed look at its components and how they work together:
Primary Coil
The primary coil is the input winding of the transformer, connected to the high voltage supply. When an alternating current (AC) flows through this coil, it creates a varying magnetic field around it.
Secondary Coil
The secondary coil is the output winding, connected to the lower voltage load. The number of turns in the secondary coil is fewer than in the primary coil, which is key to reducing the voltage.
Core
The core, typically made of laminated iron, provides a path for the magnetic field created by the primary coil. This core helps to efficiently transfer the magnetic flux to the secondary coil.
Insulation
Insulation materials are used to isolate the coils from each other and from the core to prevent electrical short circuits and ensure safety.
How It Works
- Electromagnetic Induction When an AC voltage is applied to the primary coil, it generates a magnetic field that changes with the current. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil through electromagnetic induction.
- Voltage Transformation The voltage induced in the secondary coil is proportional to the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil. Since the secondary coil has fewer turns, the voltage is reduced proportionally.
- Energy Transfer The energy is transferred from the primary coil to the secondary coil via the magnetic core. The efficiency of this transfer is enhanced by the core material, which minimizes energy loss.
- Output The secondary coil delivers the reduced voltage to the connected load. This output voltage is lower than the input voltage, making it suitable for devices that require less voltage than the main supply.
Example
For instance, if the primary coil has 1000 turns and the secondary coil has 100 turns, the voltage is reduced by a factor of 10. So, if 240V is applied to the primary coil, the secondary coil will output 24V.
Types and Specifications
Overview of Different Types of Step Down Transformers
- Isolation Transformers
- Description: Isolation transformers are designed to decouple two circuits, allowing AC power to be transferred from one circuit to another without direct electrical connection.
- Applications: Commonly used in medical devices, sensitive equipment, and audio systems to prevent electrical noise and enhance safety.
- Auto-Transformers
- Description: Auto-transformers have a single winding that acts as both the primary and secondary winding, with a part of the winding common to both sides.
- Applications: Used in voltage regulation for motors, light dimmers, and as variacs in laboratories and industrial equipment due to their efficiency and compact size.
- Toroidal Transformers
- Description: Toroidal transformers have a doughnut-shaped core and are known for their high efficiency and low electromagnetic interference.
- Applications: Ideal for audio equipment, medical devices, and compact electronic devices due to their efficient design and minimal noise production.
- High-Frequency Transformers
- Description: These transformers are designed to operate at high frequencies, making them suitable for applications like switching power supplies and radio frequency (RF) circuits.
- Applications: Used in telecommunications, computer power supplies, and inverter circuits.
Key Specifications and Ratings of Each Type
| Type | Key Specifications | Common Ratings |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation Transformer | Voltage rating, insulation resistance, leakage current | 120V to 240V, 1kVA to 10kVA |
| Auto-Transformer | Voltage adjustment range, efficiency, core type | 0-240V adjustable, 95%-98% efficiency |
| Toroidal Transformer | Core size, efficiency, EMI reduction | 50VA to 5kVA, high efficiency |
| High-Frequency Transformer | Frequency range, core material, thermal management | 20kHz to 1MHz, ferrite core, various wattages |
How to Choose the Right Step Down Transformer for Your Needs
- Determine Your Voltage Requirements
- Assess the input and output voltage requirements of your application to ensure the transformer can provide the necessary voltage conversion.
- Evaluate Power Capacity
- Consider the power rating (VA or kVA) needed for your devices. Choose a transformer with a power capacity that matches or exceeds your load requirements to avoid overloading.
- Consider Efficiency
- For applications requiring high efficiency, such as audio equipment or medical devices, opt for transformers like toroidal or high-frequency types that offer superior efficiency and minimal energy loss.
- Assess Application Specific Needs
- Identify the specific needs of your application. For instance, if electrical noise reduction is crucial, an isolation transformer would be ideal. For variable voltage needs, an auto-transformer would be more suitable.
- Check Safety and Compliance
- Ensure the transformer meets relevant safety standards and certifications (e.g., UL, IEC) to guarantee safe operation and compliance with local regulations.
- Size and Installation
- Consider the physical size and installation requirements. Toroidal transformers are compact and suitable for space-constrained environments, while larger transformers might need specific mounting arrangements.
Types and Specifications
Overview of Different Types of Step Down Transformers
1. Isolation Transformers Isolation transformers are designed to decouple two circuits, allowing AC power to be transferred from one circuit to another without direct electrical connection. They are commonly used in medical devices, sensitive equipment, and audio systems to prevent electrical noise and enhance safety.
2. Auto-Transformers Auto-transformers have a single winding that acts as both the primary and secondary winding, with a part of the winding common to both sides. They are used in voltage regulation for motors, light dimmers, and as variacs in laboratories and industrial equipment due to their efficiency and compact size.
3. Toroidal Transformers Toroidal transformers have a doughnut-shaped core and are known for their high efficiency and low electromagnetic interference. These transformers are ideal for audio equipment, medical devices, and compact electronic devices due to their efficient design and minimal noise production.
4. High-Frequency Transformers High-frequency transformers are designed to operate at high frequencies, making them suitable for applications like switching power supplies and radio frequency (RF) circuits. They are used in telecommunications, computer power supplies, and inverter circuits.
Key Specifications and Ratings of Each Type
| Type | Key Specifications | Common Ratings |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation Transformer | Voltage rating, insulation resistance, leakage current | 120V to 240V, 1kVA to 10kVA |
| Auto-Transformer | Voltage adjustment range, efficiency, core type | 0-240V adjustable, 95%-98% efficiency |
| Toroidal Transformer | Core size, efficiency, EMI reduction | 50VA to 5kVA, high efficiency |
| High-Frequency Transformer | Frequency range, core material, thermal management | 20kHz to 1MHz, ferrite core, various wattages |
How to Choose the Right Step Down Transformer for Your Needs
Determine Your Voltage Requirements Assess the input and output voltage requirements of your application to ensure the transformer can provide the necessary voltage conversion.
Evaluate Power Capacity Consider the power rating (VA or kVA) needed for your devices. Choose a transformer with a power capacity that matches or exceeds your load requirements to avoid overloading.
Consider Efficiency For applications requiring high efficiency, such as audio equipment or medical devices, opt for transformers like toroidal or high-frequency types that offer superior efficiency and minimal energy loss.
Assess Application Specific Needs Identify the specific needs of your application. For instance, if electrical noise reduction is crucial, an isolation transformer would be ideal. For variable voltage needs, an auto-transformer would be more suitable.
Check Safety and Compliance Ensure the transformer meets relevant safety standards and certifications (e.g., UL, IEC) to guarantee safe operation and compliance with local regulations.
Size and Installation Consider the physical size and installation requirements. Toroidal transformers are compact and suitable for space-constrained environments, while larger transformers might need specific mounting arrangements.
Applications of Step Down Transformers
Common Applications in Residential Settings
Lowering Voltage for Appliances:
Step down transformers are widely used in residential settings to convert high voltage from the main power supply to a lower, safer voltage suitable for household appliances. For instance, they are essential for converting the standard 220V or 240V mains electricity down to 110V for devices imported from countries with different voltage standards. This ensures that appliances like refrigerators, microwaves, and entertainment systems operate safely and efficiently without the risk of electrical damage.
Portable Electronic Devices:
Many household electronics, such as chargers for laptops, smartphones, and other portable devices, require a specific lower voltage. Step down transformers embedded in these chargers ensure that the devices receive the correct voltage, protecting them from potential overvoltage damage and prolonging their lifespan.
Commercial Applications
Voltage Regulation in Offices and Retail Spaces:
In commercial environments, step down transformers play a critical role in voltage regulation. Offices and retail spaces often require stable and precise voltage levels to power sensitive equipment such as computers, servers, and point-of-sale systems. By stepping down the high voltage from the main supply to the required lower voltage, these transformers help maintain the optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. This not only improves efficiency but also minimizes the risk of costly downtime due to electrical issues.
Lighting Systems:
Commercial lighting systems often need to operate at lower voltages to ensure energy efficiency and reduce heat generation. Step down transformers are used to convert the higher main supply voltage to the appropriate levels for various lighting solutions, including LED and fluorescent lights, ensuring consistent and reliable illumination in offices and retail spaces.
Industrial Applications
Machinery and Equipment Voltage Adjustment:
In industrial settings, step down transformers are crucial for adjusting voltage levels to meet the specific requirements of heavy machinery and equipment. Industrial machines, such as CNC machines, conveyor systems, and robotic arms, often require lower voltage inputs for safe and efficient operation. Step down transformers ensure that these machines receive the correct voltage, thereby enhancing performance, reducing the risk of electrical faults, and ensuring worker safety.
Power Tools and Equipment:
Many industrial power tools and equipment operate at lower voltages for enhanced safety and efficiency. Step down transformers convert the high voltage from the main power supply to the required levels, enabling tools like drills, saws, and welding equipment to function optimally. This is especially important in settings where precise control and high reliability are essential for productivity and safety.
Energy Distribution Systems:
In large industrial facilities, step down transformers are part of the broader energy distribution system. They help in distributing power from high-voltage transmission lines to various low-voltage systems within the facility. This ensures that different parts of the plant receive the appropriate voltage levels for their specific needs, enhancing overall energy management and operational efficiency.
Installation and Usage Guide
Step-by-Step Instructions for Installing a Step Down Transformer
- Turn Off the Main Power Supply Before starting the installation, ensure that the main power supply is completely turned off to prevent any electrical hazards. This step is crucial for your safety.
- Prepare the Installation Site Choose an appropriate location for the transformer installation. The site should be dry, well-ventilated, and free from dust and flammable materials. Ensure there is enough space for air circulation around the transformer.
- Mount the Transformer
- If the transformer is designed to be mounted, use appropriate mounting brackets or a sturdy surface. Secure the transformer firmly to prevent any movement or vibration during operation.
- For larger transformers, ensure that the mounting surface can support the weight of the transformer.
- Connect the Input Wires
- Strip the insulation off the input wires (primary side) using a wire stripper, ensuring that you expose enough wire to make a secure connection.
- Connect the input wires to the primary terminals of the transformer. Typically, these terminals are marked as “Primary” or with a high voltage rating (e.g., 220V or 240V). Tighten the terminal screws securely to ensure a solid connection.
- Connect the Output Wires
- Strip the insulation off the output wires (secondary side) as done with the input wires.
- Connect the output wires to the secondary terminals of the transformer. These terminals are usually marked as “Secondary” or with a lower voltage rating (e.g., 110V). Ensure a secure connection by tightening the terminal screws.
- Ground the Transformer
- Connect the grounding wire to the transformer’s grounding terminal. This is crucial for safety, as it prevents electrical shocks and ensures proper operation.
- Make sure the grounding connection is secure and follows local electrical codes and standards.
- Check All Connections
- Double-check all connections to ensure they are tight and secure. Loose connections can lead to poor performance and potential hazards.
- Ensure there are no exposed wires that could cause short circuits or electrical shocks.
- Power On and Test
- Once all connections are secure and verified, turn on the main power supply.
- Test the output voltage of the transformer using a multimeter to ensure it is within the expected range.
- Verify that the connected devices operate correctly and that the transformer is functioning as intended.
Tools and Materials Needed for Installation
- Screwdriver (flathead or Phillips, depending on the terminal screws)
- Wire stripper
- Insulated pliers
- Mounting brackets (if required)
- Electrical tape
- Multimeter
- Grounding wire
- Safety gloves and goggles
Best Practices for Using Step Down Transformers Safely and Efficiently
- Regular Maintenance
- Perform regular maintenance checks to ensure that all connections remain tight and secure.
- Inspect the transformer for any signs of wear, damage, or overheating.
- Proper Ventilation
- Ensure that the transformer has adequate ventilation to prevent overheating. Avoid covering or enclosing the transformer in a way that restricts airflow.
- Load Management
- Do not exceed the rated capacity of the transformer. Overloading can cause overheating and potential failure.
- Distribute the electrical load evenly across the transformer to maintain efficiency and longevity.
- Use Appropriate Fuses and Circuit Breakers
- Install appropriate fuses or circuit breakers on the input and output sides of the transformer to protect against overcurrent conditions.
- Ensure that the protective devices are rated correctly for the transformer’s capacity.
- Monitor for Unusual Behavior
- Keep an eye on the transformer for any unusual noises, vibrations, or smells. These can be signs of internal issues that need to be addressed immediately.
- If any abnormal conditions are detected, disconnect the power supply and inspect the transformer for faults.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions
- Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions for installation and usage.
- Refer to the user manual for specific recommendations and safety precautions.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips
| Issue | Troubleshooting Steps | Regular Maintenance Tips | Signs of Replacement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer Overheating | 1. Check for overloaded circuits and reduce load if necessary. 2. Ensure adequate ventilation around the transformer. 3. Inspect for dust or debris blocking airflow. | 1. Keep the transformer clean and free from dust. 2. Ensure proper ventilation and cooling. 3. Regularly monitor temperature. | 1. Persistent overheating despite troubleshooting. 2. Burnt smell or visible damage to the casing. 3. Discoloration or melting of components. |
| No Output Voltage | 1. Verify input voltage with a multimeter.<br> – Check for blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers. 2. Inspect connections for loose or broken wires. | 1. Regularly test output voltage with a multimeter. 2. Ensure all connections are tight and secure. | 1. No output despite correct input voltage. 2. Internal components appear damaged or burnt. 3. Frequent need for resetting or replacing fuses/breakers. |
| Unusual Noise or Vibration | 1. Check for loose mounting brackets or hardware. 2. Inspect internal components for signs of wear or damage. 3. Ensure proper grounding. | 1. Regularly tighten mounting brackets and hardware. 2. Inspect internal components during routine checks. | 1. Persistent noise or vibration despite securing all components. 2. Visible wear or damage to internal parts. 3. Signs of internal arcing or sparking. |
| Frequent Tripping of Breakers/Fuses | 1. Inspect for short circuits or overloaded circuits. 2. Ensure proper load distribution.<br> – Check for defective wiring or connections. | 1. Monitor load levels and distribute evenly. 2. Regularly inspect wiring and connections for wear or damage. | 1. Breakers/fuses trip frequently despite addressing load and wiring issues. 2. Evidence of repeated electrical faults. 3. Transformer fails to maintain a stable output. |
| Low or Fluctuating Output Voltage | 1. Verify input voltage stability. 2. Check for loose or corroded connections. 3. Inspect the transformer windings for damage. | 1. Ensure stable input voltage. 2. Regularly inspect and clean connections. 3. Test windings for continuity and resistance. | 1. Output voltage remains unstable despite troubleshooting. 2. Visible damage or corrosion on windings. 3. Transformer fails to maintain consistent performance. |
Comparing Different Brands and Models
| Brand & Model | Overview | Performance | Durability | Value for Money | Customer Reviews & Expert Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schneider Electric – A9T | High-quality step down transformer with advanced safety features. | Excellent performance with stable voltage output. | Highly durable with robust construction suitable for various environments. | Offers good value considering its advanced features and reliability. | Customers praise its reliability and ease of installation. Experts recommend it for both residential and commercial use due to its consistent performance and safety features. |
| Siemens – 3RL | Known for its efficiency and compact design, ideal for commercial and industrial applications. | High efficiency and reliable performance in demanding environments. | Durable design that withstands heavy usage and harsh conditions. | Priced competitively, offering great value for industrial applications. | Highly rated by customers for its efficiency and durability. Experts recommend it for industrial settings where high performance and reliability are crucial. |
| ABB – T2 | Offers a wide range of transformers with various ratings, suitable for multiple applications. | Delivers consistent performance with minimal voltage fluctuations. | Long-lasting with excellent build quality. | Slightly higher cost but justified by superior quality and performance. | Customers appreciate the reliability and long lifespan. Experts recommend ABB for critical applications requiring dependable performance and high safety standards. |
| Legrand – 041 | Versatile transformer designed for both residential and light commercial use. | Reliable performance with a focus on energy efficiency. | Good durability for everyday applications. | Affordable and offers good value for standard applications. | Positive customer feedback for ease of use and energy efficiency. Experts recommend it for residential and small commercial applications due to its affordability and reliable operation. |
| Eaton – CF | Compact and efficient transformer suitable for various applications, including sensitive equipment. | Consistent performance with a focus on protecting sensitive electronics. | Durable and well-built, ensuring longevity. | Reasonably priced, providing excellent value for protecting sensitive equipment. | Customers rate it highly for protecting electronic devices. Experts recommend it for use in environments with sensitive electronics due to its protective features and reliable performance. |
FAQ on “Step Down Transformer”
Q: What is a step down transformer?
A: It reduces high voltage to lower voltage.
Q: Where are step down transformers used?
A: In homes, offices, and industries.
Q: How does a step down transformer work?
A: By converting high voltage to lower voltage.
Q: What are the benefits of using a step down transformer?
A: Safer voltage levels and equipment protection.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we’ve delved into the essentials of step down transformers, exploring their types, specifications, and diverse applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Understanding how to install and maintain these transformers is crucial for ensuring their reliable and efficient operation. By comparing different brands and models, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs, balancing performance, durability, and value for money. Step down transformers play a vital role in modern electrical systems, enhancing safety and efficiency. Stay informed and make smart choices to protect and optimize your electrical infrastructure. Thank you for reading!