When it comes to marine engine performance, the turbocharger’s bearing lubrication system is a quiet workhorse that determines reliability, efficiency, and life expectancy. Proper lubrication isn’t just about maintaining machinery—it’s about unleashing the true potential of your ship’s engines while avoiding costly failures and downtime.marinediesel+1
Why Turbocharger Bearing Lubrication Systems Matter
Turbochargers operate under extreme speeds and loads, especially in marine environments. Their bearings face constant challenges—heat, pressure, salty air, vibration, and delays in oil delivery after startup. An optimized lubrication system keeps these bearings friction-free, reducing energy loss and maximizing efficiency.marinediesel+1
Core Turbocharger Bearing Types Explained
Ball (Rolling) Type Bearings
- Typically found on the blower side, these bearings use steel balls between inner and outer races.
- Leaf springs damp vibration and extend bearing life.
- Lubrication is provided by a shaft-driven gear pump, forming a closed loop with its own sump.
- Pros: Easy inspection, straightforward oil management, reduced friction at high speeds.
- Cons: Poor lubrication during startup or low speeds, pump failures can cause catastrophic damage.marinediesel+1
Sleeve (Journal) Type Bearings
- Utilized for their durability and lower maintenance.
- Lubricated using the ship’s main oil system, ensuring constant supply and cooling.
- Often include backup solutions and are easier to replace.
- Pros: Continuous oil supply, efficient cooling, robust under varied conditions.
- Cons: Higher initial system cost, strict quality requirements for lubricating oil.marinediesel+1
Sleeve Bearing Lubrication System
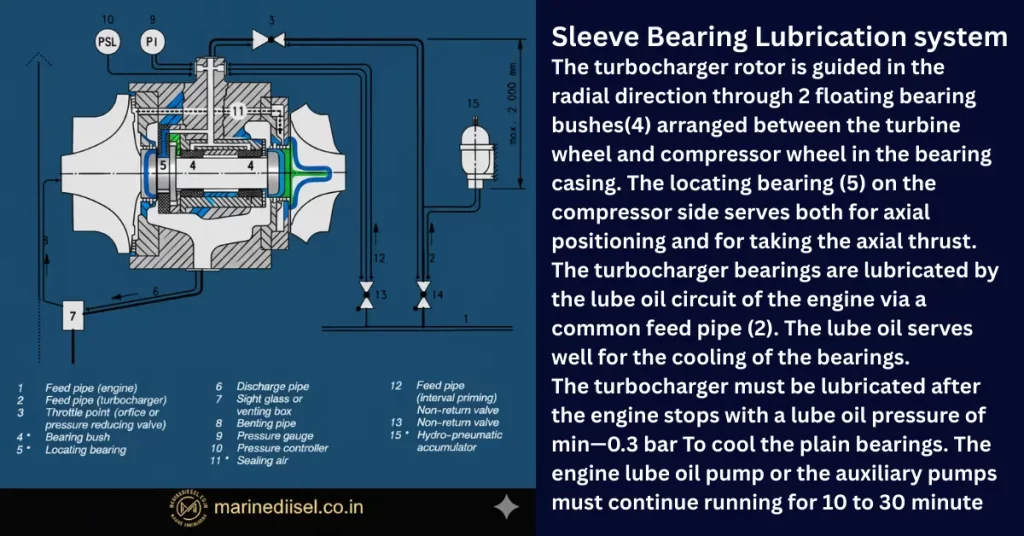
The turbocharger rotor is radially supported by two floating sleeve bearing bushes positioned between the turbine and compressor wheels within the bearing casing. Axial location and thrust are managed by a locating bearing on the compressor side, which ensures precise shaft positioning and keeps axial loads in check.
Lubricating oil is supplied to these bearings directly from the main engine’s lubrication system via a dedicated feed pipe. This oil not only lubricates but also actively cools the bearings, protecting them from high thermal loads encountered during operation.
To prevent bearing overheating after engine shutdown, lubrication must continue at a minimum oil pressure of 0.3 bar. The main or auxiliary lube oil pumps should remain active for 10–30 minutes after stopping the engine, providing essential post-run cooling for the plain (sleeve) bearings.
Advantages
- Continuous, reliable lubrication is assured as long as the main system is operational.
- No need for a separate oil supply; standard engine system oil is used.
- The constant presence of an oil film reduces the risk of static brinelling between the shaft and sleeve.
- Backup tanks can supply oil if the primary pump fails, enhancing system safety.
- Lubrication is effective across all speed ranges, with less frequent oil changes required.
Disadvantages
- Initial setup can be costly due to the need for piping, coolers, filters, and expansion tanks.
- Any contaminants or foreign matter in the lube oil line can reach the bearings and cause damage.
- If the lube oil quality deteriorates, bearing reliability and life are significantly reduced.
This design is ideal where long-term reliability and ease of integration with the main lubrication system outweigh the higher complexity and cost of installation.dieselship+2
What Makes a Great Turbocharger Bearing?
- Strength: Designed to manage high thrust and radial loads without deformation or failure, even under harsh marine conditions.
- Temperature Resilience: Built to handle rapid temperature spikes—especially critical during quick engine stops/starts.
- Material Compatibility: Bearings are crafted to avoid adverse chemical reactions with advanced synthetic oils.marinediesel+1
Five Practical Care and Troubleshooting Tips
- Regularly inspect oil supply lines and connections for leaks or blockages.
- Monitor the oil quality—contaminated or degraded oil is a top cause of bearing wear.
- Allow oil pumps to run for 10-30 minutes post-shutdown to ensure effective cooling and prevent coking.
- Use only OEM-approved lubricants with high temperature stability and anti-rust characteristics.
- Watch out for warning signs such as abnormal noise or rising bearing temperatures, which may indicate lubrication issues.marinediesel+1
Expert Checklist: Maintenance Steps for Longevity
- Check sights glass or electronic sensors for correct oil level daily.
- Replace or filter lubricating oil at intervals specified by the turbocharger manufacturer.
- Keep backup oil tanks operational as redundancy for main pumps.
- Clean the bearing housing and check for debris or contamination during routine overhauls.
Infographic: Turbocharger Bearing Failure Causes
- Oil starvation at startup
- Vibration-related wear
- Overheating events
- Oil contamination
- Chemical incompatibility
Common Turbocharger Lubrication Failures and How to Prevent Them
Here is a table summarizing common turbocharger lubrication failures and prevention strategies for marine engines:marinediesel+2
| Failure Type | Description | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Starvation | Insufficient oil supply due to faulty pumps, clogged lines or delayed priming. | – Regularly inspect/clean oil lines – Check pump condition – Use proper startup/shutdown proceduresmarinediesel+1 |
| Contaminated Oil | Presence of dirt, debris, or degraded oil causing bearing wear. | – Change oil/filter at recommended intervals – Use only OEM-approved oils – Maintain effective filtrationdieselpro+1 |
| Overheating | High friction and temperatures due to poor lubrication or exhaust issues. | – Monitor turbo/engine temp – Ensure uninterrupted oil flow – Clean oil and air passagesmarinediesel+1 |
| Oil Leaks | Oil escapes due to worn seals or high pressure, affecting efficiency. | – Inspect/replace seals – Check gaskets and pressure – Address leaks promptlymarinediesel+1 |
| Bearing Wear | Rapid deterioration from low-quality oil or infrequent maintenance. | – Use premium lubricants – Perform routine oil changes – Schedule regular turbo inspectionsgicopss+1 |
This structure visually highlights the source of each failure and the key practical steps for prevention.gicopss+2
The Impact of Lubricant Quality on Turbocharger Bearing
Here is the information in a clear table format showing how lubricant quality impacts turbocharger bearing life and the related practical steps:lubricants.totalenergies
| Impact of Lubricant Quality | Effect on Turbocharger Bearings | Practical Steps to Maximize Life |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Management | Prevents overheating and component expansion | Use high-grade synthetic oils with recommended viscositylubricants.totalenergies |
| Wear Reduction | Keeps metal parts separated, reducing friction and wear | Maintain scheduled oil and filter changeslubricants.totalenergies |
| Deposit Control | Inhibits formation of harmful deposits that block oil circulation | Use oils with detergent/dispersant additives; change oil regularlylubricants.totalenergies |
| Contaminant Removal | Removes dirt from sensitive areas, maintains cleanliness | Ensure proper filtration and timely oil changeslubricants.totalenergies |
| Correct Grade and Compatibility | Ensures optimal protection and temperature stability | Select the right grade (SAE 5W-30, 5W-40, 0W-30) per manufacturer specslubricants.totalenergies |
Ball vs Sleeve Bearings: Best Choice for Marine Turbos
Ball bearings and sleeve (journal) bearings are the two primary designs used in marine turbochargers, each offering distinct advantages and limitations. The best choice depends on specific needs such as speed, load, maintenance requirements, and vessel operating profile.marineinsight+2
| Feature | Ball Bearings | Sleeve (Journal) Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Speed & Efficiency | Lower friction, ideal for very high speeds and fast response; better energy efficiencyjiegongbearing+1 | Slightly higher friction; suitable for moderate to high speeds but less responsivejiegongbearing+1 |
| Load Handling | Good at handling both axial and radial loadsmarineinsight+1 | Primarily handles radial load; needs separate thrust bearing for axial loadsmarineinsight+1 |
| Lubrication Needs | Requires precise, high-quality lubrication; sensitive to contaminationmarineinsight | Relies on hydrodynamic oil film; continuous oil supply and quality are criticalmarineinsight+1 |
| Durability | Can fail quickly under overload or dirty oil; resilient mounting helpsmarineinsight | Generally robust if oil is kept clean; can tolerate higher loads but is more prone to heat and wear under oil failurejiegongbearing+1 |
| Maintenance | Easier to access on large units; shorter intervals between overhaulmarineinsight | Simpler design, less frequent maintenance if lubrication is well-managedpibsales |
| Noise | Can be noisier at high speedspibsales+1 | Quieter due to sliding operationpibsales+1 |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complexity and materialspibsales | More economical for basic and heavy-load applicationspibsales |
Which is Best?
- Ball Bearings: Best for high-speed, performance-critical marine engines where faster turbo response and high efficiency outweigh higher costs and the need for pristine oil quality.jiegongbearing+1
- Sleeve Bearings: Preferable in heavy-duty settings prioritizing durability, service life, simplicity, and lower cost—provided oil quality is consistently maintained.pibsales+1
Both types will serve well if applied to the correct turbocharger design and maintained as per manufacturer recommendations.marineinsight+2
Turbocharger Cleaning: Boost Lubrication Efficiency
Here is the information in a clear table format showing the best practices for cleaning turbochargers to improve lubrication efficiency:titanturboservice+3
| Best Practice | Description | Benefit for Lubrication Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Oil and Filter Changes | Replace oil/filters more frequently to prevent deposit builduptitanturboservice. | Keeps oil passages clear, prevents wear/deposits |
| Fresh Water Compressor Cleaning | Water jet cleaning of compressor (blower) side at high engine loadmarineinsight+1. | Removes carbon, maintains clean oil flow |
| Scheduled Turbine Cleaning | Water washing at reduced load and dry washing (granules) as per operating hoursaccelleron+2. | Removes hard deposits, prevents blockage |
| Air Filter Inspection/Cleaning | Clean and inspect turbo air filters at each oil changetitanturboservice+1. | Prevents dirt contamination, ensures oil quality |
| Drain Old Oil and Debris | Always drain old oil and remove debris before cleaning or overhaulmarineengineeringonline. | Minimizes contamination risk |
| Hose/Seal/Oil Passage Inspection | Inspect, clean, and replace hoses, seals, and oil passages for wear/cracksmarineengineeringonline. | Prevents leaks/blockages affecting lubrication |
| Engine Warm-Up/Cool-Down | Allow proper warm-up/cool-down for oil circulation and debris removalmotorist. | Prevents oil coking, maintains flow |
| Monitor for Abnormal Noises | Listen for siren-like noises, which indicate bearing or oil issueslubricants.totalenergies. | Early detection of lubrication-related faults |
| Avoid Over-Cleaning Air Filters | Clean only when necessary to preserve filtration efficiencyequipmentjournal. | Avoids finer dust entry, protects bearings |
How Diesel Engine Oil Handles Turbocharger Stress
Diesel engine oil is engineered to handle the extreme thermal and mechanical stresses of turbochargers by maintaining viscosity at high temperatures, keeping bearings protected, and preventing harmful sludge, varnish, and deposit buildup. Fully synthetic oils are preferred, as they offer superior thermal stability, resist breakdown, and efficiently carry heat away from turbo components.tatamotorsgenuineoil+3
Key Functions of Diesel Engine Oil Under Turbo Stress
Diesel engine oil is engineered to handle the extreme thermal and mechanical stresses of turbochargers by maintaining viscosity at high temperatures, keeping bearings protected, and preventing harmful sludge, varnish, and deposit buildup. Fully synthetic oils are preferred, as they offer superior thermal stability, resist breakdown, and efficiently carry heat away from turbo components.tatamotorsgenuineoil+3
Key Functions of Diesel Engine Oil Under Turbo Stress
- Maintaining Viscosity: High-quality oils retain proper flow even at elevated turbo temperatures, ensuring the oil film doesn’t break down and bearings remain lubricated.bestengineoilintheworld+1
- Contamination Control: Detergents and dispersants in oil prevent sludge and varnish from forming on hot turbo surfaces, maintaining clean passages for consistent cooling and oil delivery.bellperformance+1
- Thermal Protection: Synthetic and premium oils absorb and dissipate heat, preventing localized hotspots and oil coking that can block oil flow and damage the turbo.avdmm+1
- Frequent Oil Changes: Turbos stress oil rapidly, causing quicker degradation—shortened oil change intervals help avoid contamination and loss of lubricant quality.youtubebellperformance
- Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Allowing the engine to idle before shutting it off, and not over-revving when oil is cold, reduces wear by ensuring oil is circulated and turbos aren’t exposed to abrupt thermal shock.motoringassistyoutube
Using the correct diesel engine oil, maintaining clean oil and filters, and following best operational practices are crucial to maximize turbocharger life and performance under heavy-duty diesel operating conditions.tatamotorsgenuineoil+3
Q: What is a turbocharger-bearing lubrication system?
A: It’s a system that provides oil to keep the turbocharger’s bearings working smoothly.
Q: Why is lubrication important for turbocharger bearings?
A: Lubrication prevents friction and wear, helping the bearings last longer.
Q: What qualities should lubricants for turbocharger bearings have?
A: They should resist high temperatures, prevent rust, and not react with the turbocharger’s parts.
Q: How does proper lubrication affect turbocharger performance?
A: Good lubrication ensures efficient and reliable turbocharger operation.
