Under-Voltage Protection
Under-voltage protection plays a critical role in safeguarding AC generators by preventing damage and ensuring smooth operation. When the voltage supply drops below the required level, it can cause inefficiencies, overheating, and severe damage to electrical components within the generator. This not only reduces the lifespan of the equipment but can also lead to costly repairs and unexpected downtime.
In this guide, we’ll explore the essentials of under-voltage protection, why it’s vital for maintaining generator performance, and how it prevents system failures. Readers will learn about the various types of under-voltage protection devices, best practices for setting them up, and troubleshooting tips to ensure long-term efficiency. Whether you’re managing generators in an industrial, marine, or residential setting, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to keep your AC generators running optimally and safely.
What is Under-Voltage Protection?
Under-voltage protection is a critical safety mechanism designed to prevent AC generators from operating at dangerously low voltage levels. It ensures that the generator functions within its optimal voltage range, protecting the equipment and electrical system from damage caused by insufficient voltage supply.
Definition and Explanation of Under-Voltage in AC Generators
Under-voltage occurs when the voltage supplied to the generator falls below the minimum threshold required for normal operation. This can lead to inefficiencies, decreased output, and even potential damage to the generator’s internal components. AC generators are designed to operate within specific voltage ranges, and a significant drop in voltage can disrupt their performance.
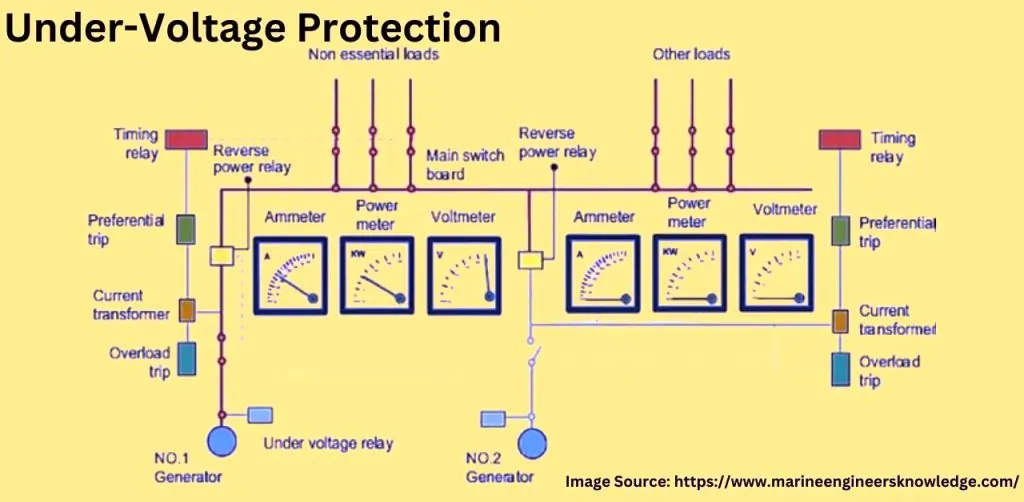
Key Role of Under-Voltage Protection in Generator Operation
Under-voltage protection continuously monitors the voltage levels and disconnects the generator if it drops below a predefined limit. This automatic response helps to prevent damage to the generator and connected electrical systems, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Common Causes of Under-Voltage in AC Generators
- Overloaded systems: Excessive demand on the generator can cause a voltage drop.
- Faulty components: Malfunctioning parts, such as voltage regulators or worn-out wiring, can lead to under-voltage.
- External factors: Fluctuations in grid supply or environmental conditions, like extreme heat, can affect the generator’s voltage output.
- Poor maintenance: Lack of regular maintenance can result in degraded performance, leading to under-voltage conditions.
How Under-Voltage Affects AC Generators
Under-voltage can significantly impact the performance and longevity of AC generators. Operating a generator at reduced voltage levels can lead to inefficiencies, increased stress on the system, and potential damage to critical components.
Impact of Under-Voltage on Generator Performance
When a generator experiences under-voltage, its ability to deliver power efficiently is compromised. The electrical output becomes unstable, causing the generator to work harder to maintain performance. This inefficiency can lead to higher fuel consumption and reduced overall output, affecting the generator’s capacity to support connected systems and devices.
Consequences of Running a Generator Under Low Voltage Conditions
Running an AC generator at low voltage can have severe consequences. Some of the most common issues include:
- Overheating: The generator may overheat due to increased current drawn to compensate for low voltage.
- Reduced efficiency: Under-voltage causes poor performance and increased wear on moving parts.
- Loss of system control: Unstable voltage affects connected devices, leading to potential system failures or outages.
Potential Damage to Electrical Components and System Instability
Prolonged under-voltage can damage sensitive electrical components, including circuit boards, relays, and insulation. System instability may also lead to breakdowns in other electrical systems relying on the generator, resulting in costly repairs and downtime. In extreme cases, the generator itself may suffer irreversible damage, requiring complete replacement.
Types of Under-Voltage Protection Devices
Under-voltage protection is essential for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of AC generators. There are several devices specifically designed to monitor and control voltage levels, preventing damage caused by under-voltage conditions.
Overview of Different Devices That Protect Against Under-Voltage
A variety of devices are used to protect AC generators from under-voltage. Each device has a unique function but serves the same goal: maintaining voltage levels within safe operating ranges. These devices include Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs), relay-based systems, and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), each offering specific advantages for different applications.
Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs)
Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs) are commonly used in AC generators to automatically maintain voltage output within a desired range. AVRs continuously monitor the generator’s voltage and adjust the excitation system to compensate for any voltage fluctuations. This ensures that the generator operates at optimal voltage levels and prevents under-voltage from occurring.
Relay-Based Protection Systems
Relay-based protection systems are designed to detect under-voltage conditions and trigger protective actions, such as disconnecting the generator from the load. These systems use under-voltage relays, which are preset to activate if the voltage falls below a specified limit. When activated, the relay opens the circuit to prevent further damage or inefficiency.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) for Monitoring and Protection
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are advanced devices that monitor various aspects of the generator’s performance, including voltage levels. In the case of under-voltage, a PLC can be programmed to trigger alarms, shutdowns, or adjustments to bring the voltage back to safe levels. PLCs are particularly useful in complex systems that require continuous monitoring and automated control for multiple parameters, ensuring comprehensive protection against under-voltage conditions.
5 Best Practices for Setting Up Under-Voltage Protection
Properly setting up under-voltage protection is crucial for ensuring that AC generators operate safely and efficiently. Below are five best practices to follow when configuring under-voltage protection systems.
How to Properly Size and Configure Under-Voltage Protection Devices
The first step in effective under-voltage protection is selecting the right device based on the generator’s capacity and application. The protection device must be appropriately sized to match the generator’s voltage and power output. Incorrect sizing can result in either insufficient protection or unnecessary tripping. Always consult the generator’s specifications to choose the correct device, ensuring it’s designed to handle the generator’s normal operating voltage range.
Ideal Voltage Thresholds for Protection Settings
Setting the right voltage thresholds is critical for under-voltage protection. Generally, the threshold should be set slightly below the generator’s nominal voltage to avoid nuisance tripping during minor fluctuations, but high enough to detect dangerous under-voltage conditions. Typical settings range from 85-90% of the generator’s rated voltage, depending on operational requirements. It’s important to tailor the threshold to the specific application.
Monitoring Systems to Ensure Voltage Stays Within Safe Ranges
An efficient under-voltage protection system requires continuous monitoring to detect voltage fluctuations. Devices like Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs) or Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) can be integrated to track voltage levels in real-time. This helps ensure that the generator operates within the safe voltage range, and any deviations are corrected immediately, reducing the risk of prolonged under-voltage conditions.
Regular Maintenance and Testing of Under-Voltage Protection Systems
Regular maintenance and periodic testing of under-voltage protection devices are crucial for ensuring long-term reliability. Over time, protection devices can degrade or become miscalibrated, leading to inadequate protection. Routine inspections, testing the voltage settings, and simulating under-voltage conditions help identify potential issues early and ensure the protection system functions as intended.
Importance of Real-Time Monitoring with Integrated Sensors
Real-time monitoring with integrated sensors is essential for modern under-voltage protection systems. Sensors continuously feed voltage data to control systems, which then adjust generator performance or trigger protective actions if needed. Integrated sensors provide accurate, up-to-the-minute data, allowing for immediate response to under-voltage events. This enhances the overall safety and reliability of the generator system, minimizing the risk of damage.
How to Troubleshoot Under-Voltage in AC Generators
| Step | Action | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Identify the Symptoms | Check for reduced generator output or inefficient performance. | Symptoms like flickering lights, reduced power to equipment, or system overload may indicate under-voltage. |
| 2. Verify Voltage Levels | Use a voltmeter to check if the generator’s voltage is below the rated value. | Confirm the actual voltage reading and compare it to the generator’s standard operating voltage. |
| 3. Inspect Load Balancing | Ensure the electrical load is evenly distributed across phases. | Uneven load distribution can cause voltage dips on one or more phases, leading to under-voltage issues. |
| 4. Check Generator Output | Evaluate if the generator is producing its rated capacity. | A drop in generator output may signal internal faults or insufficient power generation. |
| 5. Assess External Voltage Sources | Inspect external voltage sources (grid or backup supply) for fluctuations. | Fluctuations from external power sources can impact the generator’s voltage levels. |
| 6. Quick Fix: Adjust Load | Reduce the electrical load to relieve the generator. | Temporarily reducing the load can stabilize voltage but may not solve the underlying issue. |
| 7. Long-Term Fix: Repair or Replace Components | Inspect and repair faulty components such as voltage regulators or relays. | Replace worn-out or malfunctioning parts to restore proper voltage regulation and prevent future issues. |
| 8. Test and Calibrate Protection Systems | Ensure under-voltage protection devices are functioning correctly and calibrated properly. | Regularly test devices like AVRs and relays to maintain accurate voltage monitoring and protection. |
| 9. Monitor for Recurring Issues | Continuously monitor generator performance for any recurring under-voltage problems. | Implement long-term monitoring with integrated sensors or control systems to detect voltage drops early. |
Top 3 Benefits of Using Under-Voltage Protection
Implementing under-voltage protection for AC generators brings numerous advantages, from safeguarding equipment to ensuring smooth and efficient operations. Here are the top three benefits:
1. Enhanced Lifespan of the Generator
Under-voltage protection helps extend the lifespan of the generator by preventing excessive wear and tear. When voltage levels drop, the generator’s components are subjected to additional stress, leading to overheating and potential damage. By ensuring the generator operates within safe voltage ranges, under-voltage protection minimizes these risks, reducing the likelihood of premature equipment failure and prolonging its operational life.
2. Improved System Efficiency and Performance
Generators operating at proper voltage levels run more efficiently, delivering optimal performance. Under-voltage can lead to inefficiencies, as the generator has to work harder to compensate for the voltage drop. With effective under-voltage protection in place, the generator consistently performs at its best, maintaining stable output and reducing fuel consumption. This results in improved overall system efficiency.
3. Prevention of Costly Downtime and Repairs
One of the most significant benefits of under-voltage protection is the prevention of costly downtime and repairs. Under-voltage conditions can lead to system instability, damaging not only the generator but also the connected electrical components. By automatically shutting down or correcting under-voltage conditions, these protection devices prevent major system failures and expensive repairs, saving both time and money for operators.
FAQs on Under-Voltage Protection
Q- What is under-voltage protection on a generator?
A- Under-voltage protection prevents generator damage by disconnecting it when voltage drops below a safe threshold.
Q- How to protect against under-voltage?
A- Install Automatic Voltage Regulators (AVRs) or relays to monitor and maintain voltage within safe limits.
Q- What causes under-voltage in generators?
A- Under-voltage can be caused by overloaded systems, faulty components, or fluctuations in external voltage sources.
Q- Which relay is used for generator protection?
A- The SPAG 332 generator protection relays are commonly used.
Conclusion
Under-voltage protection is a crucial aspect of maintaining the efficiency, safety, and longevity of AC generators. By ensuring that voltage levels remain within a safe range, under-voltage protection devices prevent potential damage to both the generator and connected systems. From enhancing performance to avoiding costly downtime and repairs, the benefits of implementing robust under-voltage protection cannot be overstated. Whether you’re operating in industrial, marine, or residential environments, proper installation, monitoring, and maintenance of under-voltage protection systems will keep your generators running smoothly. As you move forward, consider regular testing and real-time monitoring to ensure continuous protection and reliable performance.