Wear Rings in Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are essential in many industrial and marine applications, known for their efficiency in moving fluids. A critical component in these pumps is the wear ring, which helps minimize leakage between the pump casing and impeller, ensuring smooth operation. Wear rings play a vital role in maintaining pump efficiency by reducing friction and preventing excessive wear, which ultimately extends the pump’s lifespan.
In 2024, advancements in wear ring materials and designs are enhancing their performance, especially under extreme conditions. Selecting the right wear ring, optimizing clearance, and performing timely replacements have become crucial to keeping pumps running efficiently. This guide will explore the importance of wear rings in centrifugal pumps, the latest trends, and best practices for ensuring optimal pump performance in 2024 and beyond.
What Are Wear Rings in Centrifugal Pumps?
Wear rings are critical components in centrifugal pumps, designed to reduce the clearance between the impeller and the casing. Their primary role is to minimize internal fluid leakage, which enhances pump efficiency by preventing direct contact between the rotating impeller and stationary casing.
By serving as a protective barrier, wear rings prevent excessive wear and tear on the pump’s internal components, particularly the impeller and casing. This protection results in smoother operation, improved energy efficiency, and extended pump lifespan, making wear rings a crucial element in pump maintenance and performance.
Several types of wear rings are commonly used in industrial applications, including bronze, stainless steel, and composite materials. The choice of material depends on specific factors like the fluid being pumped, operating temperatures, and corrosion resistance requirements. Selecting the appropriate wear ring type for your pump is essential for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and operational efficiency.
Materials Used in Wear Rings
Wear rings in centrifugal pumps are crafted from various materials, each selected for its specific performance characteristics based on the pump’s application and environment. The most commonly used materials include bronze, stainless steel, and composite materials, each offering unique advantages.
Bronze Wear Rings
Bronze is a popular choice due to its excellent wear resistance and compatibility with a wide range of fluids. It is often used in pumps handling water or mild chemicals, providing good corrosion resistance and durability in less aggressive environments.
Stainless Steel Wear Rings
Stainless steel is ideal for more demanding applications where higher corrosion resistance is necessary. It performs well under high temperatures and in pumps dealing with corrosive or abrasive fluids. Stainless steel wear rings are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine applications, where extreme conditions are common.
Composite Material Wear Rings
Composite materials are increasingly favored for wear rings due to their lightweight properties and superior wear resistance. These materials, often a blend of polymers reinforced with carbon or fiberglass, offer low friction and perform exceptionally well in harsh operating conditions. Composite wear rings are also known for their resilience against corrosion and abrasion.
Factors Influencing Material Selection
When choosing the appropriate material for wear rings, several factors should be considered:
- Fluid Compatibility: The wear ring material must be resistant to the fluid being pumped to prevent corrosion or material degradation.
- Operating Conditions: High temperatures, pressure, and fluid velocity can affect the material choice, requiring materials that can withstand such stresses.
- Wear Resistance: The chosen material should offer long-lasting performance under continuous operation, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance.
Wear Ring Design and Fit
The design and proper fit of wear rings are essential for the efficient operation of centrifugal pumps. A critical factor in wear ring design is the wear ring clearance, which refers to the small gap between the wear ring and the impeller. This clearance significantly influences pump performance by controlling fluid leakage from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side. If the clearance is too large, efficiency drops due to increased leakage; if the clearance is too tight, friction increases, leading to wear and potential pump damage.
Determining Proper Clearance
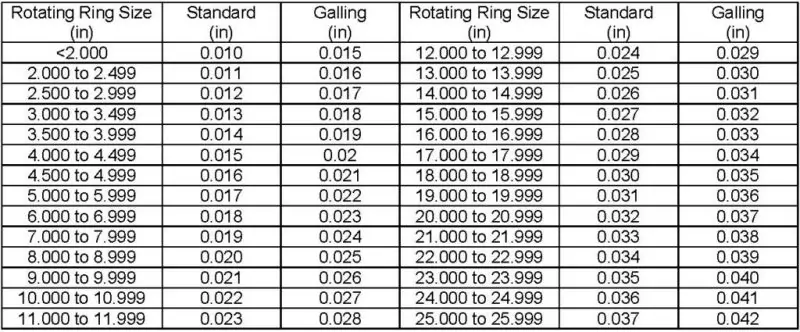
To maintain optimal pump efficiency, it’s vital to ensure the correct clearance between the impeller and casing. The proper clearance is determined by the pump’s operating conditions, including the type of fluid being handled, temperature, and pressure. Most manufacturers provide recommended clearance values for specific pump models, but regular monitoring and adjustment are essential as wear occurs over time.
API 610 Wear Ring Clearance Guide
While it is always recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for wear ring clearances, there are instances where this information may not be readily available. In such cases, the API 610 wear ring clearance guide can be used as a reliable reference.
- For wear rings with a diameter of 2 inches or less, API specifies a minimum diametral clearance of 0.010 inches.
- For every 0.5-inch increase in the impeller wear ring outer diameter (OD), the 0.010-inch clearance increases by 0.001 inches. For example, from 2.000 inches to 2.499 inches OD, the minimum diametral clearance becomes 0.011 inches.
- For impeller wear rings with an OD between 5 inches and 26 inches, each 1-inch increase in the impeller wear ring diameter adds an additional 0.001-inch of minimum diametral clearance.
This guide helps ensure optimal pump performance when manufacturer clearance specifications are unavailable.
Renewable vs. Fixed Wear Rings
Wear rings in centrifugal pumps come in two main types: renewable and fixed.
- Renewable Wear Rings: These are designed for easy replacement when they wear out. Renewable wear rings are a cost-effective solution, allowing you to extend the pump’s life without replacing the entire casing or impeller.
- Fixed Wear Rings: Fixed wear rings are integrated into the pump structure, making them more permanent. When they wear out, replacing larger components becomes necessary, which can be more expensive. However, fixed wear rings are often preferred in applications where added stability is crucial.
Signs of Wear Ring Damage
Wear rings in centrifugal pumps play a critical role in reducing internal leakage and maintaining efficiency, but they are subject to wear over time. Identifying signs of wear ring damage early can prevent costly pump failures and downtime.
Common Symptoms Indicating Wear Ring Failure
Several symptoms can signal wear ring damage, including:
- Performance Drops: A noticeable decrease in pump efficiency or output often points to increased internal leakage caused by worn wear rings.
- Increased Leakage: Fluid leakage between the high-pressure and low-pressure sides of the pump can indicate excessive wear in the clearance between the impeller and wear ring.
- Vibration: Abnormal vibration or noise during pump operation may suggest that the wear rings are no longer properly aligned, allowing impeller contact with the casing.
Detecting Wear Ring Damage
Routine performance checks can help detect wear ring damage. Sudden drops in pump pressure or flow rate are common indicators. Monitoring for excessive leakage and increased vibration also serves as an early warning of wear ring deterioration.
Methods for Routine Inspection and Monitoring
Regular inspections are key to ensuring wear rings are functioning properly. Routine checks should include:
- Visual Inspection: Look for visible signs of wear or damage to the wear rings during maintenance intervals.
- Clearance Measurement: Measure the clearance between the wear ring and impeller regularly to ensure it stays within manufacturer-recommended tolerances.
- Vibration Analysis: Use vibration monitoring tools to detect any changes in the pump’s operational stability, which may indicate wear ring issues.
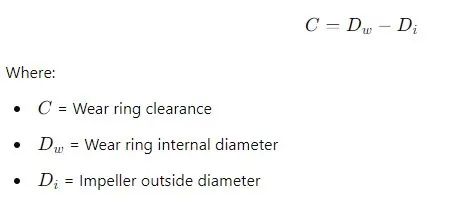
Key Formulas for Wear Rings in Centrifugal Pumps
1. Wear Ring Clearance Formula
The clearance between the wear ring and the impeller is crucial for pump efficiency.
2. Leakage Flow Rate through Wear Ring Clearance
The amount of fluid leakage through the wear ring clearance can be estimated using the orifice flow equation:

3. Wear Rate (Archard’s Law)
To estimate the wear rate of the wear ring, Archard’s law can be applied:

4. Efficiency Loss due to Clearance
Efficiency loss (η\etaη) caused by increased clearance:

Wear Ring Replacement Process
Replacing wear rings in centrifugal pumps is a critical maintenance task that helps restore the pump’s efficiency and prolong its operational life. Following a structured replacement process ensures the pump operates smoothly without unnecessary downtime.
Step-by-Step Guide to Wear Ring Replacement
- Shut Down the Pump and Isolate It
Ensure the pump is fully shut down, isolated from the system, and de-pressurized before beginning any disassembly. - Disassemble the Pump
Carefully remove the pump casing and access the wear rings by disassembling the impeller. Be cautious to avoid damaging other components during this process. - Remove the Old Wear Rings
Depending on the type of wear ring (renewable or fixed), remove the worn rings using the appropriate extraction tools. Clean the surfaces where the new wear rings will be installed to ensure proper fit. - Install the New Wear Rings
Fit the new wear rings into place. Ensure the correct alignment and secure the rings based on the pump’s design specifications. - Reassemble the Pump
Reinstall the impeller and casing. Tighten all components to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications to prevent future misalignment or leaks. - Test the Pump
After reassembly, run the pump under normal operating conditions to check for any leakage or unusual noise that may indicate improper installation.
Tools Required for Wear Ring Replacement
- Wrenches and torque tools for disassembly and reassembly.
- Extraction tools for removing old wear rings.
- Clearance measuring gauges to verify proper wear ring fitment.
- Cleaning tools to remove any debris or corrosion before installation.
Best Practices for Disassembly and Reinstallation
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always refer to the pump’s manual for specific instructions on wear ring replacement.
- Keep Components Clean: Ensure all parts are free of dirt or corrosion before reassembly.
- Use Proper Torque: Tighten bolts to the correct torque to avoid misalignment or damage.
Importance of Maintaining Proper Clearance
After installing new wear rings, it’s crucial to measure and maintain the proper clearance between the wear rings and the impeller. Incorrect clearance can lead to excessive leakage, reduced pump efficiency, and accelerated wear. Regular clearance checks and adjustments, if necessary, ensure that the pump operates at peak performance and reduces the likelihood of early wear ring failure.
Extending Wear Ring Lifespan
Proper maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of wear rings in centrifugal pumps. With the right practices, you can minimize wear, reduce the need for frequent replacements, and ensure optimal pump performance over time.
Best Maintenance Practices for Extending Wear Ring Life
- Regular Inspection: Perform routine checks to monitor wear ring clearance and identify early signs of damage. Regular visual inspections can help detect any irregularities, such as excessive wear or misalignment.
- Clearance Adjustment: Monitor and adjust the clearance between the wear ring and the impeller as recommended by the manufacturer. Keeping this clearance within the correct range is critical for reducing friction and leakage.
- Timely Replacement: Replace wear rings as soon as significant wear is detected. Running the pump with worn wear rings can lead to more extensive damage to the impeller and casing.
Factors that Accelerate Wear and How to Mitigate Them
- Incompatible Materials: Using wear ring materials that are not suitable for the pumped fluid or operating conditions can lead to rapid wear. Mitigate this by selecting materials with high wear resistance and compatibility with the pump fluid (e.g., bronze, stainless steel, or composites).
- Operating Conditions: High temperatures, pressure fluctuations, and abrasive particles in the fluid can accelerate wear. To reduce wear under these conditions, opt for wear rings designed for high-stress environments and ensure proper filtration of fluids to remove contaminants.
- Excessive Clearance: Increased clearance between the impeller and the wear ring can lead to higher leakage rates, reducing efficiency and increasing wear. Regular monitoring and maintaining the correct clearance will minimize these issues.
The Role of Lubrication and Cooling in Preventing Premature Wear
Proper lubrication and cooling are essential to prevent excessive friction and heat buildup, which can prematurely wear down wear rings. Ensuring that the pump’s lubrication system is functioning correctly, and that the cooling mechanisms (if applicable) are sufficient, helps to:
- Reduce Friction: Lubrication minimizes direct contact between moving parts, reducing wear.
- Dissipate Heat: Effective cooling systems help prevent overheating, which can weaken the material of the wear rings and accelerate their wear.
Advancements in Wear Ring Technology for 2024
As technology advances, wear rings in centrifugal pumps have seen significant innovations in materials and designs, improving their durability and performance. These developments are shaping the future of pump efficiency and longevity, especially in demanding environments.
Latest Innovations in Wear Ring Materials and Designs
2024 has brought new materials and composite blends that enhance the wear resistance and longevity of wear rings. Advanced polymers, ceramic composites, and high-performance alloys are now being used, providing superior performance in pumps handling corrosive or abrasive fluids. These new materials minimize friction and improve the overall wear life of the pump, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
In addition, improved designs have emerged that offer better alignment and clearance control, allowing wear rings to function more effectively under higher pressures and temperatures. These new designs also ensure reduced leakage and enhanced efficiency.
Improvements in Wear Resistance and Performance Under Harsh Conditions
Wear ring technology in 2024 is focused on increasing resistance to extreme conditions such as high temperatures, pressures, and abrasive or corrosive fluids. By utilizing coated wear rings and advanced composite materials, manufacturers have improved wear rings’ ability to withstand harsh environments. These innovations ensure longer service intervals and lower maintenance costs, even in the most challenging applications like marine, chemical, and oil and gas industries.
Future Trends in Wear Ring Technology for Centrifugal Pumps
Looking ahead, the focus will be on further enhancing wear ring materials to achieve self-lubricating properties and smart wear rings with embedded sensors. These future designs will provide real-time data on wear conditions and performance, allowing for predictive maintenance and reducing the risk of unexpected failures. The continued push towards sustainable materials is also expected, with manufacturers exploring eco-friendly alternatives without compromising performance.
In 2024, the advancements in wear ring technology promise not only greater efficiency and durability but also lower operational costs, setting new benchmarks in centrifugal pump performance.
FAQ on “Wear Rings in Centrifugal Pumps”
Q: What is the function of a wear ring in a centrifugal pump?
A: It minimizes internal fluid leakage and reduces wear between the impeller and casing.
Q: Where is the wear ring located on a centrifugal pump?
A: The wear ring is positioned between the impeller and the pump casing.
Q: What is the typical hardness of a pump wear ring?
A: Pump wear rings typically have a hardness of 200-300 Brinell, depending on the material.
Q: How do you check wear ring clearance in a centrifugal pump?
A: Wear ring clearance is checked using feeler gauges or micrometers during pump inspection.
Conclusion
Wear rings play a vital role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of centrifugal pumps by minimizing internal leakage and reducing wear. Understanding their design, materials, and proper clearance is essential for optimal pump performance. With advancements in wear ring technology and materials in 2024, pumps can operate more reliably even in harsh conditions. Regular maintenance and timely replacement are key to ensuring your pump remains efficient and cost-effective over time.
