Welcome to our blog post, “What Are the Major Exhaust Emissions from an Engine? The main air contaminants that engines emit into the atmosphere will be discussed in this article.
Some of these emissions, essentially the waste products of engine functioning, can be extremely harmful to the environment. So, let’s explore and learn about the top six pollutants together!
What Are the Major Exhaust Emissions from an Engine
Diesel engines have minimal running costs and high reliability, durability, and efficiency. These crucial attributes make them the most popular engines, especially for heavy-duty vehicles. Diesel engines are getting more popular because they’re used a lot and have advantages. However, they also contribute to pollution that harms the environment and human health.
Laws are changing worldwide to reduce how much harm diesel engines do to nature and people’s health. Both diesel exhaust pollutant emissions and aftertreatment emission control methods have been the subject of several studies. This study reviews diesel engine emissions and associated control mechanisms. Carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides—the four principal pollutants emitted by diesel engines—as well as the diesel oxidation catalyst, diesel particulate filter, and selective catalytic reduction—are reviewed. Comprehensive examinations of each kind of emissions and control system are conducted.
Diesel Exhaust Emissions
Emission Components from Diesel Exhaust Include:
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
- Sulfur Oxides (SOx)
- Particulate Matter (PM)
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Volatile Hydrocarbons (HC) from Lubricating Oil and Unburned Fuel
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) -Components of NOx
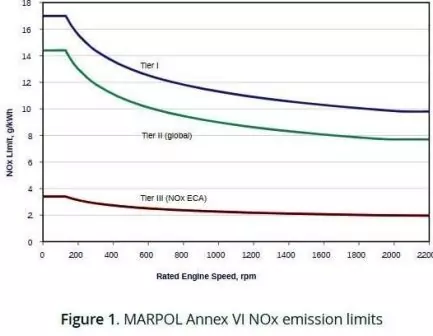
Nitrogen oxides, commonly referred to as NOx, encompass several compounds:
- Nitric oxide (NO)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
- Nitrous oxide (N2O)
- Dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5)
NOx primarily consists of NO and NO2. These compounds form during combustion processes when nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen (O2).
Unfortunately, NOx formation is inevitable during combustion, as the oxidation of nitrogen (N2) by atmospheric oxygen produces thermal NOx.
NOx is considered an air pollutant and a hazardous byproduct of combustion. It contributes to the creation of secondary pollutants, including photochemical smog.
Oxides of Sulfur (SOX)
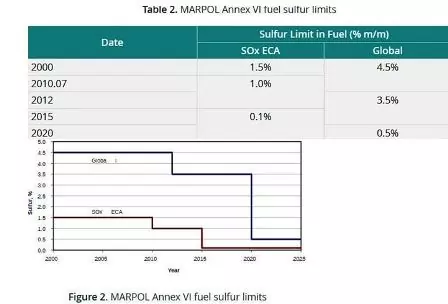
SOx consists of sulfur monoxide (SO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and sulfur trioxide (SO3). Because SO oxidizes into SO2. SO is not decomposable at room temperature under atmospheric pressure. Thus, it refers to SO2 and SO3.
Despite the fact observation of SO2 is as gas or molecules, and SO3 is as PM. In combustion processes, sulfur in fuel leads to the formation of SOx.
In cases associating fossil fuels like petroleum and coal, observe SOX formation. SOx is a bio-product and causes air Pollution along with NOx. SOx is the leading cause of fog.
Particulate Matter (PM)
PM is either a solid particle in liquid droplets. Aerosol in the Atmosphere is also particulate. A hanging particulate element confirms a particle of 10 mm or less in size.
The origination of PM is due to the emission of soot, smog, and ash in carbon.
Particulates hanging in the Atmosphere in heavy concentrations are air pollution.
Inhaling PM will affect human and other living being’s health. Because PM deposits in the lungs and respiratory tract.
PM Emissions from the diesel engine are a severe problem.
The fuel of Diesel engines contains a heavy amount of sulfur. During the combustion process in diesel engines, sulfur produces SOx, i.e., SO2 and sulfate, a PM-type
Oxides of Carbon as Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide emissions from the Diesel engine exhaust is approximately 6 %. CO2 is non-toxic. but has a significant share in Global Warming.
This gas causes the Earth’s Atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is the unavoidable output of the combustion of fossil fuels.
Diesel engine emissions are lower than other heat engines due to higher efficiency.
Efficient fuel combustion will produce less carbon dioxide.
The amount of carbon dioxide production is proportional to the volume of fuel burning.
Change over the fuel from Heavy fuel oil to Natural gas, Hydrogen, or Biofuel to decrease the CO2 emission.
Emission Reduction Technology
The diesel engine has the advantage of lower carbon dioxide. The diesel engine has more efficiency and compact size. It will be mandatory to control the emissions with the latest technology. Harmful particulates and NOx in the Diesel Engine emission.
Marine diesel exhaust emission has a high NOx concentration of 500e1000ppm.
Furthermore, diesel emissions contain sulfur oxides (SOx) and PM. The low RPM makes it easy to control the emission in Diesel Engine, from the environmental safety aspects.
The fuel injection system is the leading technology to improve efficiency and reduce emissions in Diesel engines since this technology enhances combustion.
The impulsive Valve timing system is the automated regulation mechanism. Closing the intake valve before the BDC will lower the combustion temperature. Closing the valve before BDC will cut the effective compression ratio. This operation of the valve timing will reduce the emission.
Fuel Injection with a fine spray and correct pressure will improve vaporization. This process results in perfect and cleaner combustion with reduced NOx and PM. A small amount of fuel injection into the pre-combustion chamber creates an ignition delay.
Prevention of rapid ignition by the method of ignition delay minimizes the NOx. In the following list, we are describing in brief the
Common Rail Injection System
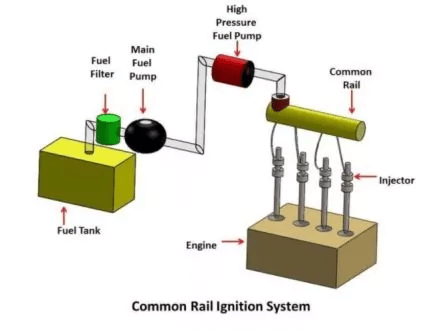
The common rail fuel injection system is the solid injection system. A bypass valve on the main fuel header maintains a constant pressure of 300 bars to 500 bars. Excess fuel is returned to the main fuel supply tank.
High pressure is supplied to a fuel header by a pimp. From the header, high-pressure fuel is forced to each injector fitted in cylinder heads. Fuel enters the cylinders at an appropriate time controlled by a mechanically operated mechanism.
The header pressure design must meet the engine’s requirements for the injector. The designed pressure must penetrate droplets deep into the combustion chamber against the compression pressure. The amount of fuel entering the cylinder is regulated by the Solenoid valve operated by ECU. ECU transmits a signal to the injector to start injecting the fuel after receiving the signal from the crank angle sensor, scavenge air temperature, engine speed, Jacket water temperature, and the load. Standard rail system helps reduce emissions, lower fuel consumption, and lower running speed. It helps in increasing combustion efficiency.
Fuel pre-treatment
This type of treatment reduces the causes that lead to the emergence of pollutants in fuel. Fuel pre-treatment is helpful since it is practical. It doesn’t need the extra device with the engine. Another advantage of the fuel treatment is that it limits the pollutants.
Combustion enhancement
The technology of combustion enhancement doesn’t need any device outside the engine. Optimization and significant reduction are the challenges to this technology. It is challenging to achieve improvement in thermal efficiency. Improvement in thermal efficiency reduces fuel consumption. Waste heat recovery can reduce fuel consumption.
Post Treatment
Post-treatment of exhaust gas will reduce the pollutants in the exhaust gas. The process of exhaust gas post-treatment can reduce many pollutants. The disadvantage of the exhaust gas post-treatment is that an extra device is necessary.
Bio Fuels
Biofuels, usually liquid or gas, are from plants instead of fossil fuels. Diesel Engines use the specified biodiesel fuel. In this process of producing BDF, vegetable oil and animal fats have glycerol.

LNG
- The engines use The Natural evaporated gas known as boil-off gas of LNG as fuel for the engines. The main benefit of LNG usage is that it reduces SOx, NOx, and CO2 emissions. SOx emission is almost zero, while NOx and CO2 will cut by 80% and 25%.
- Nonetheless, a demerit. This system will need a sizeable special tank to store LNG, which causes problems with expenditure and stock capacity in a ship.
- Fuel Engines will meet the needs of present and future stringent regulations. Dual fuel engines are very clean engines since these engines use gas as fuel. These engines emit low NOx, particulate matter (PM), CO2, and zero SOx.
- Gas engines reduce 43% of NOx, 25% of CO2, and 100% of SOx compared to oil. So, dual-fuel engines have many advantages.
Gas-fuel engines will reduce SOx, PM, and CO2 besides NOx, like the ignition of diesel fuel in diesel engines. An ignition source is necessary for combustion in gas engines.
Methods of ignition in Gas Engines
1. Spark Plug
2. Self-Ignition – In this method, the self-ignition of the diesel oil spray ignites a mixture of natural gas and air.
3. Pre-combustion chamber ignition method by the spark plug.
4. Self Ignition with the spray of diesel oil in the pre-combustion chamber.
Natural Gas
Natural gas engines have the disadvantage of Knocking. Knocking causes sharp sound with vibrations. Knocking shockwaves cause damage to the engine material.
Responsive restriction of the air-to-fuel ratio prevents the Knocking-in Dual fuel engines.
In actual operation, output control of power overcomes the Knocking.
It is possible in the dual-fuel engine to change the process from diesel to gas mode.
Besides, a few problems and difficulties persist during a change in gas property.
Due to the presence of low methane numbers in gas causing knocking.
Options of oil are also tricky due to the difference in properties of Diesel oil and gas. Generally, Marine fuel oil with a sulfur content of 3.5% is used. A lubricating oil with a high total base number (TBN) of 30e40 mg(KOH)/g.
The development of proper lubrication will improve the performance of gas and diesel engines. A natural gas fuel with % sulfur content is 0% uses lubricating oil with a low TBN of w5 mg(KOH)/g.
What are the exhaust gases?
Exhaust gases, sometimes referred to as flue gases or stack gases, are the gases that are produced when fossil fuels like coal or oil are burned in establishments like factories and power plants.
These gases are like the leftovers after the fuel combines with the air and burns.
In these exhaust gases, you’ll find a mix of things. Particulate matter is a term for some of it, which is made up of small dust particles that can be dangerous to breathe. Also, compounds like sulfur and nitrogen oxides can cause acid rain and air pollution.
Another gas you’ll find is carbon monoxide, which can be dangerous if people breathe it in because it can prevent our bodies from getting oxygen.
So, in simple terms, exhaust gases are what’s left over after fuel is burned, and they can contain some not-so-nice stuff that can harm our environment and health.
What are the examples of exhaust emissions?
Vehicle exhaust emissions are a mix of substances released into the air when vehicles run. Most of it is harmless stuff like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen, water vapor, and some extra oxygen that the engine didn’t use up. But there’s more to it.
In smaller amounts, vehicle exhaust has some not-so-friendly things. Carbon monoxide (CO) is one of them, which can be dangerous in enclosed spaces. You’ve also got unburned fuel, which is like wasted gasoline.
Then there are nitrogen oxides (NOx). These are sneaky because they lead to smog and air pollution. Finally, we’ve got particulate matter, tiny particles like dust or mercury. These can be bad news for our health.
So, when you see a car’s tailpipe puffing out what looks like just air, remember, it’s a mix of good and not-so-good stuff. Governments and scientists are working hard to make vehicles emit fewer harmful substances because cleaner air means a healthier planet.
Major Pollutants from Incomplete Combustion
Major Pollutants from Incomplete Combustion – Carbon monoxide (CO) is a harmful pollutant formed when fuels like gasoline, natural gas, oil, coal, and wood don’t burn completely. In the United States, vehicle exhaust is the biggest human-made CO source.
When you breathe in CO, it attaches to your red blood cells more easily than oxygen does.
Incomplete combustion, often caused by a lack of oxygen during the burning process, is the main reason CO is produced. If your heating system isn’t working correctly, It can occur in homes, workplaces, and automobiles.
What is a five-gas analyzer?
A 5-gas analyzer, like the Nova 5-gas Analyzer, is used to measure various gases in engine exhaust. Nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrocarbons (HC), and oxygen (O2) are among the gases that it can detect.
Additionally, it can be set up to identify sulfur dioxide (SO2). A 5-gas analyzer, such as the Nova 5-gas Analyzer, is handy for checking the gases in a car’s exhaust. It tells us exactly what gases are there and how much of each.
People who work with cars and those who make rules about pollution find this tool very useful.
Blog Conclusion
We sincerely hope you enjoyed reading about diesel engine emissions. The main cause of pollution in many cities worldwide is emissions from diesel engines. This blog article aims to provide more information regarding diesel engine emissions. We wrote an article to help readers understand how diesel engine emissions damage the environment.
FAQ on ” What Are the Major Exhaust Emissions from an Engine”
Q: What are exhaust emissions from an engine?
A: Exhaust emissions from an engine are gases and particles released into the air when the engine runs.
Q: What are the major pollutants in engine exhaust?
A: The major pollutants in engine exhaust include carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM).
Q: Why are engine emissions harmful?
A: Engine emissions are harmful because they can pollute the air, contribute to climate change, and cause human health problems.
Q: How can we reduce engine emissions?
A: Engine emissions can be reduced by using cleaner fuels, improving engine technology, and adopting emissions control measures.
