What is Reduction Gear
In marine engineering, a reduction gear plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance of marine propulsion systems. It works by reducing the high rotational speed of the engine to a lower, more efficient speed suitable for driving the propeller. This adjustment ensures that the engine operates efficiently while maximizing the thrust generated by the propeller. Reduction gears are especially important in large vessels, where engine speed must be carefully managed to balance power and fuel efficiency.
Key components of a reduction gear include input and output shafts, gears with precise teeth meshing, bearings, and a lubrication system to ensure smooth operation. These parts work together to ensure that power from the engine is transmitted effectively to the propeller, preventing unnecessary wear and tear on both systems. Understanding how reduction gears function and their importance is essential for maintaining the overall efficiency and longevity of marine engines.
Reduction Gear Explained
A reduction gear is a mechanical system used in marine propulsion to reduce the high rotational speed of an engine to a lower, more efficient speed for the propeller. This reduction allows the engine to run at its optimal speed while transmitting appropriate power to the propeller for effective thrust and maneuverability.
Definition and Working Principle:
A reduction gear system consists of interlocking gears that reduce the engine’s speed in a controlled manner. The system connects the engine’s output shaft to the propeller’s input shaft, allowing the engine to operate at high RPM while the propeller spins at a lower RPM, optimizing both fuel efficiency and performance.
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a reduction gear is to ensure smooth and efficient power transmission from the engine to the propeller. It maximizes the thrust of the propeller without overloading the engine, thus increasing the vessel’s overall performance.
Direct Drive vs. Reduction Gear Drive:
In direct drive, the engine is directly connected to the propeller, meaning both rotate at the same speed. However, this setup often results in higher engine stress and lower propeller efficiency. A reduction gear drive, on the other hand, decouples the speeds, allowing for optimal performance by reducing engine wear and improving fuel efficiency.
Types of Reduction Gears in Marine Engines
Reduction gears come in various configurations to suit the different requirements of marine propulsion systems. Below are the key types of reduction gears commonly used in marine engines:
1. Single-Stage Reduction Gear
A single-stage reduction gear consists of one set of gears that reduces the engine’s speed in a single step. It is straightforward in design and used in applications where moderate speed reduction is needed. This type is often employed in smaller vessels where the propulsion system doesn’t require significant gear reduction.
2. Double-Stage Reduction Gear
A double-stage reduction gear features two sets of gears, providing a higher reduction ratio compared to a single-stage system. The engine’s high-speed rotation is reduced in two steps, making it suitable for larger vessels with powerful engines. This type is common in ships where a significant speed reduction is necessary to ensure optimal propeller performance.
3. Epicyclic or Planetary Gear System
An epicyclic or planetary gear system involves a central sun gear, planet gears, and an outer ring gear. This system offers high torque transmission in a compact design and is ideal for marine propulsion systems requiring a high reduction ratio with minimal space. Its efficiency and durability make it suitable for large ships and specialized marine vessels.
Applications of Each Type in Marine Propulsion Systems
- Single-stage reduction gears are often used in small-to-medium-sized boats and yachts where moderate reduction suffices.
- Double-stage reduction gears are typically found in larger vessels such as cargo ships, where more significant speed reduction is required for propeller efficiency.
- Epicyclic or planetary gear systems are employed in larger marine vessels and submarines due to their ability to handle high loads while maintaining a compact size.
How Does a Reduction Gear Work?
A reduction gear is essential in marine propulsion systems to adjust the high rotational speed of the engine to match the lower speed required by the propeller. This ensures efficient power transfer, optimizing both engine performance and propeller thrust.
Detailed Explanation:
Reduction gears use interlocking gears with different sizes to reduce the engine’s speed. The engine’s output shaft connects to the input gear, which is larger than the gear driving the propeller shaft. By adjusting the ratio between the input and output gears, the system effectively lowers the speed at which the propeller rotates, allowing the engine to run at optimal speed while maintaining the propeller’s efficiency.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process:
- Engine Output: The engine generates power and rotates the output shaft at high RPM (revolutions per minute).
- Input Gear Engagement: The engine’s output shaft engages with the larger input gear of the reduction system.
- Speed Reduction: The input gear, through its connection to smaller gears, reduces the rotational speed as it transfers power through the system.
- Propeller Shaft: The reduced speed is then transmitted to the propeller shaft, which turns at a much slower, optimal RPM for propulsion.
This process allows the engine to run efficiently at high speeds while the propeller operates at a slower, more effective rate.
Mechanical Advantages Provided by the Gear Ratio:
- Efficiency: By optimizing the engine’s RPM, reduction gears minimize fuel consumption and wear on the engine.
- Torque Enhancement: The gear ratio increases the torque applied to the propeller, allowing for greater thrust without overloading the engine.
- Improved Longevity: Running the engine at an ideal speed reduces mechanical stress, extending the lifespan of both the engine and propeller components.
Key Components of a Reduction Gear
A reduction gear system is made up of several essential components that work together to reduce engine speed and ensure smooth power transmission to the propeller. Below are the key components:
1. Input and Output Shafts
- The input shaft connects directly to the engine’s output, receiving high-speed rotation.
- The output shaft is connected to the propeller, transmitting the reduced speed after passing through the gear system. The smooth transfer between these shafts is critical for efficient power delivery.
2. Gear Teeth and Meshing
- The core of any reduction gear system involves gear teeth that engage with each other, transferring power between gears of different sizes. Proper meshing ensures that the power is transmitted efficiently while reducing speed. The size and arrangement of the gear teeth determine the gear ratio and ultimately the speed reduction.
3. Bearings and Lubrication System
- Bearings support the rotating shafts, ensuring minimal friction and smooth rotation. They are crucial for maintaining alignment and reducing wear on moving parts.
- A lubrication system keeps the gears and bearings well-oiled, reducing friction and preventing overheating. Regular lubrication is essential for maintaining the longevity and performance of the reduction gear.
4. Casing and Structural Components
- The casing encloses the entire reduction gear system, protecting the internal components from external elements like water, dust, and debris. It also provides structural support to maintain proper alignment of gears and shafts.
- Structural components such as brackets and mounts ensure that the system is securely installed, preventing vibrations and misalignment during operation.
Reduction Gear: Formulas for Speed, Torque, and Efficiency
Gear Ratio
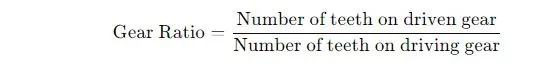
This ratio determines how much the speed is reduced from the engine to the propeller.
Output Speed (RPM)
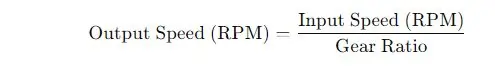
This formula calculates the reduced speed transferred to the output shaft (propeller).
Torque Output
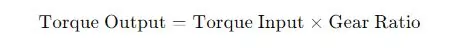
It helps determine how much torque is increased when the gear ratio is applied.
Mechanical Efficiency
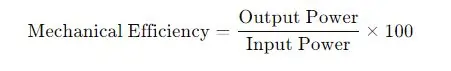
This formula measures the efficiency of power transmission through the reduction gear system.
Power Transmission
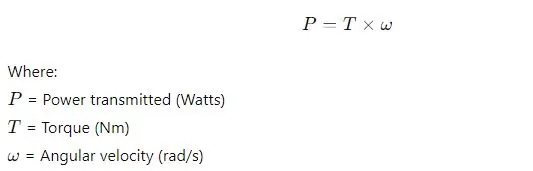
Why are Reduction Gears Essential in Marine Engines?
Reduction gears are a vital component in marine engines, playing a key role in enhancing overall vessel performance and longevity. They contribute significantly to the efficiency of marine propulsion systems by optimizing the relationship between the engine’s output and the propeller’s performance.
Role in Optimizing Propeller Performance
Reduction gears reduce the high-speed rotations of the engine to a lower, more suitable speed for the propeller. This adjustment ensures that the propeller operates within its optimal range, producing the maximum amount of thrust without causing unnecessary strain on the engine. Properly tuned propeller performance is critical for the smooth navigation and maneuvering of marine vessels.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency and Engine Lifespan
By allowing the engine to run at its optimal speed while ensuring the propeller spins at the required lower RPM, reduction gears significantly improve fuel efficiency. This reduced load on the engine also minimizes wear and tear, extending the engine’s lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Noise Reduction and Smoother Operations
Reduction gears contribute to quieter engine operations by reducing mechanical vibrations and noise. This not only enhances the onboard comfort but also leads to smoother operations, which are essential for long voyages and efficient performance in marine environments.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Reduction Gears
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Issues | |
| Wear | Gear teeth and bearings wear due to continuous operation, leading to inefficiency and potential failure. |
| Misalignment | Improper alignment of gears or shafts can cause excessive friction, leading to noise and damage. |
| Overheating | Insufficient lubrication or heavy load can cause overheating, damaging components and reducing lifespan. |
| Routine Inspection and Maintenance | |
| Lubrication Check | Regularly check and maintain the lubrication levels to prevent friction and overheating. |
| Gear Teeth Inspection | Inspect gear teeth for wear, pitting, or cracks to ensure proper meshing and function. |
| Alignment Check | Ensure correct alignment of input and output shafts to avoid vibrations and wear. |
| Temperature Monitoring | Monitor operating temperatures to detect overheating early and take corrective action. |
| Troubleshooting Methods | |
| For Wear | Replace worn gears or bearings promptly; ensure proper lubrication to avoid recurrence. |
| For Misalignment | Re-align gears and shafts using precision tools; inspect for underlying causes like loose mounts. |
| For Overheating | Check lubrication system for blockages; reduce engine load and ensure adequate cooling. |
Reduction Gear Safety Precautions
Operating reduction gears in marine engines requires strict adherence to safety protocols to prevent damage, ensure smooth operation, and maintain the safety of the crew. Below are key safety precautions that must be followed:
Safety Protocols During Operation
Operators should regularly monitor reduction gear performance, ensuring that it runs within safe operational limits. This includes checking for abnormal noises, vibrations, or fluctuations in temperature, which could signal potential issues. Routine inspections and adherence to the manufacturer’s operational guidelines are critical in preventing malfunctions.
Emergency Stop Mechanisms
Reduction gear systems are typically equipped with emergency stop mechanisms that can immediately halt the system if a critical issue arises. These mechanisms are essential in preventing severe damage to the gears and engine during emergencies like overheating, excessive vibrations, or lubrication failure. Operators must be trained in the proper use of these emergency stop systems and conduct regular drills to ensure quick and efficient responses.
Importance of Monitoring Oil Levels and Gear Wear
Proper lubrication is key to the longevity and performance of reduction gears. Regularly monitoring oil levels is crucial, as insufficient lubrication can lead to overheating, increased friction, and eventual gear failure. Additionally, routine checks for gear wear are necessary to detect early signs of damage, such as pitting or misalignment, which could compromise the entire propulsion system. Timely oil changes and component inspections can significantly extend the life of the reduction gear system.
Latest Trends in Marine Reduction Gears (2024)
The marine industry is experiencing significant advancements in reduction gear technology, driven by the demand for higher efficiency, sustainability, and integration with modern propulsion systems. Below are some of the latest trends in marine reduction gears for 2024:
Technological Advancements in Reduction Gear Design
Recent advancements in gear materials and manufacturing techniques have led to stronger, lighter, and more durable reduction gears. Improved precision in gear cutting and advanced alloys are increasing the longevity of gear systems while minimizing energy losses due to friction. Additionally, smart monitoring systems are now integrated into modern reduction gears, allowing real-time tracking of temperature, lubrication levels, and gear wear, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Integration with Hybrid Propulsion Systems
With the growing shift towards hybrid propulsion systems, reduction gears are evolving to handle the complex needs of these systems. Modern reduction gears are being designed to work seamlessly with electric motors and diesel engines, allowing ships to alternate between power sources depending on operational requirements. This flexibility enhances fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, and extends the life of marine engines.
Future of Reduction Gears in Eco-Friendly Marine Technology
As the industry moves towards eco-friendly solutions, reduction gears are becoming a key component in the push for greener technologies. Reduction gears are being optimized to work with renewable energy sources, such as wind-assisted propulsion and battery-powered systems. Furthermore, the use of low-friction coatings and advanced lubrication solutions are helping to reduce energy consumption and minimize the environmental impact of marine propulsion systems. These trends indicate that reduction gears will continue to play a critical role in the transition towards more sustainable maritime operations.
FAQ on “What is a Reduction Gear?”
Q: What does a reduction gear do?
A: A reduction gear reduces engine speed to match the optimal propeller speed.
Q: Why is a reduction gear used in ships?
A: It ensures efficient power transfer from the engine to the propeller, improving performance and fuel efficiency.
Q: Does gear reduction increase speed?
A: No, gear reduction decreases speed while increasing torque.
Q: What is the max gear reduction?
A: A reduction gear reduces engine speed to match the option
Conclusion
In marine engineering, reduction gears play a critical role in ensuring efficient power transmission from the engine to the propeller, optimizing performance, fuel efficiency, and overall vessel longevity. By reducing engine speed and increasing torque, these systems enhance the propulsion system’s functionality, while advancements in technology continue to improve their design and integration with hybrid systems. Understanding the importance of proper maintenance and staying updated on new trends ensures that reduction gears operate efficiently, contributing to a more sustainable and reliable marine industry.
