Table of Contents
Engine Storage Procedure
Diesel Engines are the heart of a Ship. They are used for ship propulsion and as a Diesel generator for producing the power to ship. If the Engine is to be kept in standby mode or a newly procured engine is to be kept longer. Preservation and proper storage are necessary to protect the engine and its external and internal parts from corrosion and other damage.
This blog post will discuss and provide the best ten storage tips. These tips are based on the author’s long experience of this post.
Engines are supplied in the best-preserved condition by the OEM. Proper storage will help maintain the engine e in good condition to be used in the future.
Let us proceed with the discussion on the Engine Storage Procedure.
Short-Term Storage of an Engine (Not in Use)
- Empty the diesel oil tank.
- Turn the diesel engine piston to the top dead center of compression.
- Store the generator indoors and cover it with a cloth.
- Avoid placing it in a damp environment.
- Please keep it away from flammable, explosive, and corrosive materials.
- Regularly turn the crankshaft.
Long-Term Storage of Automatic Diesel Generator (Not in Use)
- First, follow the steps for short-term storage.
- Clean the entire generator set surface and unit with compressed air.
- Fill the generator with desiccant and cover the generator end with thick paper, sealing air vents well and fastening them with a rope.
- Drain engine oil from the oil filter, air filter, etc.
- Inject 100-200g of oil from the exhaust manifold into each cylinder. Rotate the diesel engine’s crankshaft multiple times to evenly distribute the oil in the cylinders and position the piston at the top dead center of compression.
- After removing the valve cover, the valve structure should be lubricated with dehydrated oil.
- Seal the exhaust port, air filter, fuel tank vent, smoke vent of the low-temperature starting device, etc., with oiled paper.
- Use detergent to clean the diesel engine, alternator, coupling port, frame, components, tools, accessories, etc., and apply grease to necessary parts.
- Rotate the crankshaft 1-2 times a month, ensuring the piston is at the top dead center of compression after each rotation.
Long-term storage can have a detrimental effect on diesel engines and alternators, so proper storage is crucial. Additionally, when operating in freezing conditions, add antifreeze as recommended by the diesel engine manufacturer to prevent freezing and corrosion of the cooling system. During storage, protect the unit from overheating, supercooling, rain, and direct sunlight.
After storage, thoroughly inspect the diesel generator set for damage before installation and use. Check for oxidation in the electrical components, loose connections, dryness in the main generator coil, and cleanliness of the engine body. Take appropriate measures if necessary.
Properly storing a temporarily unused diesel generator set is also essential.
Preservation of a Diesel Engine



Diesel Engine Preservation – Preserving a diesel generator is a crucial storage aspect. It is performed to safeguard the diesel generator for various reasons:
Protection against Corrosion Before Next Use: Preservation helps shield the diesel generator from corrosion and damage during periods of inactivity, ensuring it remains in good working condition for its next use.
Before Initial Start-Up: Preservation is necessary before the initial start-up of the diesel generator. By putting the engine through this preparation procedure, potential problems brought on by prolonged inactivity are avoided.
Before Shipment and Transportation: When a diesel generator is being transported or shipped, preservation measures are applied to protect it from the rigors of transit. This helps prevent damage and ensures the generator arrives in optimal condition at its destination.
For Long-Term Standstill: Diesel generators that will be idle for an extended duration require preservation to minimize the adverse effects of storage over time. Preventing degradation and expensive repairs is possible with the right preservation techniques.
Preservation Areas



Cooling Water System
Proper Procedure for Preserving Cooling Systems in Diesel Engines:
- Drain the Cooling Water: Begin by draining the cooling water from the high-temperature, Low-Temperature, and cooling water systems.
- Address Heat Exchangers: Pay special attention to the Charge Air Cooler and Lube Oil Cooler. Ensure they are also drained.
- Remove Residual Water: Blow compressed air through the cooling water piping system, directing it from the inlet to the outlet. This step is crucial to eliminate any remaining water.
- Apply Corrosion Inhibitor: After removing impurities and rust, use an air-gun or similar tool to spray a corrosion inhibitor into the system. This inhibits corrosion and safeguards the components.
- Seal the Systems: To prevent the loss of vapor and maintain the integrity of the systems, seal them with blind covers.
- Discharge Air and Introduce Nitrogen: Remove any remaining air from the system and fill it with nitrogen gas to achieve a pressure of 1 bar. This step ensures that the cooling systems remain protected during storage.
By following these steps diligently, you can effectively preserve the cooling systems of your diesel engine, minimizing the risk of corrosion and ensuring their proper functioning when needed.



Fuel Oil System
Draining the Fuel Oil
In the context of a fuel oil system, draining involves the removal of fuel oil from the various components of the system to ensure its proper maintenance and readiness for future use.


Piping System: The piping system in a fuel oil system serves as the network that transports fuel oil from the storage tanks to the engine or burner. Draining the fuel oil from the piping system involves opening valves or drains at strategic points along the pipes to allow the fuel oil to flow out. This step is essential for several reasons:
Preventing Contamination: Draining the piping system helps prevent fuel oil contamination. Over time, sediment and impurities can settle in the pipes, and draining removes these potentially harmful particles.
Maintenance: It allows maintenance tasks such as inspection, cleaning, and repairs to be carried out effectively. With the system empty of fuel oil, technicians can work on the piping and associated components safely.
System Integrity: Draining ensures that the piping system remains in good condition. This prevents corrosion and damage caused by the presence of residual fuel oil.
Fuel Oil Filter: In addition to the piping system, the fuel oil filter is another critical component in the fuel oil system. Draining the fuel oil filter involves removing any remaining fuel oil from the filter housing. This is important because:
Cleanliness: It maintains the cleanliness and efficiency of the filter. The filter’s job is to remove impurities from the fuel oil, and draining ensures it is ready to perform this function when the system is restarted.
Preventing Clogs: Draining prevents the filter from becoming clogged with old fuel oil, which can impede the flow of clean fuel to the engine or burner.
Lubricating Oil System Maintenance: Preserving Your Diesel Generator



To ensure your diesel generator’s longevity and optimal performance, it is imperative to maintain the lubricating oil system properly. This entails several essential steps:
1. Drain Lubricating Oil: Begin by draining the lubricating oil from the entire system, including the cooler and filter. This process removes used oil and prepares the system for preservation during storage.
2. Clean the Crankcase and Oil Sump Tank: Thoroughly clean the inside of the crankcase and oil sump tank. Removing any residual oil and contaminants is crucial to prevent corrosion and maintain a clean environment for the system.
3. Apply Rust Preventative Agent: To safeguard critical components from corrosion during storage, apply a high-quality rust preventative agent. Coat the following components meticulously:
- Crankcase interior
- Connecting Rod
- Crankshaft
- Lower Piston
- Cylinder Liner
- Camshaft
- Cam Roller and Chamber Interior
- Gear Train and Chamber Interior
- Cylinder Head Top Cover Interior
- Rocker Gear
4. Ensure Proper Rust Protection Oil: Using rust protection oil with the appropriate lubricating properties is vital. This oil should not cause any defects when mixed with engine oil. Ensure the selected product is high quality and compatible with your diesel generator.
By following these maintenance steps diligently, you can effectively preserve your diesel generator’s lubricating oil system, preventing corrosion and ensuring the engine components remain in excellent condition. Proper preservation is key to the longevity and reliable performance of your generator.
Combustion Chamber
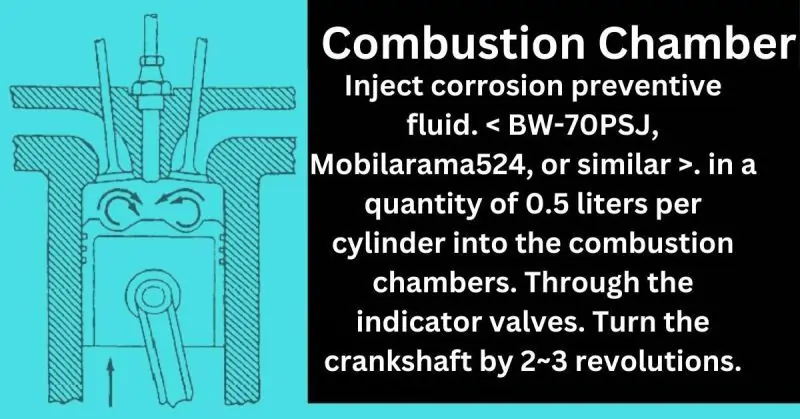


Inject a corrosion preventive fluid (e.g., BW-70PSJ, Mobilarama524, or similar) into the combustion chambers at a rate of 0.5 liters per cylinder through the indicator valves.
Rotate the crankshaft by 2 to 3 revolutions. This method prevents rust and corrosion inside the combustion chambers and is a more efficient alternative to the traditional preservation method.
Intake Air Chamber (Diesel Generator Storage):
Remove any impurities, such as rust, from the intake air chamber.
Spray a volatile corrosion inhibitor (e.g., VCiR-3P or similar, VpCI-377) into the system using an air gun or similar tool.
Seal the intake air chamber with blind covers to prevent vapor loss, ensuring protection against corrosion.
External Machined Surfaces:
Clean all unpainted areas of external machined surfaces thoroughly.
Apply a protective agent to these cleaned areas to prevent corrosion.
Other Maintenance Activities (Diesel Generator Storage):
Lubricate all hinging parts with high-quality grease (e.g., Mobil 1 Synthetic Grease or similar).
Apply a protective agent (e.g., TECTYL-506, Mobilarma 247, or similar) to other parts of the control linkage between the fuel pumps and the governor after cleaning them.
Seal the turbocharger gas outlet with a plate and open the drain valve.
Cover the turbocharger air filter with a protective sheet.
Seal all openings in the piping system with plastic caps or blind covers.
Inspect the sealed condition of the packing and gland seals in the electric control and terminal boxes.
Use a volatile corrosion inhibitor at 50 to 100g per 1m³, adjusting as needed based on preservation period, packing method, temperature, humidity, and seal quality.
By following these preservation procedures, you can ensure that your engine remains in optimal condition during periods of inactivity, minimizing the risk of corrosion and damage and ensuring its readiness for future use.
Proper Storage of a Diesel Generator
Storing a diesel generator correctly is vital to ensure its reliability and longevity. Follow these guidelines for effective storage:
Short-Term Storage (Under Three Months):
Remove the Waterproof Tarpaulin: Start by removing the waterproof tarpaulin covering the generator. Store the generator in a well-ventilated area under a roof to protect it from the elements.
Drain the Cooling System: Prevent potential freezing damage by draining the cooling water from both the High-Temperature (HT) and Low-Temperature (LT) systems, including the charge air cooler and lube oil cooler, by opening their drain valves.
Keep Blind Covers Sealed: Do not open the blind covers of the cooling water lines until the engine is ready to run, except when adding a Volatile Corrosion Inhibitor (VCI). Pay attention to caution stickers on blind covers containing VCIs.
Use Volatile Corrosion Inhibitor: Fill the sump tank with a Volatile Corrosion Inhibitor. Also, apply VCIs to blind covers of HT & LT water inlet/outlet lines and the last cylinder’s cylinder head and water guide jacket.
Long-Term Storage (Over Three Months):
VCI Replenishment: Refill the sump tank with the Volatile Corrosion Inhibitor every three months. Apply VCIs to blind covers as before.
Inspect and Repair: Regularly check the painting condition of the generator and make necessary repairs. Examine the following engine parts every three months for corrosion:
Crank chamber
Cylinder liner
Connecting rod
Crankshaft
Cams
Gears
Rocker’s arm
Engine moving components
Corrosion Prevention: If corrosion persists, apply a protective oil to affected areas after removing rust.
Combustion Chamber Preservation: Inject a corrosion-preventing fluid (0.5 liters per cylinder) into the combustion chambers through the indicator valves. Turn the crankshaft by 2-3 revolutions.
Before Initial Starting:
Clean the Exterior: Use turpentine or petroleum to clean the outside of the engine. Do not remove the preservation oil coating inside the machine or the liquefied VCIs in the sump tank and cooling water system.
Air Chamber: Open the cover for the air chamber and clean up the VCIs inside it.
Tool and Spare Part Storage
Refer to quality specifications for tool preservation.
Store tools and spare parts indoors or in waterproof boxes, covering them with tarpaulin if kept in open spaces.
Clean tools and spare parts with petroleum or a cleaning solvent.
Store spare parts in lubrication oil or grease for short-term storage.
Storage Conditions:
Keep storage boxes under a roof, protecting them from rain, sea fog, and dust.
Open and inspect boxes upon arrival, repairing any preservation damage if necessary.
Depending on storage conditions, repeat inspections every 2-4 months.
FAQ on ” Engine Storage Procedure
Q: How often should you inspect a stored engine?
A: Inspect a stored engine every 2-4 months to ensure preservation integrity.
Q: Why is engine storage important?
A: Engine storage is vital to prevent corrosion and maintain engine performance during inactivity.
Q: What should you do before storing an engine?
A: Before storage, drain fluids, apply rust inhibitors, and protect sensitive components.
Q: What’s the role of Volatile Corrosion Inhibitors (VCIs)?
A: VCIs protect engine components from corrosion during storage by creating a protective barrier.
Conclusion
Properly storing a diesel generator is essential for its reliability. These guidelines will help you maintain your generator effectively, ensuring it remains in excellent condition for future use.
