Table of Contents
Marine Centrifuge Separator
Marine Centrifuges are devices used by ships to remove any contaminants from liquids such as fuel and oil. Removal of Contaminants is done with a high-speed centrifugal force that separates the solid particles from the liquid. It is essential to ship operation and maintenance, as it keeps the fuel clean for use in the ship’s engines.
Marine centrifuges can also be used to separate solid particles from liquids such as water or sewage, ensuring marine vessels’ clean and safe operation.
A centrifuge is a high-speed machine used to separate or remove contaminations from fuel and Lube oils. It is mandatory to undertake this Treatment to separate and remove water and solid impurities before supplying to the marine engine. A centrifuge works on the principles of centrifugal force, accelerating molecules to physically separate the particles of different masses in a gradient along the periphery of a rotating container.
A centrifuge separates the particles from a solution according to their size, shape, density, viscosity of the molecule, and rotor speed.
In this post on centrifuge machines, we will discuss the complete process and uses of centrifuge machines and the devices used to carry out Lubricating and fuel Oils Treatment.
Centrifuges are the most important types of machinery on board ships. 4Th Engineer is responsible for maintaining the centrifuges on board a Merchant ship
Essential Terms in Separators
Separator Terminology Explained
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Clarifier Disc | (Optional) Replaces gravity disc in separator bowl for clarifier mode. Seals off the heavy phase outlet, eliminating the liquid seal. |
| Sludge Discharge | Process of expelling sludge from the separator bowls. |
| Interface | The boundary layer between the lighter phase (oil) and heavier phase (water) in the separator bowl. |
| Phase | Refers to the distinct states of matter present in the separator. There are two phases: * Heavy Phase: Heavier liquid, typically water. * Lighter Phase: Lighter liquid, typically oil. |
| Throughput | The rate at which liquid is fed into the separator, typically expressed in M³/hour or liters/hour. |
| Sediment (Sludge) | Solid particles separated from a liquid. |
| Gravity Disc | Positions the interface between the disc stack and the outer edge of the top disc. Used only in separator purifier mode. |
| Water Seal | A seal created by water in the solid space of the separator bowl. Prevents the lighter phase from leaving the bowl through the heavier phase outlet during purifier mode. |
Tips for safe operation of Centrifuge
Safe Separator Operation Guidelines
| Safety Instruction | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-Start Checks | Ensure the bowl is completely assembled and all fastenings are securely tightened. |
| Emergency Stop | Always stop the separator using the emergency stop button before discharging a vibrating separator. |
| Disassembly | Only disassemble a separator after it has come to a complete standstill. |
| Discharge Intervals | Set the discharge intervals following the instructions in the separator’s instruction book. |
| Alarm Response | Take alarms seriously. Investigate the cause of the alarm and eliminate it before resuming separator operation. |
| Suitable Separator | Use a separator specifically designed for the type of liquid being processed. |
| Power Supply | Ensure the power supply frequency matches the specifications stated on the machine plate. |
| Cleaning | Clean the operating system at specified intervals to prevent sludge discharge malfunctions. |
| Qualified Personnel | Only fully trained personnel with complete knowledge of installation, operation, maintenance, and emergency procedures should operate the separator. |
| Spare Parts | Use only genuine spare parts and the special tools supplied by the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM). |
Engine Lubricating Oil Cleaning Necessity
Engine oil plays a vital role in keeping your engine running smoothly and efficiently. However, over time, it inevitably becomes contaminated. This contamination can lead to a breakdown of the oil’s properties, compromising its ability to lubricate and protect your engine.
Sources of Engine Oil Contamination:
- Internal Sources: The majority of contaminants are generated within the engine itself. These contaminants include:
- Combustion Products: Byproducts of the combustion process, like soot and unburned fuel, can enter the oil.
- Blow-by: A small amount of combustion gases can leak past the piston rings into the crankcase, contaminating the oil.
- Wear Debris: Friction between engine parts can generate metal particles that wear off components.
- External Sources: While less common, some contaminants can enter the oil from external sources:
- Oil Refill: Contaminants can be introduced if proper care isn’t taken during oil changes.
- Vent Pipes: Dust and dirt can be drawn into the engine through the crankcase ventilation system.
The Importance of Oil Treatment:
As oil gets contaminated, it loses its effectiveness. To counteract this degradation and restore the oil’s lubricating properties, treatment is necessary.
- Engine-Mounted Centrifugal Filters: These filters provide a first line of defense, removing larger particles and impurities from the oil as it circulates through the engine.
- Centrifugal Separators: For engines running on Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO), which can generate a higher level of contamination, additional treatment is often required. Centrifugal separators are more powerful filtration systems that can remove finer particles and water from the oil.
By maintaining a clean oil supply through filtration and treatment, you can ensure your engine’s optimal performance, reliability, and lifespan.
Centrifugal Purifier Working Principle
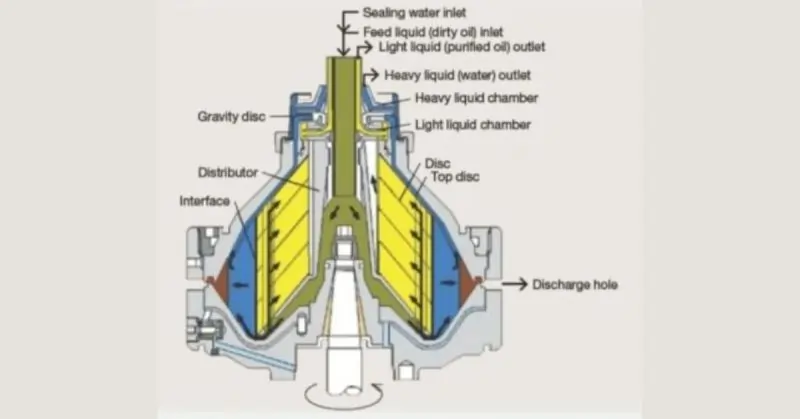


Oil Purifier Operation:
- Dirty Oil Feed: The dirty oil is first supplied to the center of the separator bowl from the settling tank.
- Centrifugal Separation: As the oil spins within the bowl due to centrifugal force, separation between the oil and water occurs based on their different densities. Water, being heavier than oil, gets pushed outwards towards the wall of the bowl. The oil, being lighter, concentrates towards the center.
- Water Seal Establishment: Water is introduced into the separator before the oil. This is crucial because if oil were directly introduced, it could leak out through the water outlet. The water flow is initially high and then gradually reduced as a stable “seal” is formed.
- Seal Water Management: Introducing seal water too quickly can cause some water to mix with the oil. This creates an unwanted “interference line” between the water and oil, also known as the E-line.
- Gravity Disc & Interface Control: The position of this E-line within the purifier is critical for proper operation. A gravity disc, located within the disc stack, helps maintain this interface at the outlet.
- Gravity Disc Selection: Several gravity discs with different diameters are provided with the purifier. These discs are chosen based on the specific density of the oil being purified. If the type of oil being used changes, the gravity disc needs to be replaced with the appropriate one.
- Gravity Disc Size: As a general rule, a larger diameter gravity disc should be used, as long as it doesn’t disrupt the water seal.
- Top Disc Stack: The top disc stack is capped with a “blind disc,” which has no openings.
Marine Centrifuge Separator Types
Purifier



Oil Purifier Bowl Assembly
The oil purifier bowl assembly is the heart of the system. It consists of:
- Outer Framework: This encases the bowl and provides connection points for the oil’s journey through the separator.
- Inlet and Outlet Connections: These connections allow for:
- Dirty Oil Entry: Contaminated oil enters the center of the bowl.
- Treated Oil Discharge: Cleaned oil exits through the top of the bowl.
Centrifugal Separation and Interface Control:
Inside the bowl, centrifugal force separates the oil and water based on their differing densities. However, precise positioning of the separation zone (interface) between the oil and water is crucial for optimal operation.
- Gravity Disc: This component, located within a stack of discs, plays a vital role. It helps maintain the correct interface location at the outlet.
- Disc Selection: Different sized gravity discs are provided to accommodate oils with varying densities. When the type of oil being processed changes, the appropriate gravity disc needs to be selected for optimal separation efficiency.
Clarifier



The Clarifier: Keeping Liquids Clean and Clear
A clarifier is a type of centrifuge machine that acts as a champion of clean liquids. Imagine a high-speed washing machine for industrial applications! It utilizes centrifugal force to separate solids and liquids, such as particles, sediments, and oil, from a mixture.
Here’s a breakdown of how a clarifier works:
The Separation Process:
- Feeding the Mixture: The dirty liquid containing solids is fed into the clarifier.
- Centrifugal Force Takes Over: Inside the clarifier, the mixture spins at high speeds, generating a powerful centrifugal force. This force pushes denser solids outwards, towards the periphery (edge) of the bowl.
- Clean Liquid Emerges: The clarified, cleaned liquid, free from most solids, exits the center of the bowl.
- Impurity Collection: The separated solids accumulate at the periphery of the bowl, where they can be easily removed for disposal.
Key Advantages of Clarifiers:
- High Efficiency: Clarifiers operate at maximum separating efficiency, ensuring a thorough cleaning process.
- No Interface Management: Unlike purifiers that separate two liquids, clarifiers focus solely on removing solids from liquids. This eliminates the need for a gravity disc (a component used in purifiers to maintain the separation zone between liquids).
- Ideal for Low-Water Oil: Clarifiers are particularly effective for cleaning oil with minimal water content.
In essence, a clarifier acts as a dedicated workhorse for removing solid contaminants from liquids, ensuring a clean and purified final product.
Fault Finding- centrifuge machine
Separator Vibration
A separator will vibrate while passing through its critical speeds during Starting and stopping. Vibration also exists up to some extent during the operation of the separator. Operators should get acquainted with these expected conditions. Excessive vibration with noise is a positive indication of severe abnormality in the separator. Under such circumstances, the separator should be stopped immediately and the cause. Carry out the condition monitoring at specified intervals and record the level of vibrations. The level of vibration shouldn’t exceed 9 mm/s.
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Bowl Unbalance Improper CleaningWrong AssemblyWrong Disc stack CompressionBowl assembled with the parts from other separator | Check the assembly and cleaning after dismantling the separator |
| Abnormal deposition of sludge in the sludge space | Clean the separator Bowls |
| Wrong adjustment of Paring Disc height | Stop the separator, measure and re-adjust the correct height. |
| Bent Bowl Spindle | Change the Bowl Spindle with a new one |
| Worn out frame feet | Replace the frame feet |
| Worn or damaged bearings | Renew the bearings |
| Top bearing spring of spindle broken | Renew the springs |
Smell
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| It is Normal after starting; friction pad slippage causes the smell. | No action is to be taken. If the smell continues when the separator has gained full speed, stop the separator and change the worn-out friction pads. |
| Too low oil level in the sump | Check and top up the oil level to the correct level |
Noise
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Wrong Height of Paring Disc | Stop the separator, and adjust the height |
| Worn or damaged bearings | Replace all the bearings |
Too low Speed of the centrifuge machine
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Friction pads are slippery with oil or warned out | Clean or replace the friction pads |
| Leaky or non- operative bowls | Dismantle and check the bowls |
| Motor failed | Repair / replace the motor |
| Damaged Bearings | Replace all the bearings |
| Incorrect fitment of transmission parts ( 60 Hz Pulley for 50 Hz Pulley) Power Supply | Change the belt transmission to suit the supply frequency. |
The high speed of the centrifuge machine
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Incorrect fitment of transmission parts (50 Hz Pulley for 60 Hz Pulley) Power Supply | Change the belt transmission to suit the supply frequency. |
Too high starting power
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Incorrect fitment of transmission parts ( 60 Hz Pulley for 50 Hz Pulley) Power supply | Change the belt transmission to suit the supply frequency. |
| Incorrect direction or rotation | Change the phase connection of motor |
Too low starting power
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Incorrect fitment of transmission parts (50 Hz Pulley for 60 Hz Pulley) Power Supply | Change the belt transmission to suit the supply frequency. |
| Friction pads are slippery with oil or warned out | Clean or replace the friction pads |
| Motor failed | Repair / replace the motor |
Too long starting time taken by centrifuge machine
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Friction pads are slippery with oil or warned out | Clean or replace the friction pads |
| Wrong Height of Paring Disc | Stop the separator, and adjust the height |
| Worn or damaged bearings | Replace all the bearings |
| Motor failed | Repair / replace the motor |
Separating Operations
Accidentally opened of bowl of the centrifuge machine during operation
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Chocked strainer in the water supply | Clean the strainer |
| Insufficient water in the operating water system | Ensure the opening of the water supply valve |
| Incorrect fitment of Hoses between supply valve and the separator | Correct the fitment |
| Clogged operating side nozzle | Clean the nozzle |
| Defective rectangular ring in discharge slide | Replace the rectangular ring |
| Defective valve plugs | Replace all the plugs |
| Leaky supply valve for opening water | Correct the leakage |
Failure of Bowls to open for sludge discharge
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Chocked strainer in the water supply | Clean the strainer |
| Insufficient water in the operating water system | Ensure the opening of the water supply valve |
| Incorrect fitment of Hoses between supply valve and the separator | Correct the fitment |
| Clogged operating side nozzle | Clean the nozzle |
| Defective rectangular ring in discharge slide | Replace the rectangular ring |
Poor Separation results of centrifuge machine
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Wrong Operating temperature | Adjust the temperature |
| Clogged disc stack | Clean the disc stack |
| Too high throughput | Adjust the throughput |
| Filled sludge space | Clean and re adjust the time of sludge discharge |
| Too low bowl speed | Inspect the motor andpower transmission including the clutch |
| Wrong direction of bowl rotation | Check the electrical connections to themotor |
Bowls Failure to close in a centrifuge machine
| Cause | Corrective Action |
| Clogged nozzle in operating slide | Clean the nozzle |
| Reversed Hoses | Adjust |
| Defective rectangular ring in discharge slide | Replace the rectangular ring |
| Defective or missing valve plugs in the operating slide | Replace valve plugs |
| No water | Turn on the water supply. |
Maintenance procedure
Ensuring your oil purifier operates safely and efficiently requires regular maintenance. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Pre-Maintenance Safety:
- Complete Stoppage: Before opening the purifier, ensure it is completely stopped and not rotating. This is critical to avoid any injuries.
Disassembly:
- Careful Handling: Use special care when transferring the main bowl components to prevent damage to the sealing surfaces. These seals form a vital barrier within the purifier.
Replacement and Inspection:
- Fresh Seals: Replace all seals with new ones to ensure optimal performance and prevent leaks.
- Clutch Drive Check: Inspect the clutch drive and replace the lining if necessary to maintain proper engagement.
- Gearbox Inspection: Carefully examine the gearbox for any signs of unusual wear. Ensure the bearings are within the manufacturer’s recommended operating time limits. Change the gearbox oil as well.
Reassembly:
- Lubrication: Thoroughly grease all sliding surfaces before reassembling the purifier. This reduces friction and ensures smooth operation.
- Bowl Height Adjustment: Following the manufacturer’s instructions, measure and adjust the bowl height if needed. Document this adjustment for future reference.
- Manual Rotation Check: Before securing the top cover, rotate the bowl by hand to check for any obstructions that might hinder its operation.
Post-Maintenance Checks:
- Performance Evaluation: Once the purifier reaches its normal operating speed, evaluate its separation efficiency based on the chosen gravity disc or plug. This ensures the purifier is functioning properly.
- Proper Torque: Always tighten all components with the correct torque as specified by the manufacturer’s manual. This ensures proper assembly and prevents leaks.
Record Keeping:
- Maintenance Log: Maintain a detailed record of all maintenance procedures performed, including the date, replaced parts, and any adjustments made.
General Safety Reminder:
- Centrifuge Power: Remember, a centrifuge operates at very high speeds and is meticulously balanced. Always exercise caution during disassembly, transportation, and maintenance procedures.
By following these steps and adhering to safety precautions, you can ensure your oil purifier receives the proper care it needs for optimal performance and longevity.
What is separator type P 605?
The Alfa Laval P 605 is a high-performance champion in the world of oil purification. This workhorse utilizes centrifugal separation technology to effectively remove impurities from mineral oils. Here’s a closer look at its capabilities:
- Applications: The P 605 is a versatile separator, finding its place in both marine and land-based applications. This makes it suitable for a wide range of industries that rely on clean oil for their operations.
- Targeted Impurities: The P 605 specifically targets two main contaminants in oil:
- Water: This can be present in oil due to various factors, such as condensation or leaks. The P 605 efficiently removes water from the oil, ensuring its purity.
- Solid Matter (Sludge): Over time, oil can accumulate sludge, a collection of solid particles and contaminants. The P 605 effectively removes this sludge, keeping the oil clean and free of harmful particulates.
- Dual Discharge System: The P 605 boasts a two-stage discharge process:
- Continuous Clean Oil Discharge: The purified oil is continuously discharged from the separator, ensuring a steady stream of clean oil for your operations.
- Intermittent Sludge Discharge: The separated sludge accumulates within the separator and is discharged periodically. This allows for efficient removal of contaminants without interrupting the oil purification process.
In essence, the Alfa Laval P 605 stands as a reliable and efficient solution for keeping your mineral oil clean and free of water and sludge, ensuring the smooth operation of your machinery.
What is a 2-phase separator vs. a 3-phase separator?
4-Phase Separator: A Multitasking Champion
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Separates complex mixtures containing four components. |
| Components Separated | * Gas (air or natural gas) * Water * Oil * Solids (sand, debris) |
| Separation Techniques | Utilizes a combination of: * Centrifugal force: High-speed spinning separates components based on density. * Gravity: Heavier components like water settle out. * Specialized internal components: Enhance separation efficiency for each component. |
| Monitoring | Advanced systems track flow rates of: * Water * Gas * Oil This allows for real-time adjustments and ensures optimal separation during processes like: * Well testing * Flowbacks * Pigging activities (oil & gas) |
| Benefits | * Efficiently separates all four components in complex mixtures. * Enables continuous operation during various industrial processes. |
What is a 4-phase separator?
4-Phase Separator: A Powerful Separation Solution
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Application | Separates complex mixtures with four components |
| Components Separated | * Gas (air or natural gas) * Water * Oil * Solids (sand, debris) |
| Separation Techniques | * Centrifugal Force * Gravity * Specialized Internal Components |
| Monitoring | Real-time monitoring of water, gas, and oil flow rates |
| Benefits | * Efficient separation of all four components * Valuable tool in various industrial applications |
| Examples of Applications | Well testing, flowbacks, and pigging activities (oil & gas industry) |
Marine separator brands
Marine Separator Brands: A Look at Key Players
Marine separators play a vital role in keeping ships running smoothly by removing impurities from various fluids. Here’s a table highlighting some prominent brands in the marine separator market:
| Brand | Description |
|---|---|
| Alfa Laval | A globally recognized leader in separation technology. Renowned for their high-quality separators used for oil-water separation and other applications on ships. |
| Westfalia | Another major player, offering a range of marine separators known for their reliability and efficiency. |
| Mitsubishi | A respected brand known for their technologically advanced separators, catering to diverse needs in the maritime industry. |
| GEA | A prominent supplier of industrial machinery, including marine separators known for their robust design and performance. |
| Wärtsilä | A global leader in marine solutions, offering separators alongside their comprehensive engine and power generation offerings. |
| Centrifugal | While “Centrifugal” might not be a specific brand, it refers to the separation technology itself, often used in separator names (e.g., Alfa Laval Centrifuge Separators). |
| Kangwei | A Chinese manufacturer gaining recognition for their cost-effective and efficient marine separator solutions. |
| Andritz | A diversified industrial equipment supplier, offering separators alongside their focus on hydropower, pulp & paper, and other sectors. |
| Yanmar | A Japanese brand known for their marine engines, with some models also featuring integrated separators. |
| RWO (Reverse Osmosis Watermakers) | While RWO specializes in watermakers, some may also offer separator systems for ships. |
Additional Notes:
- The choice of brand often depends on factors like specific application, budget, and desired features.
- Alfa Laval is a popular choice due to their established reputation and proven performance in the maritime industry.
Conclusion
We hope this article on Centrifuge Machines will be useful to you all during your sea time for the operation and maintenance of Centrifuge machines. This article has been written based on my 45 years of experience having worked on various vessels and in Powerplant industries.
We have also looked into the many kinds of centrifuges that are used to treat oil.
Understanding how to centrifuge machines function can assist you in maintaining engines better, ensuring they stay efficient and functional for a long time.. So, whether you’re really into this stuff or you do it for work, recognizing how important centrifuge machines are can help keep engines humming along smoothly.
FAQ on ” Marine Centrifuge Separator”
Q A marine centrifuge separator is what, exactly?
A1: In marine applications, it is a device that separates liquids from solids.
Q A marine centrifuge separator functions in what manner?
A- A: Depending on the densities of the various components, it separates them via spinning.
Q: How are marine centrifuge separators used?
A: They are employed in ships and boats to clean and purify fluids like oils.
Q: What are the benefits of marine centrifuge separators?
A: By keeping fluids clean, they maintain engine performance and lessen wear.
