Table of Contents
Types Of Electric Motor
An electric motor is like a magical machine that turns electricity into movement. It does this by using magnets and wires. This movement can make things spin or move in a straight line.
Electric motors can run on different kinds of electricity, like the kind from batteries or the kind from your wall outlet. They come in all shapes and sizes and can be used in many things, like machines, tools, and even vehicles.
Some of the biggest ones power huge things like ships and Industries. Smaller ones can be found in everyday items like fans, power tools, and watches.
One cool thing about electric motors is that they can also work the other way around. They can turn movement into electricity, like when they help a car slow down and save energy.
So, electric motors are like the silent helpers that make our machines go, whether it’s a big factory or a small watch, and they can do it in different ways and sizes to fit the job.
This blog post will discover the many kinds of motors and how they operate.
We’ve got you covered whether you’re curious or need to pick the right motor for a specific job.
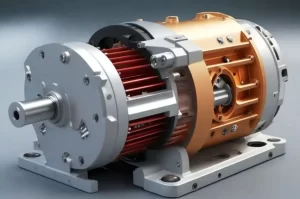
What is an Electric Motor?


An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. They take electricity and turn it into a spinning motion. They function according to the laws of electromagnetism, which demonstrate that a force is exerted when an electric current is in a magnetic field.
Electric motors are unidirectional, and the direction of rotation will depend upon the current direction.
How does an electric motor work?
An electric motor is a machine that changes electricity into movement but works differently from a generator.
Electric motors work because of something called electromagnetism. This means that when you have electricity in a magnetic field, it makes things push or pull. This pushing or pulling force makes the parts inside the motor spin, and that’s how it makes power.
Inside an electric motor, you’ll find important parts like the stator, rotor, commutator, power source (that’s where the electricity comes from), and brushes.
Types of Electric Motor
AC Motor
An AC motor converts the Alternating current into mechanical output using magnetism combined with alternating current. In an AC motor, the winding works as the armature and field winding, and the Coils produce a rotating Magnetic field inside the rotor attached to the output shaft. This rotor generates a secondary magnetic field. When the stator connects to an AC supply flux, it produces an air gap and rotates the flux at an established synchronous speed, producing the voltage in the stator and rotor winding.
The AC motor has different variants, including Single phase, brake synchronous, asynchronous, two-speed, and three-speed single phase. Differences variants are associated with the kind of work the motor has to perform. Some AC motors have to perform simple and small jobs, while the design of other variants is to perform the bigger and heavy-duty jobs in industries. The main difference is the kind of phase of the electrical feed. The phase of electrical feed is different for Industrial and domestic applications.
Industrial application motors have three phases, whereas residential application motors have single or double phases.
Advantages of AC Motor
AC motors offer several advantages that make them popular in various applications:
- Efficiency: AC motors are highly efficient, converting approximately 85% of incoming power into mechanical output. They don’t suffer from overheating, braking, or rapid wear and tear.
- Longevity: These motors have a long lifespan, typically requiring only bearing replacements during their entire working life. Bearing replacement is cost-effective and straightforward, and AC motor bearings need periodic lubrication. Their durability makes them suitable for demanding conditions.
- Low Noise: AC motors operate quietly, making them ideal for settings where noise reduction is important, such as in the hospitality industry (restaurants, hotels, etc.).
- Adaptability: AC motors are versatile and flexible. They can operate with a simple on/off switch and offer reversible operation. This adaptability is valuable for applications requiring variable speed and power output, serving multiple users.
- Variety: AC motors come in various shapes and sizes, catering to specific industrial needs and accommodating multiple power sources.
- Simplicity: These motors have a straightforward design with only one moving part. The stator design is similar for synchronous and asynchronous AC motors, keeping production costs low and ensuring longevity.
- Cool Operation: AC motors do not have brushes and commutators, which can generate heat due to friction. This absence of friction components leads to cooler operation and improved efficiency.
- Ease of Starting: AC motors have a simple starting mechanism, requiring minimal additional components. Excitation is typically the only requirement to operate an AC machine.
- Speed Control: Changing the frequency of AC power can easily adjust the speed of the motor, providing convenient speed control.
- Single-Phase Operation: AC motors can be operated using single-phase input for three-phase machines, eliminating the need for three-phase power sources.
Key Components of an AC Motor:
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor that generates a rotating magnetic field.
- Static External Drum: Part of the motor housing that surrounds the stator.
- Rotor: The rotating component that interacts with the stator’s magnetic field to produce mechanical motion.
Types of AC Motors Explained:
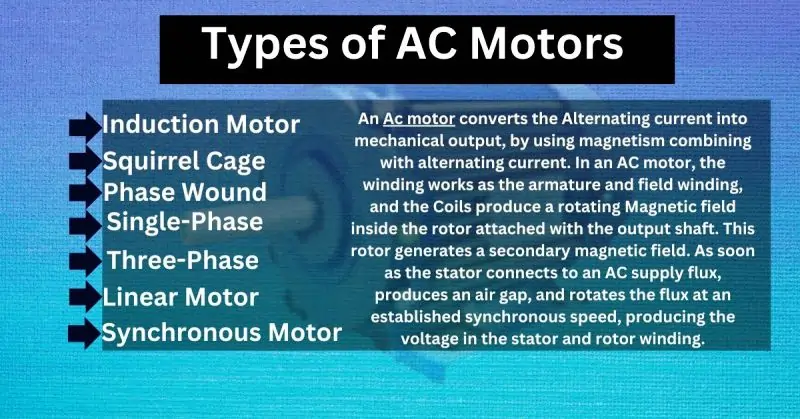


- Induction Motor:
- Induction motors use electricity to create rotating motion.
- They are used in lights, fans, motors, and generators.
- Ideal for high-torque and high-speed applications.
- It is efficient and requires minimal maintenance.
- Used in home appliances and easy to operate.
- Squirrel Cage Induction Motor:
- Part of the induction motor family.
- Known for reducing abnormal noise.
- Phase Wound Induction Motor:
- Another type of induction motor uses slip rings.
- Offers specific motor characteristics.
- Single-Phase Induction Motor:
- Converts single-phase AC power into mechanical power.
- Common in household appliances.
- Three-Phase Induction Motor:
- Converts 3-phase AC power into mechanical power.
- Widely used in industrial applications.
- Linear Motor:
- Generates linear force instead of rotational force.
- Used in sliding doors and actuators.
- Synchronous Motor:
- Converts AC into mechanical energy at a chosen frequency.
- Maintains synchronization of speed and supply current frequency.
- Includes Reluctance and Hysteresis motors.
DC Motor
In a Direct current motor, DC power gets converted into Mechanical Power. DC motor works on the principle that when a conductor carrying current is placed in the magnetic field, an exertion of force develops the torque.
Types of DC Motors



Separately Excited Motor;- In a separately excited motor, the Excitation of the DC motor is with the aid of an external source. Energizing motor armature winding is by a separate source to produce the flux.
Self-Excited Motor;- In a self-excited motor, the excitation is by the connection of field winding. The self-excited motor is of the following categories.
Shunt Motor
Shunt motors are a type of direct current (DC) motor. Shunt motors have a winding in their field with many twists, making a strong magnetic field.
The armature winding, on the other hand, can handle higher electric current. Why? Because the power (or torque) these motors produce depends on the armature’s electric current and the magnetic field’s strength.
A cool thing about shunt motors is that they’re “self-excited.” That means they don’t need an outside source to energize their field and armature windings.
In simple terms, shunt motors are built to handle a lot of current and use it to generate powerful motion.
Type of Shunt Motor
Series Motor
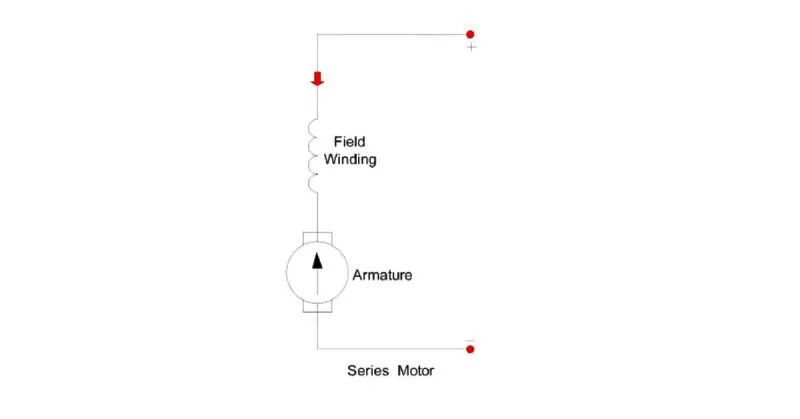


A series motor is a type of direct current (DC) motor. What’s special about it is that it has two windings connected in a series, and they both carry the same electric current.
Now, where do we find these series motors in action? They’re not everywhere because they’re best suited for situations where you need much power to start a machine. Think about elevators and hoists that need a big push to start moving. That’s where you often find series motors doing their job.
In simple terms, series motors are like the heavy lifters of the motor world. They’re the muscle when you need to move something hefty, but you don’t see them in everyday gadgets because they’re built for heavy-duty tasks.
Compound wound motor
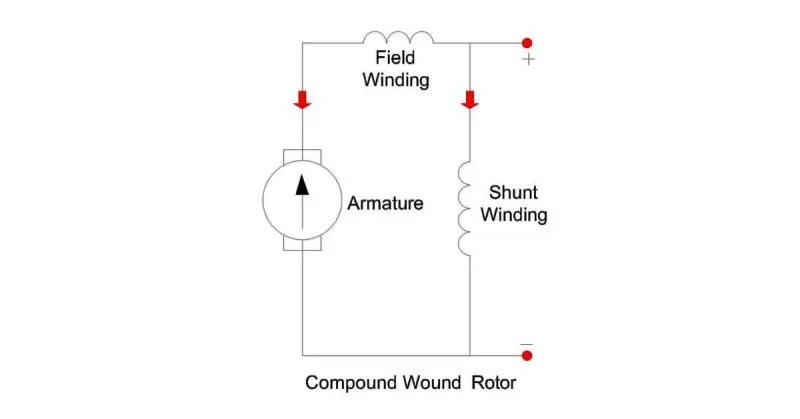


Compound wound DC motors are like the best of both worlds in the motor realm. They mix two other motor types: series wound and shunt wound.
Let’s break it down:
Series Wound Motors: These motors are all about powering up quickly. They give a big push to get things moving but may need to improve at maintaining a steady speed once they’re running.
Shunt Wound Motors: Conversely, these motors are like the marathon runners. They can keep a steady pace once they start and are known for their efficient speed regulation.
Now, back to compound wound motors. They take the strong starting boost from series wound motors and pair it up with the speed control finesse of shunt wound motors. It’s like having a motor that’s great at sprinting and excellent at keeping a consistent speed in a marathon.
These motors are handy when you need a powerful kickstart and the ability to keep things running smoothly. So, when you see compound wound DC motors, know they’re the best of both worlds, offering the advantages of high starting torque and efficient speed regulation.
Steps to Improve Power Factor in Motors
If you’re dealing with poor power factor in your motors, don’t worry; there are simple steps to fix it:
- Reduce Motor Idling: Motors often run when they’re not doing any real work, and this idling operation can lower the power factor. So, if a motor doesn’t need running, turn it off. It’s like switching off a light when you leave the room to save energy.
- Maintain Voltage and Balance: Motors work best when they get the right amount of electricity at the right balance. If the voltage is too high or too low or the phases aren’t balanced, it can mess up the power factor. Regular checks and adjustments can keep things in line.
- Install Capacitors: One of the most effective ways to fix power factor issues is by using capacitors. These handy devices help balance the electrical load, making motors run more efficiently. It’s like adding weights to a seesaw to keep it level.
By following these steps, you can ensure your motors work efficiently and use electricity wisely. It’s not just good for your motors but also for your energy bills and the environment. So, remember to reduce idling, maintain voltage and balance, and use capacitors when needed to keep your motors in top shape.
FAQ on ” Types Of Electric Motor
Q: What are the main types of electric motors?
A: The main types are DC motors and AC motors.
Q: How do AC motors differ from DC motors?
A: AC motors use alternating current, while DC motors use direct current.
Q: Can you give examples of AC motor types?
A: Sure, some examples are induction motors and synchronous motors.
Q: What’s a common application of DC motors?
A: DC motors are commonly used in tools, appliances, and electric vehicles.
Blog Post Conclusion
Electric motors are secretly everywhere in our daily lives, doing important jobs like keeping us cool with fans and running big factory machines.
We discussed the numerous electric motor types created for certain tasks and power requirements.
There’s a motor for every purpose, from the reliable induction motor to the precise synchronous and versatile DC motor.
On the other hand, DC motors offer simplicity and come in different types to suit specific needs.
Knowing the right capacitor size and what causes motor losses is important to make electric motors work well.
Whether you’re picking an appliance for your home or a motor for your machines at work, the things we’ve learned can help you choose wisely.